Infectious meningitis is a serious bacterial disease with a mortality rate of 10%.The cause of its development in older children and adults are meningococci, pneumococci and hemophils.
Infectious meningitis is a serious bacterial disease with a mortality rate of 10%.The cause of its development in older children and adults are meningococci, pneumococci and hemophils.
Meningococcal and hemophilic meningitis refers to the drop infections that most often occur in young children moving in closed large groups.
Pneumococcal and staphylococcal meningitis originate from a staphylococcal infection that spreads from purulent foci( eg, paranasal sinuses or lung abscess), or may arise from an open wound. The mortality rate is at the level of 20-30%.
In adults, the disease develops rapidly, within an hour the temperature rises, vomiting, headache and confusion occur that  leads to impaired consciousness. There may also be petechial bleeding, sometimes even a clotting disorder - disseminated intravascular coagulation( DVS).
leads to impaired consciousness. There may also be petechial bleeding, sometimes even a clotting disorder - disseminated intravascular coagulation( DVS).
In infants, the disease usually develops gradually. A fatal complication is a hemorrhage in the adrenal cortex. The disease almost always leaves lasting effects( impairment of mobility, intelligence or secondary epilepsy).
Contents
- Pathogenesis of the disorder
- Spread of the infection
- Infectious forms of the meningitis
- Signs and symptoms of the disease
- Diagnosis and set of therapeutic measures
- Complications of the infectious disorder
- Vaccination and a set of preventive measures
The pathogenesis of the
violation The entrance gates for infection are the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx. Some bacteria can persist in the epithelium of the nasopharynx, which subsequently in asymptomatic healthy people.
In rare cases, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract, which lead to nasopharyngitis, may occur. From the mucous nasopharynx, the causative agent of meningitis penetrates further into the blood and cerebrospinal fluid at certain stages;this occurs by using a transmittance that fights against phagocytosis and antibodies.
Meningococcal capsular polysaccharides refer to heterogeneous antigens that occur in different serotypes - A, B, C, D, X, Y, Z, 29 E, W135.Differences can be found in the chemical composition.
 For example, the serotype C and A are found in Africa and cause epidemics, the serotype Y can cause an epidemic of pneumonia. We most often have serotype B, which causes sporadic cases, and serotype C, but unfortunately, it has not been possible to find and prepare the vaccine against them.
For example, the serotype C and A are found in Africa and cause epidemics, the serotype Y can cause an epidemic of pneumonia. We most often have serotype B, which causes sporadic cases, and serotype C, but unfortunately, it has not been possible to find and prepare the vaccine against them.
Isolated meningococcus can identify the serotype, subtype and immunotype. Isolated serotypes are sensitive to penicillin, but this is a temporary statement, because, in the world, serotypes of meningitis are already resistant to this substance.
The highest mortality was recorded during the first year of life and during pneumococcal infection. In newborns, mortality is high, and survivors have significant long-term consequences.
Spread of infection
The source of the infection is an infected person, the culprit of the disease is the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis. Up to 10% of the population are asymptomatic carriers, the bacteria are present in the nasopharynx, but do not create any difficulties.
Infection occurs by airborne droplets with closer contact with the patient or carrier. Bacteria are transmitted by a drip, that is, through the air( during a conversation, coughing, sneezing) or through objects on which there are discharges from the respiratory tract.
Infectious forms of meningitis
Infectious meningitis includes: 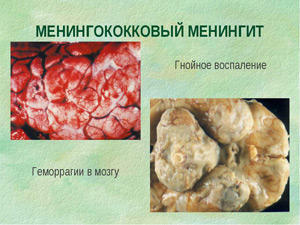
- Meningococcal .As a rule, it affects children, adolescents and young adults. Meningococcal drip infection spreads from patients or asymptomatic carriers.
- Hemophilous .This form is the most common type of meningitis in infants and children under the age of 5( up to 90%).In adults, it is mainly about the secondary spread of infection in the inflammation of the middle ear or paranasal sinuses.
- Pneumococcal .Usually, it occurs as a secondary infection in another inflammation. It develops at any age, but most of the patients are babies or people over 50 years old.
Signs and symptoms of
The early stage of meningitis can be very difficult to distinguish from a common cold, because it is characterized by fever and a headache.
Further, however, the disease develops specifically: there is hardening of the neck muscles( it is impossible to bow your head to the chest), nausea and vomiting. In addition, a person becomes sensitive to light( which is caused by irritation of the optic nerve), tired and confused, a rash appears on the face.
As the bacteria spread through the blood throughout the body, the symptoms become more visible. The rash, for example, manifests itself in the form of small blue spots on the skin, cramps and pains in the muscles are present throughout the body, there may be loss of consciousness.
In young children, the symptoms of infectious meningitis are not so pronounced, and can vary greatly for different children. For example, some children become sleepy, others, on the contrary, are very restless, crying for no reason.
The disease in children further develops in such a way that, within 1-3 days, the vagina of the fontanel becomes noticeable, convulsions or vomiting appear. In infants, meningitis also manifests itself with cold hands / feet and refusal to drink.
