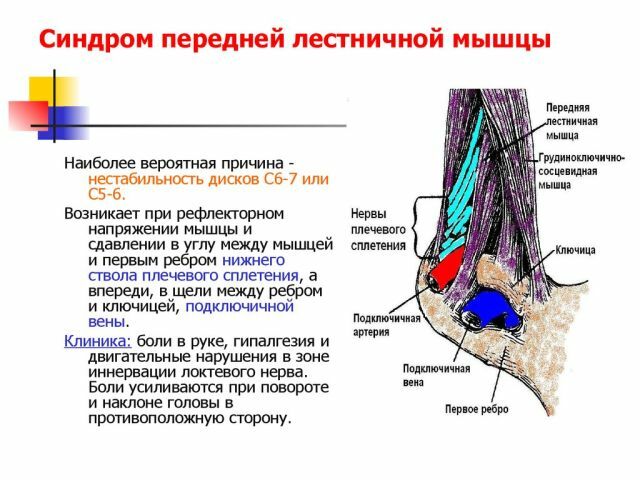
 To understand what is a Scalenus syndrome( other names - Nuffziger syndrome, a syndrome of the front staircase or SLM - TOS), first of all it is necessary to know that the ladder muscles in man are not one, not two, but three whole on each side of the body,and between each of them there are gaps.
To understand what is a Scalenus syndrome( other names - Nuffziger syndrome, a syndrome of the front staircase or SLM - TOS), first of all it is necessary to know that the ladder muscles in man are not one, not two, but three whole on each side of the body,and between each of them there are gaps.
And since nothing is wasted in a prudent and wise nature, it accommodates any free space to pass either individual large vessels and nerves, or for whole vascular-neural bundles, or places "constellations" of lymph nodes in them.
And the gap between the front and middle scalenus muscles is an exception to this rule.
The anterior of the above named muscles is located closest to the middle of the body, the middle staircase muscle is right behind it, and both are attached to the edge of the 1st rib in front. Only the first with its other end is incremented to the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae - from III to VI, and the second - to the same formations in general of all the vertebrae of the cervical spine column.
In a triangle called an interstitial, with boundaries indicated by an anterior ribbon, an anterior ribbing, a middle ribus muscle, and a path of the brachial plexus and the subclavian artery.
On the opposite side, the triangle between the muscles: the anterior scalenus and the two sublinguals - the hypoglossal and the breast-lingual - becomes the place of the subclavian artery passage together with the large lymphatic trunks.
The staircase muscles are available: location, anatomy, physiology and functions:
Features and causes of the
Scalenos syndrome The focus of the scalenus syndrome is that any of the two stair muscles, for one reason or another "coming into disgust"caught in the "scissors" between the structures. Most often it happens with the most loaded front muscle, so the term refers mostly to it.
The symptomatology emerging in the developing process fully corresponds to the degree of "deletion" -compression:
- subclavian artery;
- brachial plexus;
- subclavian vein and lymphatic vessels.
The degree of wall stiffness is the least compressible artery, it is much easier to transfer other structures of this area( nerves and arteries).
Hence the natural division of the symptoms of compression into:
- venous;
- arterial;
- is neurogenic.
By the onset of the scalenus syndrome - persistent or transient - leads to a breakdown in the activity of both scalens in the form of their hypertonicity, as well as changes in the sizes and shapes of the natural openings between them for the following reasons:
- episode or episodes of the traumatic nature of ( accident, industrial or domestic damage);

- of congenital anomalies of : "excessive" ribs, rigidity of ligaments between the rib and spine with a reduction in the rib and clavicular space;
- incorrectness of posture - either with "saggy" shoulders, or due to habit to tilt the head unnecessarily, which causes clamping of vessels and nerves in the area where they leave the thorax;
- wear of tissues due to the frequent repetition of intense gestures with the raising of hands - sports or being necessary in production( when the collarbone is lowered, the rib-key space is narrowed).
The motivation for squeezing structures located inside the intermuscular spaces can also be a change in the anatomical ratio of their components due to:
- excessive development of muscle tissue ( exercise with power sports) or fat ( for obesity, pregnancy, hypothyroidism, diabetes);
- fixation of the hands ( hands) in one pose for a long period of time ( plaster bandage, hours of work at the table).
The most common development of Nuffziger syndrome is observed in the most productive age( from 20 to 50 years), as well as in women( relative muscle weakness and propensity to obesity) and due to other diseases: trauma of the rotator humeral cuff, cervical osteochondrosis, damage to the brachial plexus.
