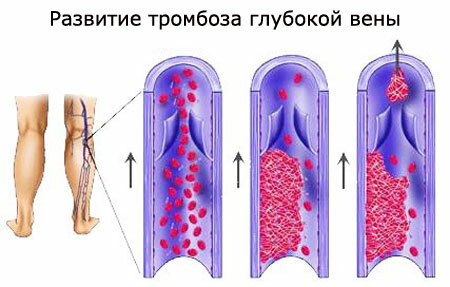
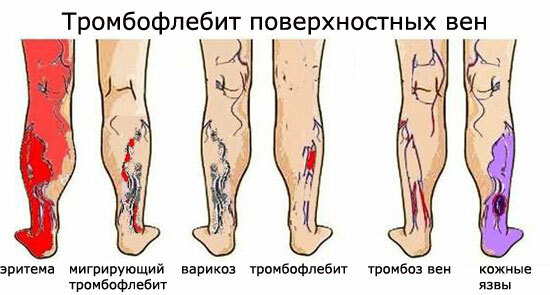
Angina is one of the forms of coronary heart disease( CHD), which is characterized by paroxysmal pains on the breastbone with an increase in the load on the cardiovascular system on the background of emotional and physical stress. The cause of the disease is a violation of blood supply to the heart muscle. Unstable angina is a dangerous condition, threatening the development of myocardial infarction and related complications.
Contents of
- 1 Causes of unstable angina
- 1.1 Atherosclerosis as the cause of coronary heart disease
- 2 Types of the disease
- 2.1 Braunvald classification for the severity of the attack - table
- 3 Diagnosis
- 3.1 Symptoms and differential diagnosis - table
- 4 Treatment of astable angina
- 4.1 Drugs that a patient can take before contacting a doctor
- 4.2 Healing interventions that reduce the percentage have occurredveniya complications
- 4.2.1 administered drugs in the photo
- 5 Recommendations for prevention of disease prognosis
- 6 treatment
- 7 How to protect your heart - video
reasons for unstable angina
Violation of the blood supply to the heart muscle( myocardium) may be due to various reasons. Allocate certain risk factors, which include:
- age - the chances of developing the disease increase in patients older than 45 years;
- heredity;
- the presence of predisposing diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension;
- is overweight;
- lifestyle - smoking, alcohol abuse, stress, inactivity.
In men, the disease is diagnosed more often. In women before menopause, the risk of unstable angina is extremely low due to the development of sex hormones( estrogens) that preserve blood vessels. But after 50-55 years, the risk of developing the disease in women increases.
Atherosclerosis as the cause of coronary heart disease
Cardiovascular diseases, more than 2/3 of which are ischemic heart disease, stroke and peripheral arterial damage, are associated with atherosclerosis and remain the leading cause of death worldwide. Coronary artery disease and angina often occur due to a violation of the blood supply to the myocardium due to atherosclerosis of the coronary( heart-feeding) vessels. Plaque deposition occurs on their inner surface. Vessels in this case lose elasticity, their walls ulcerate, which leads to the formation of thrombi. Atherosclerotic plaque can grow, deforming and narrowing the lumen of the artery, which causes a chronic impairment of the blood supply to the organ. A local decrease in the diameter of the vessel by more than 50% can trigger an attack of unstable angina. Plaque can be destroyed due to inflammatory processes, hemodynamic disorders, excess fatty deposits, lack of collagen. An unstable form of angina occurs in the case of rupture of the plaque with the formation of a thrombus, which prevents normal blood supply to the heart muscle.
