 For the first time, the Louis-Bar syndrome was seen and described in France in 1941.Since then, his frequency of appearance has increased noticeably and began to occur around the globe.
For the first time, the Louis-Bar syndrome was seen and described in France in 1941.Since then, his frequency of appearance has increased noticeably and began to occur around the globe.
Statistics say, in today's society, 1 person out of 40 thousand people has a chance to have this syndrome.
Its essence lies in the congenital abnormal immune state of the body , which in particular affects the T-link and begins to manifest itself in abnormal changes throughout the body.
People with the syndrome are prone to frequent infectious diseases, and also have a high chance of developing malignant tumors throughout the body.
Most often, if the Louis-Bar syndrome begins to appear in children at the very birth, then it is fraught with fatalities, even without the chance to diagnose such a patient correctly and on time.
Disease in the same proportion affects both men and women, as quickly as possible, destroying their nervous system and skin.
Causes of
The syndrome can occur at the genetic level, with the slightest malfunction or abnormality.
A similar failure is fraught with neuroectodermal dysplasia, which is innate in such people.
Pathology refers to autosomal recessive diseases, which can occur if the gene disorders were present simultaneously in both parents.
The disease tends to completely change and destroy the tissues of the cerebellum, reaching even to its core.
Similar situations lead to degenerative changes in the cerebral cortex, as well as spinal cord.
It is possible to show it only after long and difficult treatment of infectious diseases, which do not give the desired result.
Strong immune disorders lead to the formation of malignant tumors, which originate in the lymphoreticular system.
Symptoms of
Syndrome In modern medicine, pathology is rare, but doctors are afraid of the possible development of 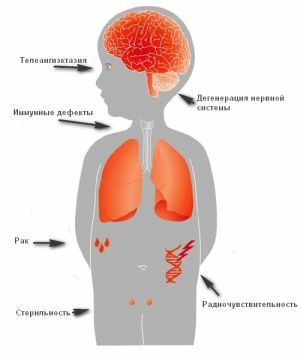 .
.
Since this genetic disease partially or completely destroys cellular immunity, it has a pathological character and can not be treated. A full life is almost unreal.
Symptomatic disease in adulthood can not be expressed immediately.
Most often it is detected by the gradual deterioration of the internal organs, the defeat of the immune system, complete or partial absence of the thymus.
If the Louis-Bar syndrome developed in utero, affecting the cerebellum and the cerebral cortex of the child, the newborn from the very birth of it has degenerative changes and a doomed diagnosis .
If at birth, the baby did not notice the first signs of the disease, then at the age of 3-24 months the syndrome will start to manifest rather quickly.
Most often this is expressed in the complete absence of movements, poor coordination, stagnation of mental development and external signs of development of the face and limbs.
It can be:
- muscle hypotension;
- strabismus;
- lack of reflexes and functionality of muscles and eyes.
The Louis-Bar syndrome often manifests itself in persistent infectious diseases that concern the airways and ears.
This can be otitis media, pharyngitis, bronchitis, sinusitis and other diseases.
Pneumonia and pneumonia are almost never manifested. Each subsequent disease has a more acute form and complications that are not amenable to treatment.
The sign of the symptom is also considered to be vascular asterisks, which can appear throughout the body at the age of 3 years.
Most often this is associated with the expansion of capillaries, but in the presence of only this symptom you need to look for other variants of possible diseases.
With regard to the external appearance of the face and eyes, here in the first place begins to manifest telangiectasia on the eyeball.
It is fraught with permanent conjunctivitis, the visual signs of which can manifest not only in the eyes, but also on the neck, cheeks, ears, eyelids and even on the palms.
In addition to this code, the whole body becomes dry and flaky, the hair cover is abundant.
In the most neglected situations, the syndrome can provoke malignancies, leukemia and lymphoma.
What is done for the diagnosis?
 At the first sign or suspicion of a disease of this kind, any doctor makes an appointment and referral to a doctor of a narrower specialization.
At the first sign or suspicion of a disease of this kind, any doctor makes an appointment and referral to a doctor of a narrower specialization.
Quite often, such patients are simultaneously observed by several doctors who prescribe treatment by a joint consultation.
It can be an immunologist, dermatologist, ophthalmologist, neurologist, oncologist and otolaryngologist. Only their joint consultations will be able to distinguish this symptom from other rare and dangerous types of diseases.
The final diagnosis in such a disease is always put only by a neurologist if he has all the results of clinical tests and laboratory tests on hand.
Most often, some indicators help to establish the diagnosis, which do not correspond to the norm. In particular, the blood can completely lack lymphocytes, and the level of immunoglobulin will be much lower than normal.
At the same time, absolutely no antibodies will be available to combat viral infections and diseases.
When the final diagnosis is for a neurologist on his hands, then you can prescribe a specific course and treatment regimen for such a patient.
How to prolong a patient's life?
At present, unfortunately, the level of medicine has not reached the level to find effective and rapid methods of combating this genetic disease.
Methods of treatment are still subject to the search and study of many scientists. However, to maintain the life-support of such patients it is customary to use palliative symptomatic treatment. 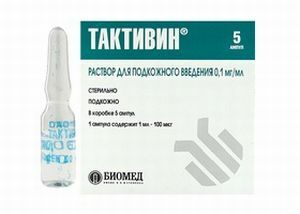
To prolong the life of such patients, a special immune therapy is prescribed, which can include different dosages of T-activatedin and gamma-globulin preparations.
At the same time, a constant high dosage of vitamin preparations is mandatory, which are introduced in a complex manner to maintain the proper functioning of the whole organism.
If, at the same time, a patient with Louis-Bar syndrome has some kind of infectious disease, then he is treated primarily with intensive therapy to start the process of maintaining the body at the proper level without unnecessary bacteria and viruses.
Depending on the disorders that are observed in the body, drugs and their dosages can vary significantly. Often the course of therapy is complemented by antifungal and antiviral drugs, as well as strong antibiotics.
 Unauthorized and unreasonable inflaming of the psyche about non-existent diseases - hypochondriacal neurosis. What needs to be done to treat the disorder?
Unauthorized and unreasonable inflaming of the psyche about non-existent diseases - hypochondriacal neurosis. What needs to be done to treat the disorder? Than Jackson's epilepsy differs from other types of disease. Methods of diagnosis and treatment are discussed here.
Real forecasts
Because the Louis-Bar syndrome is quite new and completely unexplored, it is impossible to talk about high chances for treatment and even more so for the patient's recovery.
The pathology has an unfavorable prognosis, which, depending on various factors, can both take place on the same level for many years, and rapidly roll down.
The most common symptom is found in deep childhood or at the birth of a child. The average age of these children is about 3 years.
If the symptoms are manifested later, such patients survive to a maximum of 20 years of age.
Most often, the cause of their death is not the disease itself, but the complete destruction of immunity and the rapid development of oncological formations throughout the body.