Symptomatology by type of
syndrome Neurogenic type of stairway syndrome is the most common characterizing such symptoms:
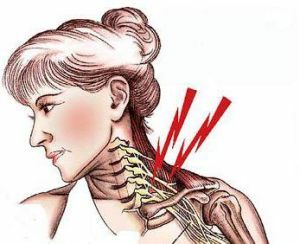
- with pain sensations of varying severity at the neck, shoulder, and arm level;
- disorders of sensitivity in the form of a state of "vatnosti", or tingling, or areas of "failure" of sensitivity in the same sections of the shoulder girdle and limb;
- weakness in the individual muscles of the hand or hands, leading to difficulties in performing operations with fine motor skills, as well as their rapid fatigue.
Venous type of anterior staircase syndrome, manifested itself in 4% of cases, has the following symptoms:
- feeling of "swelling" or "heaviness" of the hand;
- different pain or deep pain, or numbness, tingling in the area: neck - shoulder - arm;
- by changing the color of the skin of the limb - the fingers or the entire limb acquire a cyanotic-bluish color;
- has become a distinct venous "mesh" on the anterior chest wall;
- by compaction in the region of passage of the subclavian vein.
The arterial, the rarest type of syndrome, with compression of the artery is manifested:
- swelling of the limb or both - expressed by a feeling of "burdens" in the parts of the body;
- with superficial pain or deep soreness in the neck, in the shoulder, or in the hand;
- by a sensitivity disorder in the hand( tingling, "withering-numbness");
- by changing the color of the skin of the limb - fingers( or the whole body part) turn pale, and also by changing its temperature - the fingers or the entire limb are colder to the touch than other skin areas;
- by the appearance of small black spots on the skin of the fingers;
- weakness of the pulse on the arm or its complete absence;
- marked pulsation of the "tumor" in the zone of the clavicle.

Clarify the diagnosis allows. ..
Given the variability of manifestations of the symptom of the staircase, it is not necessary to focus exclusively on the physical method of investigation.
Therefore, for the formulation of an absolutely accurate diagnosis, the following methods are used:
- EMG( electromyography);
- radiography, MRI, CT;
- angiography and ultrasound;
- laboratory tests of general blood, as well as on the level of sugar and hormones.
Different degrees of development - different levels of treatment
 Drug medications are used in cases of moderate, non-neglected course of the process.
Drug medications are used in cases of moderate, non-neglected course of the process.
This is the purpose of the various effects of NSAIDs with a view to stop inflammatory manifestations in problem areas: Ibuprofen, Aspirin, Naproxen, Movalis, Celecoxib( Celebrex).
Treatment options with Cioblobenzaprine( Flekseril), Carisoprodol( or Soma), Diazepam( Valium), Metocarbamol( Robaxin), and Tizanidine( Zanaflex) are applicable for the preparation of the muscle relaxant class for the removal of spastic conditions.
Also used group of drugs that reduce the level of transmission of pain impulses in the brain and spinal cord:
- Fluoxetine( Prozac);
- Sertraline( Zoloft);
- Paroxetine( Paxil);
- Citalopram( Cellex);
- Venlafaxine( Effector).
Equally relevant is the following group of drugs:
- Amitriptyline( Elavil);
- Imipramine( Tofranil);
- Desipramine( Norpramine);
- Doxepine( Sinequan);
- Amoxapine( Ascendene).
When achievable pain limit values are used drugs class opioids - narcotic analgesics( both in the form of a mono drug, and in combination with NSAIDs), as well as the method of blockade.
Of the non-drug therapies that apply if staircase syndrome is diagnosed, the following techniques are used to improve blood and lymph circulation in problem tissues, to rid them of toxic metabolic products, restore proper posture and  biomechanics movements:
biomechanics movements:
- exercise therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- manual therapy;
- acupuncture( acupuncture);
- massage.
Exercises for spasms caused by stairway muscle syndrome:
In far-reaching cases, staircase syndrome uses surgical methods to correct the condition of ligaments, muscles and vessels with subsequent orthopedic measures and long-term spa treatment.
In such an important process as treating the syndrome of the anterior staircase, none of the therapy methods should be neglected.
About the most serious complications of
The stagnation of blood in the narrowed rib and clavicular space can lead not only to the limb function disorder due to the formation and growth of the thrombus, but also to its loss due to thrombus embolism in the vessels of the upper limb.
The course of the syndrome may also be complicated by pulmonary thromboembolism with a fatal outcome.
The compression of the brachial plexus leads to a disruption of the function of one or both extremities of the neurogenic etiology.
No less serious is the prognosis in case of worsening cerebral circulation, because the vertebral artery is a branch of the subclavian artery.