 Meningiomyelitis is an inflammatory process that directly affects the substance of the spinal cord and its membranes. It is not characterized by an independent occurrence, but by a reaction to the underlying, underlying disease.
Meningiomyelitis is an inflammatory process that directly affects the substance of the spinal cord and its membranes. It is not characterized by an independent occurrence, but by a reaction to the underlying, underlying disease.
In etiology, meningomyelitis is represented by various local and systemic infections. Typically, infection( scarlet fever, measles, fever) and allergic inflammation starters( rheumatoid arthritis) are often expressed only at the onset of the disease.
The most dangerous is chronic meningomyelitis, observed with syphilis, brucellosis, chronostasis, and sometimes tuberculosis. In these cases, there is a coarsening of the soft meninges, creating a rigid shell with the spinal cord and inner surface.
The spinal cord appears thinned, more dense than usual. In a soft shell, redness, infiltration of the walls of blood vessels, sometimes - lymph nodes and fibrosis of membrane tissues;the inflammation of the blood vessels spreads through the spinal cord, often to the thoracic area, mainly it affects the white matter, sometimes involving the gray matter in the process.
Further the process extends to the spinal roots, especially in the early stages of the disease.
Complex of causes of
Meningiomyelitis is a secondary pathology that occurs against the backdrop of other diseases by getting the causative agent into the spinal cord together in the bloodstream.
Among others, the disease provokes:
- Syphilis .This is one of the most common causes of meningomyelitis. This is a chronic disease that provokes
 densification of the spinal cord, resulting in the appearance of adhesions that cause compression of the spinal cord.
densification of the spinal cord, resulting in the appearance of adhesions that cause compression of the spinal cord. - Tuberculosis .No less frequent cause of the disease. Mycobacteria from the source of the disease fall into the spinal cord with blood. The result is the emergence of miliary seals, causing the formation of serous fluid and a local allergic reaction. In the absence of treatment, it is necessary to replace the fluid with a fibrous connective tissue, which subsequently leads to adhesions. With a prolonged course of meningomyelitis can also reach the formation of centers of calcification of the spinal cord.
Symptoms of
disorder In the initial stages, paresthesias of damage to roots and spinal cord appear, pain in the chest, abdominal cavity of the  and limbs. Paresthesias are expressed by numbness, burning and tingling.
and limbs. Paresthesias are expressed by numbness, burning and tingling.
In the course of the disease, weakness develops in the limbs, often with an increase to full paraplegia, increased muscle tone, difficulty with urination and constipation, impaired sensitivity of the extremities and trunk at the level of the affected area.
At the initial stage of the disease, an increase in protein in the cerebrospinal fluid is observed.
If meningomyelitis is based on infection or an allergic reaction, CSF is dominated by lymphatic elements, and in septic processes - long neutrophilia.
With spinal syphilis, Wassermann's reaction in cerebrospinal fluid and blood may be positive. Syphilis meningomyelitis is characterized by the weakening of the limbs until their paralysis.
The disease caused by tuberculosis usually develops slowly;there may be some differences in the intensity and short-term remission of symptoms, in which complete abating of symptoms is possible. This complicates the recognition of the disease.
The main symptoms include spinal cord tightening, which provokes a violation of sensitivity and arbitrary movements of the limbs.
Diagnostic criteria and methods
Diagnosis of the disease is conducted by a neuropathologist on the basis of medical history and a characteristic clinical picture. It is carried out in the framework of laboratory research.
During the diagnosis of the disease, it is necessary to take into account the fact that meninomiomyelitis in humans can be a consequence of another disease.
For this reason, the diagnosis starts with a comprehensive survey. In its framework, the following methods are used: 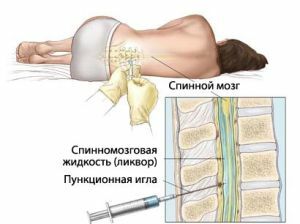
- lumbar puncture;
- tests for syphilis;
- assay for tuberculin;
- chest X-ray.
To determine the cause of the disease, an analysis of cerebrospinal fluid is performed. If the cause of meningomyelitis is in syphilis, the analysis will show pleocytosis and a positive Wasserman reaction. The pathology caused by rheumatism is determined by the presence of lymphocytes in the CSF, in the case of infection - of leukocytes.
Medical care
Methods of treating meningomyelitis directly depends on the underlying disease, a complication which it is. That is, to get rid of such undesirable consequences as meningomyelitis, the therapy focuses on the treatment of the underlying disease:
- In the case of tuberculosis , as the first causes, therapy is prescribed, including the taking of medications such as Pyrazinamide, Isoniazid, Rifampicin. In order to prevent their side effects, it is recommended to take vitamins of group B.
- Meningomihelitis, triggered by measles , involves hospitalization. In view of the fact that today there are no effective drugs for the treatment of measles, the therapy is based on the provision of measures aimed at the normalization of water-sodium, blood circulation in the vessels and general cleansing of the body.
- If typhoid and brucellosis are identified as starters, the therapy involves the administration of antibiotics, which are assigned accordingly to the degree of sensitivity to them of the particular patient.
- Penicillin is used to treat syphilis .Nevertheless, such therapy will show a positive result only if the optimal concentration of the drug will be present in the patient's blood for a long time. Otherwise, a complete victory over syphilis is not possible. In view of this, along with Penicillin, the reception of the medicament Probenecid, preventing the leaching of the main drug from the body, is shown.
On treatment of the primary disease that contributed to the appearance of meningomyelitis, treatment does not end. After the process of therapy, the body is weakened, which makes it susceptible to other diseases.
Thus, it is advisable to include in therapeutic therapy physical therapy, physiotherapy, introduction of changes in the diet( increased intake of vitamins), preferably also sanatorium treatment.
Prognosis and consequences of
 The prognosis in patients with meningomyelitis, first of all, directly depends on the reasons that led to its development. The effectiveness of therapy is closely related to the course of the disease: the more acute its course, the more positive the treatment will show.
The prognosis in patients with meningomyelitis, first of all, directly depends on the reasons that led to its development. The effectiveness of therapy is closely related to the course of the disease: the more acute its course, the more positive the treatment will show.
In relation to "favorable" for the body, the disease that results from infectious pathologies or allergic reactions is best suited( in this case, the initial diseases are brucellosis, typhoid, measles, rheumatism).
In the early stages of the disease, further complications may occur that require special treatment, and sometimes are a sign of increased severity of the disease. Infection can cause sepsis, a syndrome of a systemic inflammatory response, a drop in blood pressure, an increase in the heart rate, a high or abnormally low temperature, and rapid breathing.
How not to admit?
First of all, the prevention of meningomyelitis is based on the diagnosis and treatment of potentially dangerous diseases that can lead to pathology.
In order to prevent the formation of an immunocompromised disease, it is advisable to refuse new vaccination during the acute stage of the disease or in case of suspected presence of the myelitis index.
Important maintenance therapy with sunlight and vitamin D, smoking cessation and weight control.


