 Among the many varieties of epilepsy, it is also customary to isolate cryptogenic. At first glance, it looks like other types of disturbances, manifests the same symptoms, but with detailed study, you can find some features.
Among the many varieties of epilepsy, it is also customary to isolate cryptogenic. At first glance, it looks like other types of disturbances, manifests the same symptoms, but with detailed study, you can find some features.
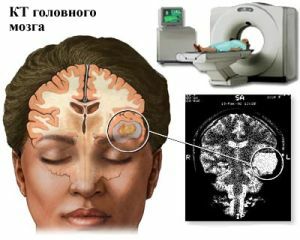
The very word "cryptogenic", with respect to whatever disease it is used, means - of unknown origin. Accordingly, the concept of "cryptogenic epilepsy" means that there are no visible foci in the brain that would cause epileptic seizures.
And yet, epileptic seizures occur, sometimes, completely without reason. The symptomatology with them is similar to that of ordinary epilepsy. The only difference is in the absence of a focus of pathological activity.
Content
- little history
- anatomical reference
- The reasons for
- clinical picture
- syndrome Vesta
- Syndrome Lenox-Gastaut
- myoclonic-astatic version
- Partial seizures
- Automatisms
- secondarily generalized seizure
- absences
- Generalized seizures
- Diagnostic criteria
- Treatment
disease Fewhistory
Epilepsy, as a disease, is known to the world for a very long time. However, officially it was only after the 18th century that she was considered a disease. Until that time, its origin was explained by different versions.
The most famous doctors of the ancient world considered this disease a pathology of the heart and blood vessels. And only Hippocrates put forward the assumption that the essence of  epilepsy lies in the defeat of the brain. However, he did not advance beyond this assumption.
epilepsy lies in the defeat of the brain. However, he did not advance beyond this assumption.
In times of the Middle Ages it was believed that epilepsy is a disease of the soul, the result of "devil's machinations".People who developed epileptic seizures were considered possessed and tortured and even killed in order to drive out the devil.
After the emergence of psychiatry as a science, epilepsy was again spoken of as a disease of the body. With the development of diagnostic methods, organic causes of epilepsy began to appear. And only cryptogenic epilepsy is still a mystery.
Anatomical reference
With normal epilepsy in the substance of the brain, or rather, in its cortex, foci of pathological neural activity are formed. They arise in those areas where a healthy person should not be. The functioning of such pathological sites externally manifests itself as a characteristic epileptic fit.
Cryptogenic epilepsy manifests itself with the same symptoms that fit into the picture of the usual variant of the disease. But with the help of methods known at the moment, it is not possible to detect a pathologically altered area of the brain.
Therefore it remains unclear what causes a characteristic picture of this type of violation.
The level of modern medicine allows you to accurately diagnose only 40% of cases of epilepsy. The remaining 60% of cases are related to cryptogenic epilepsy. The disease occurs sporadically, regardless of the sex and age of the person. The territorial features of the spread of this disease are also not revealed.
EEG patterns
About the causes of
Since there is no visible focus due to which epileptic activity could form, there is no precise epilepsy for cryptogenic epilepsy, the exact causes of its occurrence are unknown. At the moment, the same causes are considered as probable causes of the classic type of violation:
- , the main cause is the hereditary weighed ;
- the formation of the disease in some cases may be a consequence of craniocerebral injury ;
- disorder may be a consequence of strokes ;
- intoxication by certain substances is also capable of leading to the onset of the disease.
Clinical picture of
Cryptogenic epilepsy is characterized by the same symptoms as the classical one. Epileptic seizures with it can  classify the same as usual. There are several features of the disease:
classify the same as usual. There are several features of the disease:
- attack is somewhat more severe than with the classical version;
- is difficult to select the appropriate treatment, because the disease responds poorly to the main groups of drugs used;
- regression of personality occurs several times faster;
- the results of the survey, especially the methods of neuroimaging, each time turn out to be different.
However, there are a few special focal forms that are attributed to this variant of the disease.
Vest syndrome
Vest syndrome is the earliest manifestation of cryptogenic epilepsy, it is usually diagnosed in children aged two to  for four months.
for four months.
Symptom is sudden seizures, which also stop suddenly.
They lead to a delay in the mental development of the child.
Once a child reaches the age of one year, the syndrome may stop on its own or be transformed into another variant of the disease.
Lenox-Gasto Syndrome
Lenox Gasto Syndrome is also a pediatric form of the disease, but at a later age - from two to eight years. This syndrome can appear independently, or develop from the Vest syndrome.
The state of sudden episodes of loss of balance in a child or short-term stun conditions. In this case, loss of consciousness is not observed.
Frequent occurrence of seizures leads to traumatism of the child and impaired mental development.
Myoclonic-astatic variant of
This type of cryptogenic epilepsy is typical for children aged five months to ten years. It appears at the age of one or more years by the onset of seizures of generalized seizures( a large seizure).
After the children begin to walk, they have attacks of sudden loss of balance.
Other variants of cryptogenic epilepsy, manifested both in childhood and in adults, are clinically similar to the classical course of the disease. All seizures can be divided into two large groups - partial and generalized. In each group, several subspecies are identified.
