 The genetic disease of Werdnig-Hoffmann belongs to the group of spinal amyotrophies, is inherited in an autosomal recessive type.
The genetic disease of Werdnig-Hoffmann belongs to the group of spinal amyotrophies, is inherited in an autosomal recessive type.
Spinal muscular atrophy( CMA) is characterized by congenital or acquired degenerative changes in striated muscles, symmetrical muscle weakness of the trunk, extremities, absence or decrease of tendon reflexes while maintaining sensitivity.
Morphological studies of reveal the pathology of motor neurons of the spinal cord , "beam atrophy" in skeletal muscles with a characteristic alternation of affected fibers and healthy ones.
There is a violation of the conduction function of nerve fibers, a decrease in the contractile ability of muscles.
Statistics
1 out of 40-50 people are carriers of the mutant SMN gene. There is a pathology with a frequency of 1: 6 000 - 10 000 newborns.
Content
- Causes
- forms of spinal amyotrophy Verdniga Hoffmann
- Symptoms of the disease
- form of spinal amyotrophy Verdniga CMA 1
- Form CMA 2
- course of the disease
- Diagnostics
- Differential diagnosis
- Therapeutic techniques
- Types of spinal amyotrophy
- Video: Spinal amyotrophy adults
reasons
diseaseThe main cause of Verdnig Hoffmann's spinal amyotrophy is the SMN gene mutation( from the English survival motor neuron).The motoneuron survival gene is located on the 5 chromosome, it is represented by two copies:
- SMNt - telomeric copy, functionally active;
- SMNc is a centromeric copy of the gene, partially active.
The product of this gene is the SMN protein involved in the formation and regeneration of RNA.
A lack of protein causes pathology of the motor neuron.
In 95% of cases of Verdnig-Hoffmann disease there is a deletion( loss) of SMNt, which causes a deficiency of the SMN protein. A copy of SMNc only partially compensates for the lack of a telomeric copy.
The number of copies of SMNc is from 1 to 5. The greater the number of centromeric copies, the more fully reproduced the protein and less pronounced pathology of the neuron.
In addition to the number of copies of SMNc, the severity of the disease is determined by the length of the deletion site and gene conversions of 3 more genes: NAIP, H4F5, GTF2H2.The participation of additional modifying factors explains the clinical variety of symptoms.
Forms of spinal amyotrophy of Verdnig Hoffmann
I distinguish such species:
- early infantile or SMA 1 - signs of the disease appear up to 6 months of age;
- late form or SMA 2 - symptoms appear after 6 months to 1 year.
Symptoms of the disease
CMA 1 and CMA 2 have different symptoms and signs.
 What are the long-term consequences of craniocerebral trauma and how to protect yourself from getting a head injury.
What are the long-term consequences of craniocerebral trauma and how to protect yourself from getting a head injury.
A rupture of veins and cerebral vessels causes a disease such as subdural hematoma of the brain. What is the complexity of treatment and diagnosis of the disease.
Spinal amyotrophy form of Verdig CMA 1
The first symptoms are revealed during pregnancy due to faint perturbation of the fetus.

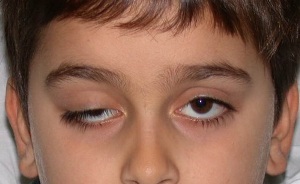
Photo: spinal amyotrophy of Verdnig Hoffmann
Since birth, respiratory failure has been observed in children, Verdnig Hoffmann's congenital spinal amyotrophy is noted:
- is low in muscle tone, the child does not hold a head, can not roll over;
- lack of reflexes;
- breach of sucking, swallowing, twitching of the tongue, fingers, weak crying.
The kid takes the characteristic "frog" posture with his arms and legs bent in the joints, lying on his stomach. When SMA 1 is often noted partial diaphragm paralysis - Cofferat syndrome.
The phenomenon is characterized by difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, cyanosis.
On the side of paralysis, chest swelling is observed, the risk of pneumonia increases.
Form CMA 2
The first months of life the children develop normally: they start holding the head in time, sit, stand.