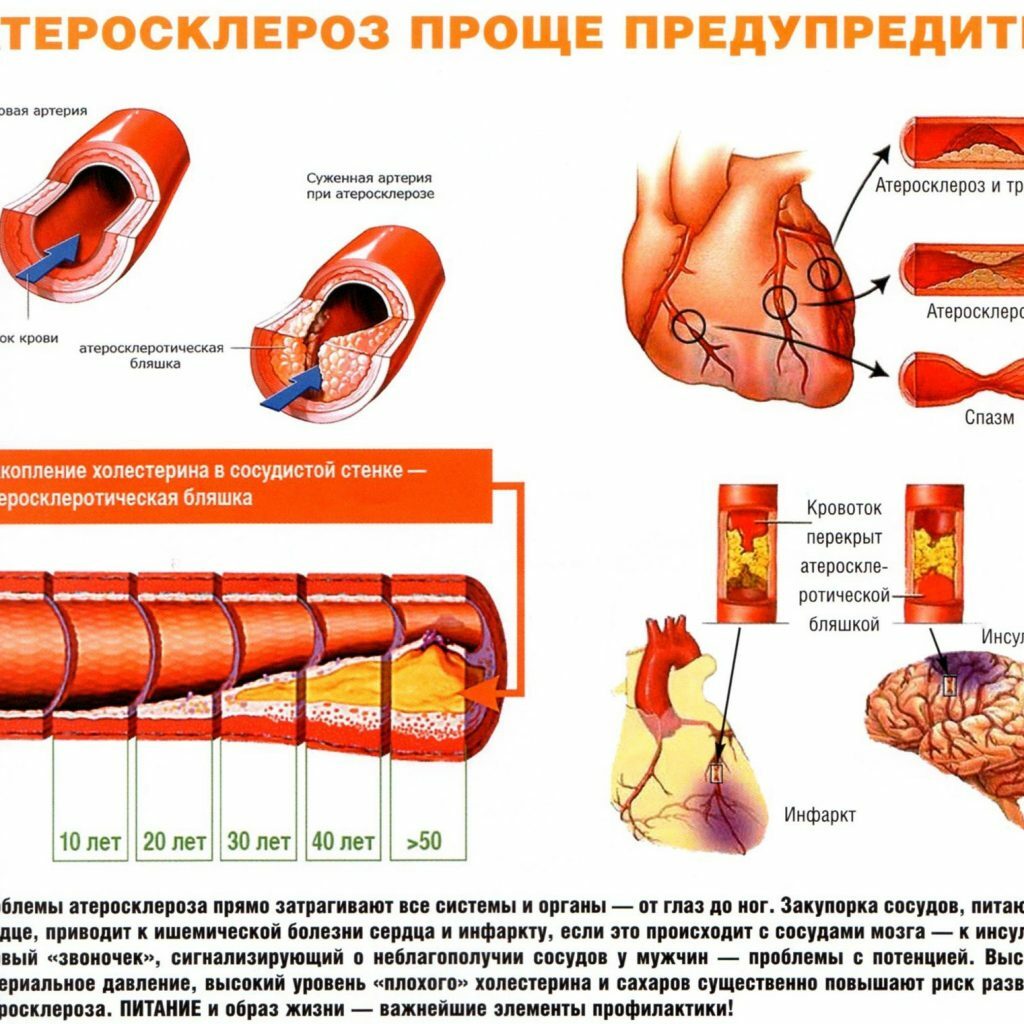
Consequences of atherosclerotic disease
Along with atherosclerosis, there are other causes of unstable angina:
- congenital malformations;
- rupture of capillaries followed by hemorrhage into the plaque;
- is an inflammatory process in the vessels;
- increased ability of platelets to glue;
- spasm of the heart vessels in infectious and rheumatoid diseases, a number of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- release of serotonin or other biologically active agent into the blood, in which there is a sharp narrowing of the lumen of the coronary vessels;
- decreased antithrombotic properties of the endothelium( cells of the inner surface of the vessels).
Types of the disease
The severity of the pain syndrome depends on the degree of arterial damage, the number and location of lesions. Depending on the peculiarities of circulatory disorders in the coronary vessels, angina may occur:
- First emerged. The first attacks can occur with severe physical exertion and vary in intensity. They last from a few minutes to half an hour. They can build up or have a place in peace. The prognosis is less favorable, when already from the first attacks the pain is increasing, prolonged and associated with changes in the ECG( electrocardiogram).