Partial attacks
The following types of partial seizures are distinguished:
- Motor attack .With this attack, there is a reduction in the musculature of a particular part of the body. These can be
 muscles of the limbs, back, abdomen, facial muscles. The attack occurs suddenly, and also passes. Loss of consciousness is not observed.
muscles of the limbs, back, abdomen, facial muscles. The attack occurs suddenly, and also passes. Loss of consciousness is not observed. - Sensory attack .This option is characterized by the sudden appearance of any sensations. It can be paresthesia - a sensation of heat or cold, crawling, crawling, burning, burning in the extremities, as well as sensory disorders - visual, auditory, taste and olfactory hallucinations. Loss of consciousness as such in sensory seizures is not, but there is a certain aura in the form of stunning or noise in the ears.
- Vegetative attack .This attack is characterized by the appearance of various vegetative disorders without loss of consciousness. There may be hyperemia of individual skin areas, increased sweating, fluctuations in heart rate and blood pressure.
- Mental Attack .Characterized by a sudden violation of mental functions - speech, thinking, cognition. There may be various hallucinations, imbalance and coordination of movements.
Automatisms
This is a more complex version of the epileptic attack, characterized by the occurrence of often repeated human movements, and he does them unconsciously. Movements are diverse in nature:
- mimic;
- gestures;
- twitching of limbs;
- gait violation.
Secondary generalized attack
The onset of such an attack can take place according to any of the above options, but it ends always with the formation of generalized seizures, sometimes with loss of consciousness.
Absence
Absence is already generalized and is characterized by a sudden loss of consciousness lasting no more than five minutes. It may be accompanied by the appearance of any of the partial seizures, most often these are automatisms.
Generalized convulsions
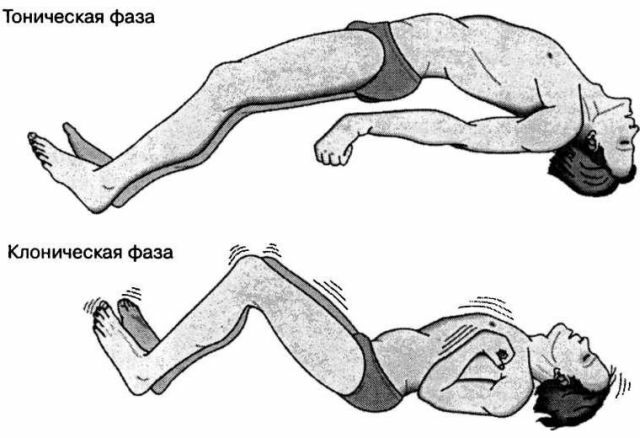
Cryptogenic generalized epilepsy is the most severe form of the disease. For a while before the development of immediate seizures, there is a period of aura - headache, autonomic disorders, panic conditions.
After this, tonic and clonic seizures develop, lasting an average of ten minutes. This episode ends with an involuntary emptying of the intestine and bladder.
In the post-attack period, amnesia is observed.
Diagnostic criteria
The main diagnostic criterion of cryptogenic epilepsy is the complete elimination of visible organic brain damage. In order to exclude this, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- A thorough and complete collection of an anamnesis of for the life and illness of a patient. It is aimed at determining the possible cause of
 for the formation of epilepsy.
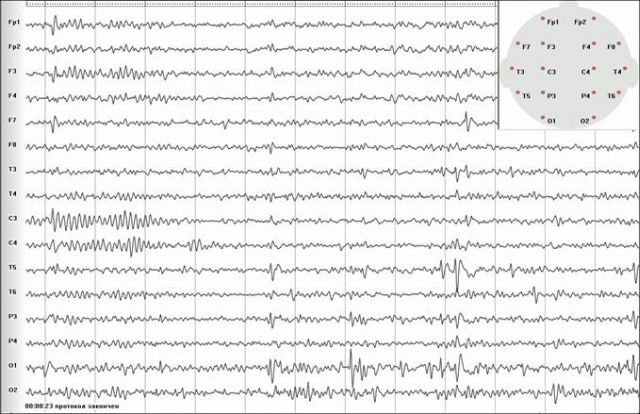
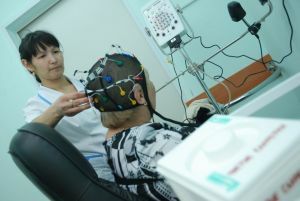
for the formation of epilepsy. - The basic diagnostic method is electroencephalography .The essence of the method is to record with the help of a special device electrical activity of the brain. In the presence of pathological activity, changes will occur on the film.
- Methods of neuroimaging the are aimed at finding a pathological focus. These include ultrasound, computer and magnetic resonance imaging. In cryptogenic epilepsy, these methods will confirm the absence of organic brain damage.
So, cryptogenic epilepsy is characterized only by the presence of characteristic seizures and changes registered at this time on the electroencephalogram. Neither possible causes, nor organic pathology can not be identified.
Treatment of the disease
Cryptogenic epilepsy does not respond well to conventional therapies. Perhaps this is due to the absence of a pathological focus. However, other methods of treatment, except for the classical not invented.
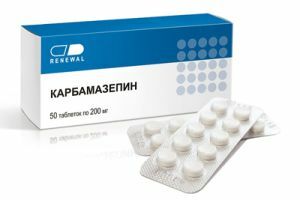
The basis of treatment is the reception of antiepileptic drugs:
- Carbamazepine;
- valproic acid group;
- Lamotrigine;
- Topiramate;
- Gabapentin;
- Phenobarbital.
Treatment with antiepileptic drugs always begins with a single remedy - most often carbamazepine or valproate. If treatment is ineffective, the drug is replaced with another drug or a combination of several drugs is used.
Parallel correction of other accompanying disorders is also carried out. Cryptogenic epilepsy is a disease that is unclear, with its own flow characteristics. Cure it can be difficult, because the cause of its occurrence is unknown.