The thyroid gland is the organ of the endocrine system of the body that produces specific iodine-containing hormones:
- triiodothyronine( T3),
- tetraiodothyronine( T4).
Another biologically active substance that is synthesized by special structures( C-cells) is calcitonin. Thanks to them, the organ plays an important role in the vital activity of the whole organism.
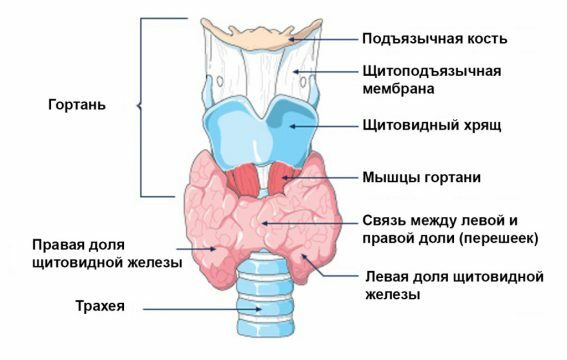
The gland is located at the level of the thyroid cartilage. Most often consists of 3 parts:
- right lobe,
- left lobe,
- isthmus.
The approximate weight of this organ in adult men and women is 15-30 g, depending on the individual characteristics. On the sides of it, parathyroid glands are often located, which play the role of satellites and thyroid antagonists. They produce a special parathyroid hormone, which, according to the principle of action, is completely opposed to calcitonin.
Functions
It is difficult to overestimate the significance of this small gland. It is one of the most important "controllers" of all metabolic processes in the body and is responsible for:
- metabolic reactions in the body( basic metabolism),
- growth and development of all structures,
- maintenance of constant body temperature,
- prevention of osteoporosis of bones,
- stress resistance,
- statenervous system, and in particular, memory and the ability to concentrate.
An increase in the thyroid gland can cause or result from any violation of one of these functions, both in men and in women. Often parallel parathyroid glands suffer.
Prevalence of the incidence of
It is necessary to know that the diseases of this organ take the second place among all endocrine pathologies after diabetes mellitus. More than half a billion people on Earth suffer from such ailments. Whether the appearance of nodes, changes in the size of the gland or the appearance of malignant neoplasms, nevertheless the symptoms develop on the same principle. Allocate:
- hypothyroidism( decreased functional capabilities),
- hyperthyroidism( increased synthesis of hormones),
- euthyroidism( a certain balance is retained inside the parenchyma).
Thyroid enlargement most often develops as a type of hyper- and euthyroidism and requires adequate treatment. Common ailments that affect men, women and children and manifest themselves as characteristic symptoms are:
- diffuse toxic goiter( Bazedova disease),
- endemic goiter,
- acute thyroiditis,
- subacute thyroiditis,
- autoimmune thyroiditis( Zob Hashimoto),
- adenoma of the thyroidwith the formation of benign nodes,
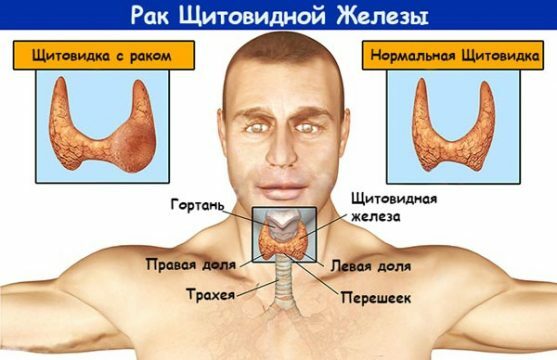
- thyroid cancer.
These diseases are manifested by a number of symptoms that are relatively easy to identify. If you do not start treating the disease in time, the consequences can become deplorable. Often, parathyroid glands are drawn into the pathological process with the appearance of characteristic symptoms.
Reasons for
At the moment, there are several basic reasons that can lead to growth of the parenchyma of the body:
- Infection. The most common pathology is caused by bacteria. As a result, infectious inflammation develops in men or women - thyroiditis.
- Lack of iodine in food. To compensate for this deficiency, the thyroid gland cells increase in size to capture more iodine from the blood. Since there is also no serum in the serum, a slow but constant increase in all lobes is observed. The result is an endemic goiter.