Diagnostics and set of therapeutic measures
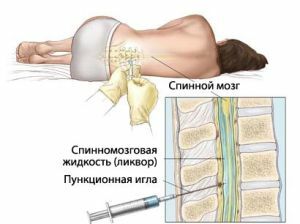 It is necessary that the diagnosis is carried out as soon as possible after the onset of the disease. Timely medical intervention can significantly improve a patient's prognosis and save his life.
It is necessary that the diagnosis is carried out as soon as possible after the onset of the disease. Timely medical intervention can significantly improve a patient's prognosis and save his life.
A standard examination to confirm meningitis is to assess the freedom of mobility of the neck and spinal puncture of the patient. When examining spinal puncture, the doctor takes fluid from the zone around the 4th and 5th vertebrae. If the liquid is clear, it means that the patient is likely to be healthy.
If the collected cerebrospinal fluid is turbid, there is a possibility of having an infectious meningitis. To complete the diagnosis, the sample is sent to the laboratory for examination.
Immediately after diagnosis, it is necessary to begin treatment. With this disease, even a minute can save a life. Since a patient with infectious meningitis is prone, mainly, to edema of the brain, he receives drugs against puffiness.
Other important drugs are antibiotics that kill a wide range of bacteria and have the ability to penetrate well into the brain. Antibiotics can be administered orally or intravenously. 
In addition, it is necessary that the patient has a sufficient supply of water and minerals. During treatment, spinal puncture is repeatedly performed in 48-hour intervals and the contents of the cerebrospinal fluid are analyzed.
A patient who has a life-threatening problem lies in intensive care, so that doctors can monitor his vital organs. With successful treatment, the main symptoms subsided, after about 4 days.
Nevertheless, for at least 2 weeks, it is necessary to continue taking antibiotics to prevent recurrence of the disease.
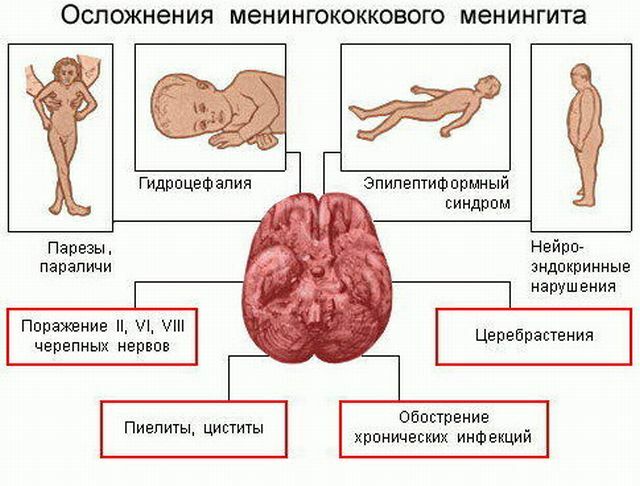
Complications of an infectious disorder
The most serious consequence, which occurs not so often, is a lethal outcome. It is observed in 5-10% of cases, usually within 1-2 days after the onset of the disease.
Another complication arising from this disease is the damage to the cranial nerves. The most common is a disorder of the auditory nerve, which, as a rule, is irreversible and leads to complete deafness of the patient.
Rarely does damage to the optic nerve, also capable of leading to irreversible damage. Just another complication, no less serious, is an inflammation of the heart muscle.
On the body, where a bluish eruption develops during the course of the illness, so-called necrosis - a dead tissue, which later separates, can develop.
 In children, meningitis can also lead to behavioral disorders, epilepsy, or an easy onset of development.
In children, meningitis can also lead to behavioral disorders, epilepsy, or an easy onset of development.
In terms of prognosis, long-term convulsions are unfavorable, especially if they last longer than the 4th day of hospitalization. On the other hand, convulsions occurring during the first 3 days of hospitalization are not prognostically significant.
Only in 6% of patients there may be signs of DIC-syndrome or endotoxin shock. The prognosis for these patients is much worse.
Vaccination and a set of preventive measures
The most effective protection against meningitis A and C is vaccination. It is able to protect the body for several years. 
Vaccination against meningitis, in particular, is recommended for young people, because, they are at greatest risk of disease.
In addition, there is a vaccine against the bacterium that causes bacterial meningitis( Hemophilem influenzae).Unfortunately, an effective vaccine against C. meningitis has not yet been developed.
A healthy lifestyle is a good prevention of infection. In view of the fact that weakened immunity allows the microbes that cause the disease to penetrate the membranes of the brain and cause inflammation, it is also important to maintain a good supply of vitamins, to maintain good eating habits, to indulge in regular physical exercises in the open air, to pay attention to quality sleep and to avoidstressful situations.
The risk of infection can also increase smoking, even passive. In a nationwide study, it was shown that children under the age of 15 years who have a parent as a smoker are 3 times more likely to receive meningitis than children from non-smokers. If both parents are smokers, the risk increases by 8 times.