- Progressive. Occurs already with the diagnosis of stable angina. It differs from its usual manifestations by a much more prolonged and intense attack. Usually, the usual dosages of nitroglycerin are not enough. In addition, progressive angina attacks include attacks with various types of arrhythmias at rest. Post-infarction( recurrent). Begins after 24 hours or up to 8 weeks after myocardial infarction. According to statistics, repeated seizures are associated with the patient's activity or massive heart disease. In 20-40% can lead to a lethal outcome or repeated myocardial infarction.
- Variant, or angina of princemetal. The reason is the narrowing of the coronary vessels in the form of a spasm. It usually occurs at the same time and causes characteristic changes in the ECG, which disappear after the attack.
- With the outcome of a small-focal myocardial infarction. Flows without visible rhythm disturbances and severe pain. It differs from other types of angina pectoris with pronounced changes on the ECG.The outlook is often favorable.
The Braunwald classification for the severity of the attack - table
| A - secondary unstable angina. Attacks provoked by external causes( anemia, thyrotoxicosis, acute infection, etc.) | B - primary unstable angina. Associated with heart diseases | C - postinfarction angina. Occurs within 2 weeks after myocardial infarction | |
| I-first-occurred, progressive angina pectoris without resting angina | IA | IB | IC |
| II-resting stenocardia for a month, but not in the next 48 hours | IIA | IIB | IIC |
| III - resting angina in the next 48 hours | IIIA | IIIB | IIIC |
This method allows you to assess the risk of myocardial infarction in the clinic and the causes of a pain attack.
Diagnosis