- Autoimmune lesion. Nodes appear due to hormonal imbalance in the body. This leads to a pathological response of T cells to their own structures. Changes can also have a diffuse character. Anatomically, the gland is covered with a capsule that, during the development of the body, protected it from "getting to know" the immune system. If such a barrier is damaged, their own defense mechanisms begin to recognize thyroid cells and parathyroid gland cells as foreign and attack them. It is statistically proven that this type of disorder is more common in women. This is due to more frequent fluctuations in the hormonal background( adolescence, pregnancy, menopause).
- Oncological disease. Allocate benign and malignant nodes in the structure of the organ. The statistics speak in favor of an adenoma, rather than a cancer. Only 5% of the nodes are potentially life-threatening.
- Other unexplained causes of an increase in the thyroid gland.
Common Symptoms of

Depending on the pathogenesis and cause, the enlarged thyroid gland may behave differently. Nevertheless, there are a number of characteristic symptoms that can help a person to suspect the presence of a disease. To the doctor they allow to define the diagnosis. These include:
- Changes in body temperature. Most often they are manifested fever, which is difficult to treat with usual aspirin or other analogues.
- Mental disorders. Patients become irritable, sleep poorly, relatively aggressive.
- Increased sweating.
- Weight loss. Often patients can lose weight by 5-10 kg in just a month.
- Presence of knots on the neck, which can not disturb a person or cause painful sensations.
Thyroid enlargement, depending on the cause, has several other, more specific symptoms.
Diffuse toxic goiter
A pathology that develops as an autoimmune process. It is characterized by an increase in the whole parenchyma of the organ. Pathological synthesis of iodine-containing hormones leads to hypertrophy of cells of internal structure. In the absence of adequate treatment, thyrotoxicosis develops, a condition of a significant excess of biologically active substances in the blood. A critical outcome is a thyrotoxic crisis. If it is not treated, the patient may die. In addition to the diffuse nature of the disease, it can be manifested by the formation of single nodes.
This pathology is more common in women due to fluctuations in their hormonal background. Injuries, infectious diseases, stress can be risk factors for the development of ailment. Additional symptoms of the disease:
- Rapid heart rate( tachycardia), arrhythmias, hypertension. In the absence of treatment, these problems can develop into atrial fibrillation or ventricles, heart failure with the development of anasarca( the presence of fluid in all body cavities).
- Weakness, headache, sleep disturbance.
- Tremor limbs, the inability to maintain balance.
- Women often have a menstrual cycle. Sometimes because of this pathology it is impossible to become pregnant.
- Eye protrusion( exophthalmos).
- Diarrhea, vomiting, nausea. Other digestive disorders.
- Nodes in the parenchyma.
If the time does not begin to treat the disease, it quickly progresses, and the consequences can be deplorable.
Endemic goiter
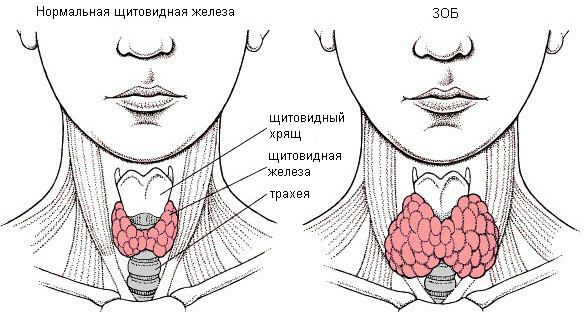
An increase in the thyroid gland in this case is due to a shortage of iodine in food. The most common development in children and women with a genetic predisposition. Parathyroid glands do not take part in the pathogenesis of this disease. If there is a shortage of a trace element, it causes compensatory growth of the parenchyma of the organ, which tries to gain more iodine from the blood due to its increase. However, this is mostly ineffective. Depending on the functionality of the gland, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Euthyroid. This happens if the body releases a normal amount of hormones.
- Hypothyroid. The function is reduced.
If you determine the size of the shares, then allocate such degrees of pathology:
- goiter is absent,
- is fixed increase in thyroid gland, but only with manual palpation,
- goiter is visible to the naked eye.
There is also a classification according to the form of organ damage:
- Diffuse. Parenchyma grows completely.
- Nodal. The appearance of individual compaction points is observed.
- Mixed.
The main characteristic symptoms of the disease are:
- general weakness,
- sleep disorder,
- unpleasant, sometimes painful, sensations when swallowing food,
- neck looks thick, as the gland increases in volume,
- cough,
- mental retardation in young children.
