Epilepsy as a disease occurs in early childhood or against a background of pubertal age. In modern medical practice, there is no reliable data on the causes of the appearance of the episodrom.
Epilepsy as a disease occurs in early childhood or against a background of pubertal age. In modern medical practice, there is no reliable data on the causes of the appearance of the episodrom.
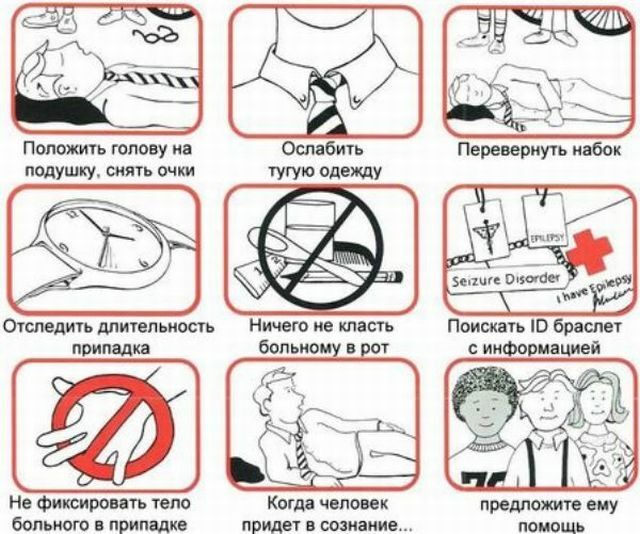
Due to epilepsy, not only psychoemotional, but also cognitive impairments may occur. And in the case of severe seizures, you can even die. Therefore, you need to know how to act during the exacerbation of the disease, as well as its clinical manifestations, in time to help and alleviate the suffering of the patient.
Contents
- From the history and statistics
- Etiology of the disease
- Basic forms of the disease
- Symptomatic manifestations
- Diagnosis of the episodrome
- Therapeutic package
- Possible medical complications
- Preventative measures
From the history and statistics
In ancient times, epilepsy was very wary, considering it a mental illness. Such people were avoided and humiliated in every way, believing that the disease was "from the devil".
Many countries with a low level of civilization have not changed their attitude to this disease until now, although the achievements of modern medicine have denied the groundlessness of such stereotypical thinking.
New therapeutic approaches to treatment dramatically changed public attitudes in developed countries and contributed to positive social adaptation, alleviation of somatic suffering of epileptic patients.
According to doctors, epilepsy is a chronic disorder of brain activity with specific clinical changes in the form of seizures. According to WHO statistics around the world, about 50 million people suffer from these diseases.
Approximately their number is from 4 to 9 cases per 1000 people. More than half of the patients live in countries with a low standard of living. Epilepsy can not be diagnosed with one convulsive fit. As a rule, they occur more often with a certain gap in time.
Convulsive seizures appear involuntarily and briefly in the form of involuntary convulsions of any part of the body, or the entire body. 
Often such convulsive conditions are accompanied by loss of consciousness, vomiting, convulsions of the extremities. Fertility conditions can occur at any time of the day. Depending on the clinical course of the disease( primary or concomitant), their number varies from one year to several seizures per day.
The number of epileptics in the last decade has increased significantly, so research in this area continues. Especially in countries with a low standard of living( from 7-14 per 1000 people).
Annually in the world of epilepsy diagnose in 2.3 million people. Outbreaks of the disease are typical for countries with a high risk of endogenous organic diseases, low level of medical care( birth injuries, no emergency assistance in road accidents, financial difficulties in obtaining quality medical care).In 65% of cases, epilepsy lends itself to medical treatment.
Etiology of the disease
The causes of epileptic seizures are not fully understood. Many studies prove the hereditary nature of the disease.
In addition to the hereditary factor, as reasons, scientists consider the conditions of intrauterine fetal development and early postnatal trauma of the child's brain during childbirth or infection in the natal period with staphylococcal, or streptococcal infection. In 25% of cases, the pathogenesis of the disease could not be determined. In general, the researchers managed to make a classification of the main causes of epilepsy  .