First of all, the doctor takes into account the patient's complaints, conducts a general examination of the patient, listens to the heart sounds and collects an anamnesis( history of the disease).For the diagnosis is also used instrumental diagnosis, which primarily includes an ECG.When an attack of angina occurs, a number of characteristic changes can be seen on the cardiogram.
In addition, blood and urine tests are prescribed. With unstable angina, biochemical parameters( glucose, cholesterol, triglycerides, creatine kinase, etc.) can be changed.
A special diagnostic role is played by cardiac markers - troponins. They show the presence of damaged myocardial cells.
In the future, for in-patient treatment, ultrasound of the heart - echocardiography, bicycle ergometry, coronary angiography, Holter monitoring, is performed for in-depth diagnosis. On ultrasound it is possible to detect a violation of cardiac contractility and congenital malformations.
Velgoergometry is a test in which a patient receives a load on an exercise bike to the maximum possible for him. At the same time, changes are constantly recorded on the ECG.
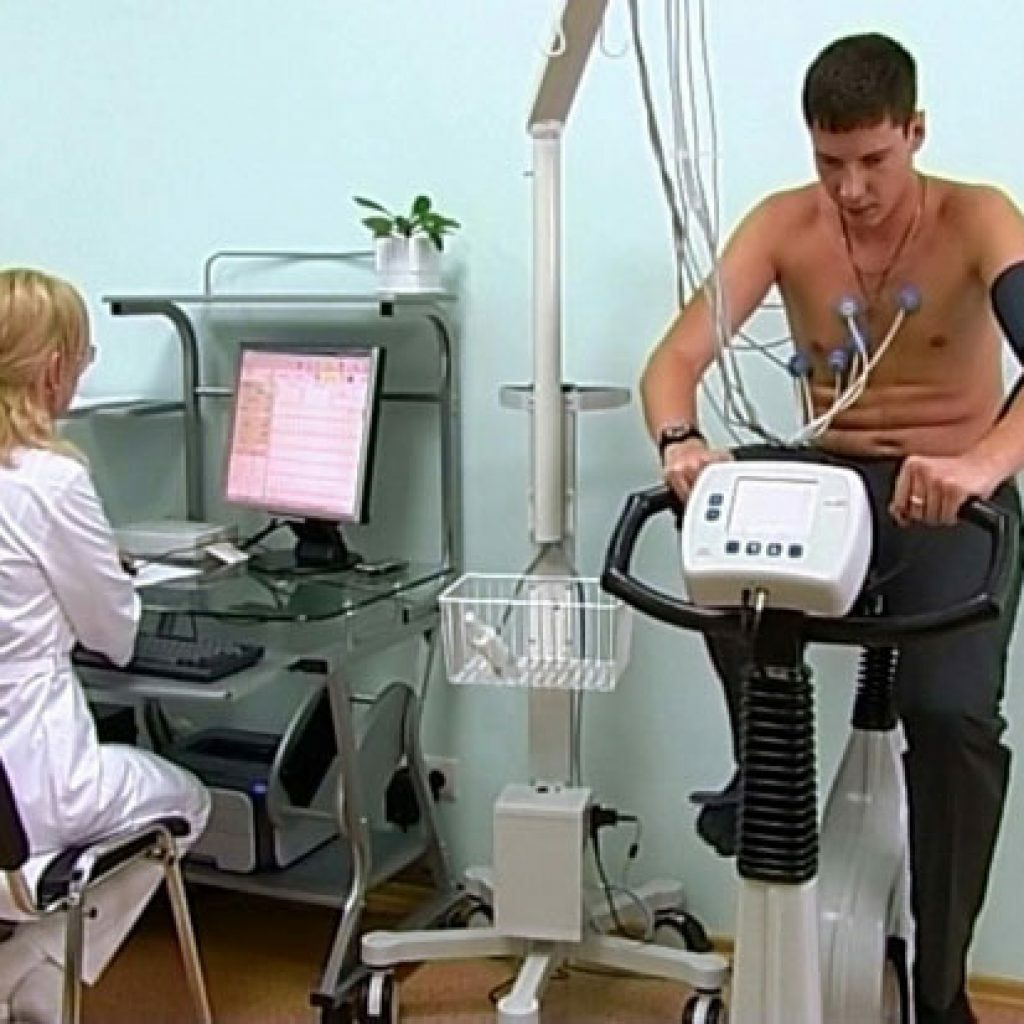
Functional test for unstable angina
Coronarography is perhaps the most informative method. It is the introduction of a contrast medium into the blood vessels of the heart, which makes it possible to determine the ischemic area using an X-ray.
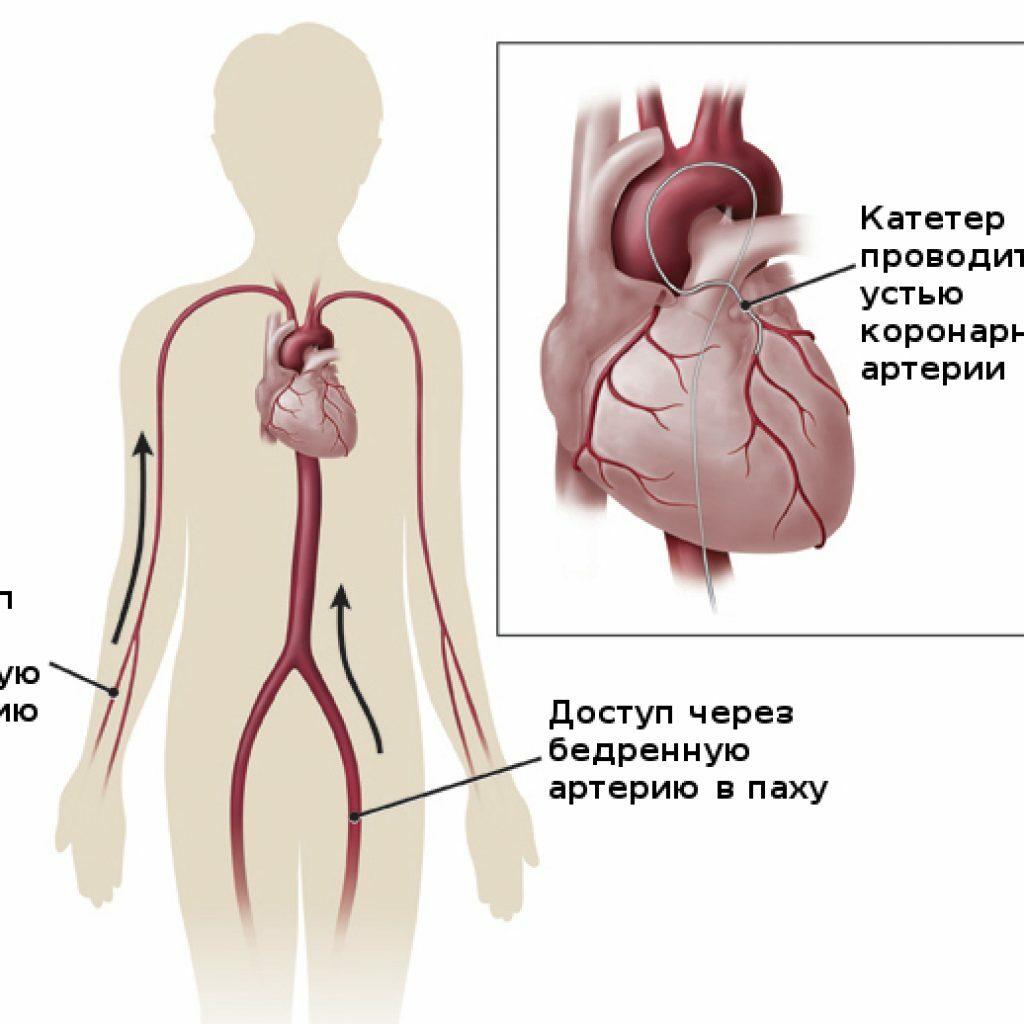
Access routes for coronarography
Holter monitoring is performed more to diagnose rhythm disturbances at the time of angina attack. Results are recorded within 24 hours.
Symptoms and Differential Diagnosis - Table
| Symptom | Unstable angina | Stable angina | Intercostal neuralgia |