Acute and subacute thyroiditis
Thyroid enlargement occurs due to inflammation of its parenchyma. The causative agent is a bacterial or viral invasion with the formation of specific granulomas. Multiple nodes may appear. Often pathology develops in women or children after having had angina or influenza. Characteristic symptoms are:
- Unpleasant sensations in the neck. Often it hurts.
- There is a local increase in temperature, redness of the skin.
- Rapid heart rate. Sweating and changes in mood.
- On the surface of the neck, you can palpate enlarged nodes of the gland.
Parathyroid glands are often involved in the inflammatory process, however, there are no specific manifestations of this.
Treatment is based on the intake of antibacterial agents.
Autoimmune thyroiditis( Zob Hashimoto)
Body enlargement occurs only in the hypertrophic form of the disease. Parathyroid glands are rarely involved in the pathological process. Due to changes in the adequate immune response, T cells begin to attack the thyroid cells. After their destruction, the endocrine active tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue - nodes are formed. Characteristic symptoms remain:
- swallowing disorder,
- cough or upper airway compression,
- feeling of "knotty" in palpation,
- general weakness.
Adenoma and cancer
The cause of the appearance of tumors is a complex disturbance in the body's immune system and the effect of external carcinogenic factors. Approximately 5% of all nodes are malignant. Equally often occur both in men and in women. If the patient is not treated in time, the consequences can be very negative( death).Nevertheless, it is important to be able to differentiate pathology from other diseases, which are accompanied by an increase in thyroid gland. In the pathological process, one of the parathyroid glands is often indirectly involved.
Additional symptoms that can help to correctly diagnose are:
- weight loss patient,
- general weakness,
- skin discoloration( it is green),
- are palpated with painless dense nodes on the surface of the gland.
Timely treatment started can save a person's life.
Diagnostics
The most accessible method for detecting changes in the thyroid gland and parathyroid glands in size is simple palpation. Several distinct stages of growths parenchyma:
- gland is not palpable,
- swallowing can determine the isthmus,
- swallowing grope both lobes,
- visually can identify an increase in cancer( neck looks swollen),
- naked eye can see that there is an asymmetry in the parenchyma of the organ,
- visually there is an increase in thyroid gland, several times higher than normal.
Thanks to this simple method you can find out how much the process is started and what you need to do with the patient.
Additional diagnostic methods are the following:
- ultrasound. Helps on the screen to fix how nodes look inside the organ. You can specify their size and location.
- Scintigraphy using technetium. It visualizes the individual nodes of the structure, which are more active or, conversely, poorly absorbed radioactive material( "cold").CTD and MRI.Dear survey methods, which show in detail the image of the organ in 3D format. Allow to assess the size, location and other subtleties of pathological changes in the gland tissue. But why conduct such a study, if you can limit yourself to cheaper? Everything depends on each individual pathology and doctor's appointments. Puncture and biopsy. An irreplaceable method for suspected malignant degeneration of nodes. Allows you to under a microscope to evaluate the morphological and histological structure of altered structures. Nevertheless, most surgeons prefer not to do it, because there is a risk of spreading cancer cells. It is better to limit yourself to scintigraphy.
Treatment of
Thyroid enlargement requires adequate therapy. Depending on the cause of the disease, the treatment will be different.
Drug medications mainly depress the functions of the body and reduce the amount of hormones in the blood. The most popular drug remains Mercazolil. It blocks the synthesis of T3 and T4 and normalizes the patient's condition. It is used for diffuse toxic goiter, thyrotoxicosis and thyroiditis. During infectious inflammation, parenchyma is additionally attributed to antibiotics.
Surgical treatment is aimed at eliminating the nodes. What not to do is to hurry with the intervention. The fact is that if at the initial stages it is possible to eliminate the process with the help of tablets, then we must try. And only in the absence of effect can we move to more radical measures. A very frequent complication of the removal of the thyroid is the parallel excision of the parathyroid gland or several such ones. This situation requires immediate hormone replacement therapy and lifelong medication.
Thyroid cancer can be treated additionally using irradiation and powerful chemotherapy drugs. Malignant nodes absorb more radiation than normal tissue and are destroyed, which does not happen to the normal part of the organ.
volumes of drugs, the choice of surgery or irradiation selection options depend on the individual patient, and the pathological characteristics of the nodes in the gland. You can not do therapy at home, without a doctor. Qualitative treatment is possible only after a comprehensive examination and diagnosis. The consequences of such recovery depend directly on the patient. If there is a desire to recover - everything will be fine.