After 6 months, the first symptoms of appear , usually after acute respiratory or foodborne infections.
First of all, the limbs of suffer, especially the legs, the tendon reflexes decrease.
Then the muscles of the trunk and hands, intercostal muscles, diaphragm are gradually involved in the process, which causes deformation of the chest. The gait changes, acquiring a resemblance to the "clockwork doll".
Children become awkward, often fall. There are twitchings of the tongue, trembling of the fingers.
The course of the disease
CMA 1 is characterized by malignant course. Severe disorders of respiratory function, cardiovascular failure often lead to death in the first months of life. Up to 5 years 12% of patients survive.
Diagnosis
 With spinal amyotrophy of Verdnik, the diagnosis is to perform a genetic analysis, detecting the mutation or deletion of the SMN gene.
With spinal amyotrophy of Verdnik, the diagnosis is to perform a genetic analysis, detecting the mutation or deletion of the SMN gene.
If a deletion of the telomere copy of SMNt is found, the diagnosis is confirmed.
In the absence of a deletion, additional studies are performed:
- electonejromiography;
- study of nerve conduction;
- test for creatine kinase;
- biopsy of muscles and nervous tissue.
With normal creatine kinase enzyme values, SMNc copies are counted. In the case of a single copy, a point mutation is identified, taking the final decision.
Differential diagnosis
Similar symptoms are observed with congenital myopathy - a muscle tone disorder.
Completely eliminate muscle hypotension allow biopsy results.
Certain similarities with the disease of Verdnig-Hoffmann have acute poliomyelitis. It begins violently, with a sharp rise in temperature, asymmetrical multiple paralysis.
The acute period lasts a few days, then the process goes to the recovery stage.
Glikogenozy and congenital myopathies are also characterized by a decreased muscle tone. Changes are caused, in contrast to spinal muscular amyotrophy, metabolic disorders, carcinoma, hormonal imbalance. It should also exclude Gaucher disease, Down's syndrome, botulism.
Treatment methods
Treatment of spinal amyotrophy is symptomatic and is aimed at stabilizing the patient's condition.
Assign medicinal remedy:
- metabolizing improves - cerebrolysin, lipocerebine, aminalone;

- affecting the trophism of muscle tissue - potassium orotate, glutamic acid, methionine, tocopherol acetate;
- promoting neuromuscular conduction - proserine, galantamine, dibazol;
- stimulating blood circulation in capillaries - komplamin, nicotinic acid;
- supporting the viability of motor neurons - valproic acid, riluzole, L-carnitine.
Patients prescribed orthopedic procedures in combination with with warm baths, therapeutic exercises, soft massage, oxygen therapy, sulfide baths are shown.
Types of spinal amyotrophies
The proximal and distal forms of CMA are conventionally distinguished.80% of all spinal amyotrophies are proximal.
These include, in addition to the disease Verdnig-Hoffmann:
- CMA 3 or disease Culdberg-Wellander - become ill at the age of 2 to 20, the first to suffer from the pelvic muscles. There is a tremor of brushes, lordosis.
- The lethal X-linked form of - described in 1994 by Baumbach, is inherited by a recessive trait, mainly affecting the pelvic and shoulder muscles.
- Infantile degeneration of - reflexes of sucking, swallowing, and breathing are violated. Death can follow at the age of up to 5 months.
- SPA Ryukyu - the clutch gene is not detected, there is a lack of reflexes, muscle weakness of the limbs after birth.
This group also includes Norman's disease, AGR with congenital arthrogryposis, SMA with congenital fractures.
The distal spinal amyotrophies include Fazio-Londe's progressive infantile paralysis, Brown-Villette-van Lare's disease, CMA with diaphragm paralysis, epilepsy and oculomotor disorders.
Video: Spinal amyotrophy of adults
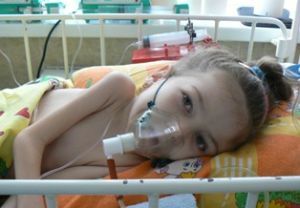
Girl diagnosed with spinal amyotrophy of Verdnig Goffman