| Pain character | A painful attack is burning, sometimes unbearable. | Has a typical burning nature of chest pain. | Nasal, intensifying on palpation along the nerve, paroxysmal, sometimes can be manifested by burning or tingling. |
| Localization of pain | Localized behind the breastbone and is widely distributed. | Localized behind the sternum. | Localized in intercostal spaces. |
| Irrigation( spread) of pain | Pain radiates to the right or left arm, shoulders, under the scapula, in the abdomen, neck, lower jaw. | The pain is usually localized only behind the sternum, it can rarely give to the left arm. | Pain radiates to the waist, back, under the scapula, is localized in intercostal spaces. |
| Duration of pain attack | More than 30 minutes. | Up to 30 minutes after discontinuation of any physical activity. | The appearance of pain in all movements, at rest, is completely absent. |
| Start of attack | During exercise, at rest, in sleep, under stress. | During exercise, at rest, in sleep, under stress. | When you rotate your body, take a deep breath, after sharp turns or inclines, when you cough or sneeze. |
| Seizure reason |
| Intensive physical activity, stress, atherosclerosis, systemic diseases. | Physical overstrain on the eve, being in a draft. |
| Pain relief | Do not stop with the previous dosages of nitroglycerin | It is dosed with three nitroglycerin tablets. | Pain is not stopped by nitroglycerin, but is quickly removed by systemic analgesics( Analgin, Ketorolac, Diclofenac, Diclober, etc.). |
| Other symptoms |
| May be accompanied by an increase in blood pressure. | Possible increase in blood pressure. |
Treatment of unstable angina
In the treatment of unstable angina, several tasks must be achieved:
- to restore the patency of vessels;
- relieve the pain;
- to prevent myocardial infarction;
- to eliminate complications.