.
Among them:
- brain injury during labor or perinatal period;
- congenital genetic abnormalities in development;
- head injury;
- hemorrhage in the brain;
- meningococcal, encephalitic, streptococcal infections;
- genetic syndromes;
- tumor processes;
- eclampsia;
- alcoholic abstinence.
Basic forms of the disease
In medicine, the types of epilepsy were classified based on the likely etiology and localization of the lesion focus of the brain. Distinguish the following types of disease:
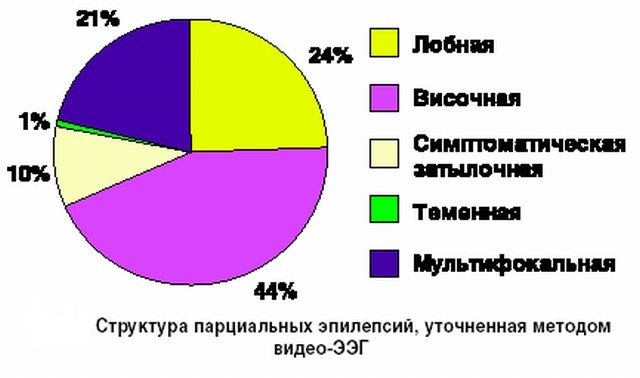
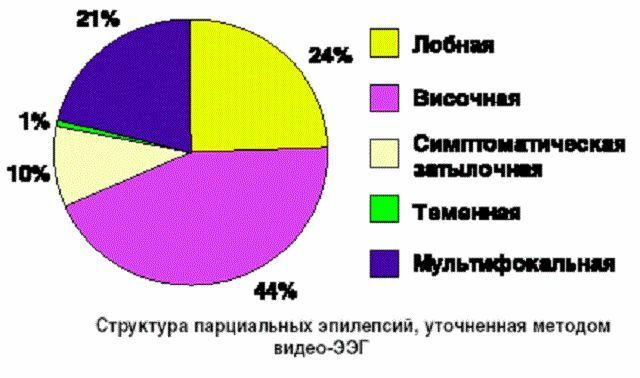
- Focal form .It is determined in the case of local manifestation. Symptomatic( frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital), idiopathic( due to organic brain damage, cryptogenic( without specific etiology))
- Generalized form of Convulsive states involving both hemispheres of the brain
Symptomatic manifestations of
The main symptomatic symptom is seizures with loss of consciousness. The characteristic features of additional symptoms indicate a certain area of brain damage.and simple convulsive conditions. In simple cases short-term convulsions of the head and limbs without loss of consciousness are observed. In complex convulsive fits, consciousness is completely disconnected
The focal form of epilepsy is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- When the frontal lobes of are affected: one-half of the body is involved: arms, legs,a person who convulsively strains. It appears profuse salivation and involuntary shouting. Eyes and head are convulsively diverted to the side.
- In the temporal focus of lesions auditory hallucinations, fever, increased heart rate, sweating, abdominal pain and nausea are observed. Visual, hearing and speech impairment is possible. For sick women, this attack can be repeated in the premenstrual period. For temporal epilepsy sleepwalking is characteristic.
- Signs of parietal epilepsy is the numbness of individual body parts, dizziness, loss of spatial orientation, impaired consciousness.
- In the case of occipital , an episodroma on the skin around the eyes appears colored circular spots, frequent jerking of the eyelids and partial loss of vision.
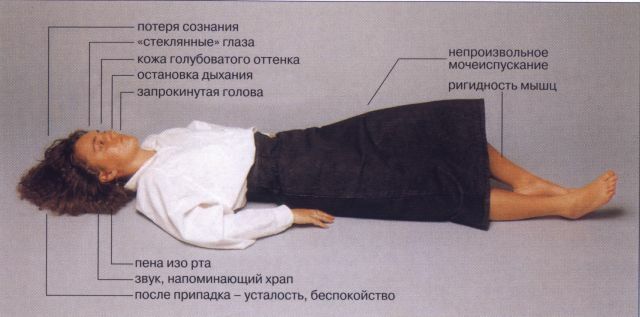
Short-term focal seizures can go into a complex( generalized) form. Symptomatically it looks like a complete loss of consciousness, the victim's dying with open eyes and a "petrified" face.