Drugs that a patient can take before contacting a doctor
Treatment can be divided into pre-medical and medical care. Independently during an attack a patient can take an aspirin tablet and up to 3 nitroglycerin tablets with a difference in intake of 5 minutes. If the attack does not stop, you should see a doctor or call an ambulance.
It should be remembered that nitroglycerin should be taken in a horizontal or sitting position under the control of blood pressure. If you have an allergy to aspirin, then its reception should be limited.
Treatment measures that reduce the incidence of complications
At the medical prehospital stage, intravenously inject drugs that remove the angiogenic attack( nitroglycerin, Isomyc, Isosorbide dinitrite, etc.), contributing to the prevention of thrombosis( Heparin, Streptokinase, MetaLysis, Alteplase).With a severe pain syndrome, it is possible to administer narcotic analgesics( Morphine, Fentanyl).
In outpatient or inpatient treatment, regardless of the type of unstable angina, different groups of drugs are added to the above treatment:
- extended nitrates( used as nitroglycerin, but longer in action) - Molsidomine, Monocaps;
- beta-blockers( drugs for pulse reduction) Bisoprolol, Metoprolol, Bicard, Propanolol;
- alpha-blockers( necessary for the normalization of blood pressure) - lisinopril, ramipril, captopril;
- diuretics( used in the presence of edema and heart failure) - Torasemide, Veroshpiron, Indap, Furosemide, Spironolactone;
- statins( used to lower blood cholesterol) - Zocor, Atorvastatin, Rosuvastatin.
Do not take these drugs without prescribing a doctor!
Applied medications on photo
 Atorvastatin is prescribed by a doctor to lower blood cholesterol
Atorvastatin is prescribed by a doctor to lower blood cholesterol  Bisoprolol - a drug that normalizes the heart rhythm
Bisoprolol - a drug that normalizes the heart rhythm 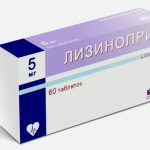 Lysinopril is a drug designed to lower blood pressure
Lysinopril is a drug designed to lower blood pressure 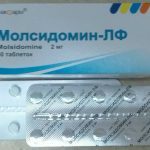 Molsidomine-LF drug affects smooth muscle vessels, reducing their tone
Molsidomine-LF drug affects smooth muscle vessels, reducing their tone  Monocaps -a tool for normalizing the tone of the coronary vessels
Monocaps -a tool for normalizing the tone of the coronary vessels 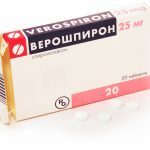 Veroshpiron - an effective drug for removing edema
Veroshpiron - an effective drug for removing edema  Ramipril is prescribed to lower blood pressure
Ramipril is prescribed to lower blood pressure  Furosid - a means to treat edematous syndrome
Furosid - a means to treat edematous syndrome  streptokinase - an effective drug for the treatment of blood clots
streptokinase - an effective drug for the treatment of blood clots  Aspirin - antiplastic
Aspirin - antiplastic Recommendations for prevention of the disease plays an important role dieting. The patient should limit the amount of fatty foods, you can not eat salty, spicy, fried, smoked. It is worth to give up smoking and alcohol. Positive influence on the state of the body is exerted by physical exertion, staying in the fresh air, limiting stressful situations.
In addition, you must not miss the intake of medications prescribed by your doctor, you must follow prescribed dosages.
But do not forget that medication is only part of the prevention of unstable angina, it is equally important to follow a healthy lifestyle.
Prognosis of treatment
Unstable angina is an intermediate stage between the stable course of IHD and the complication. In the absence of adequate care, the percentage of myocardial infarction is high. However, with timely hospitalization and started qualified treatment, the prognosis may be favorable.
How to protect your heart - video
Observance of the doctor's recommendations, timely diagnosis and taking prolonged nitrates can delay the repeated attacks, and in most cases, and prevent a heart attack. The role of prophylaxis of this disease also increases: the fight against the risk factors of atherosclerosis, adequate nutrition, exercise at any age.