Further, the patient raises blood pressure, observed foamy discharge from the mouth, involuntary urination and defecation. This state can be followed from a few seconds to a minute and passes by itself. After the attack the patient regains consciousness, but what has happened to him does not remember.
Diagnosis of the episodrome
To begin with, the doctor collects an anamnesis of the disease: the type of seizure, the conditions for the appearance of seizures, the cause of this condition, the patient's feelings.
 The neurological examination is then carried out. As an additional study, electroencephalography of the frontal lobes is prescribed. As a method, completely harmless, but informative, as it determines the focus of the lesion and epileptic activity in the cerebral cortex.
The neurological examination is then carried out. As an additional study, electroencephalography of the frontal lobes is prescribed. As a method, completely harmless, but informative, as it determines the focus of the lesion and epileptic activity in the cerebral cortex.
Diagnosis is carried out for 20 minutes and uses different stimuli( sound, visual), change the rhythm of breathing. This determines the possible pathological electrical activity. Diagnosis is carried out in a hospital. To compare the indicators of brain activity, it is carried out during sleep and throughout the day.
To exclude malignant etiology, computer tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are performed. The latter will help to determine circulatory disorders and other structural changes in the cerebral cortex.
Complex of therapeutic measures
Treatment of epilepsy begins after the recurrence of seizures. As drugs, Valproate and  Carbamazepine are more commonly prescribed.
Carbamazepine are more commonly prescribed.
After the course of treatment( approximately a month), they are prescribed Levetiracetam and Topiramate. A month later, the general condition of the patient and the nature of recurrence of attacks are assessed. If the convulsions do not stop, one of the drugs is replaced and the treatment continues.
Unfortunately, it is only by such an experimental method that optimal treatment can be selected, which can last up to 3 years. At the same time, you can take two anticonvulsants. They are considered not entirely harmless and have side effects on the body.
Patients with an epileptic symptom should be examined once a month by a specialized specialist and once every six months to monitor the overall health of related specialists. If the dynamics of recovery is positive, the doctor may prescribe a smaller dose or cancel the treatment. If, on this background, the symptom is activated, then the treatment is continued.
Possible physical complications of
Patients with an epistatus are "at risk" and may have concomitant somatic disorders:
- Pneumonia .During the attacks, small particles of food can enter the respiratory tract. They can provoke an inflammatory process.
- Puffiness of the lungs .Convulsions increase blood pressure, oxygen starvation develops. Against this background, lung edema develops.
- Different injuries .During an attack the patient can damage the muscles, break down limbs or damage the spine.
- Toxic disturbances of .There are pains in the abdomen, constipation.
- Allergic reactions of in the form of dizziness, headaches, fever, fatigue, hives and irritability.
- Disorders of psychoemotional character : depression, psychopathy, neurasthenia.
Preventive measures
Based on the etiology of the episodroma, it is possible to reduce the risk of getting a symptomatic( acquired) form of the disease. As preventive measures, doctors recommend: 
- to avoid excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- to limit the consumption of coffee and fatty foods;
- provide a set of medical procedures for the care of newborns in the perinatal period;
- to patients with an episode card, in order to avoid recurrence of seizures, work at altitude, on water, contact with industrial poisons, professional activity requiring high concentration of attention and monotonous actions is strictly forbidden.
In general, the cause of epileptic seizures can be congenital and acquired factors. Treatment of the disease is symptomatic.
The effectiveness of recovery depends on continuous monitoring, the use of drugs and preventive measures. In chronic conditions, medications are taken for life.