Diseases of the endocrine system - a real scourge of the twenty-first century. Among the leaders in terms of the incidence of the population, the first place is occupied by cardiovascular diseases, the second - endocrine, in particular, the problems of the pancreas and thyroid glands. In the latter case, common diseases are thyrotoxicosis, hypothyroidism and thyroiditis.
Basics of the disease
Autoimmune thyroiditis, like other diseases of the thyroid gland, is associated with its actual physical state - if the cells of the gland are damaged, an irregular production of hormones produced by the thyroid gland begins.
Speaking specifically about the chronic form of autoimmune thyroiditis, the disease has an inflammatory nature. The process of inflammation occurs under the influence of antibodies of the immune system to the gland, which mistakenly regard it as a foreign body. In a healthy organism, antibodies should be produced only for bodies that are not native to the body, in the same case they affect the cells of the thyroid gland.
Causes of
Most pathology affects patients in the age category from forty to fifty years. Women suffer from thyroid gland diseases three times more often than the male sex. In recent years, the disease occurs in people and younger age, as well as in children, which is considered a problem of world ecology and a wrong way of life.
The source of the disease can be heredity - it is proved that autoimmune thyroiditis in close relatives is more common than without such a factor, besides, a genetic manifestation is possible in other diseases of the endocrine system - diabetes, pancreatitis.

But in order for hereditary facts to be realized, it is necessary to have at least one provoking factor:
- Frequent diseases of the upper respiratory tract viral or infectious;
- Foci of constant infection in the body itself - it's tonsils, sinuses of the nose, teeth with caries;
- Prolonged intake of drugs with iodine;
- Long-term exposure to radiation.
Under the influence of these factors, lymphocytes are produced in the body that promote the pathological reaction of producing antibodies attacking the thyroid gland. As a result, antibodies attack the thyrocytes - the cells of the thyroid gland - and destroy them.
The structure of the thyrocytes is follicular, so if the cell wall is damaged, the secret of the thyroid gland, as well as the damaged cell membranes, is released into the blood. These very remnants of cells cause a re-wave of antibodies to the gland, so the process of destruction cyclically repeats.
Mechanism of autoimmune action
In this case, the process of self-destruction of the gland by the body is complex, but the general scheme of the occurring processes in the body is largely studied:
- To distinguish between own and alien cells, the immune system is able to distinguish proteins that make up different cells of the body. To recognize the protein in the immune system, there is a cell-macrophage. He contacts the cells, recognizing their proteins.
- Information about the origin of the cell is delivered by the macrophage to the T-lymphocytes. The latter may be so-called T-suppressors and T-helpers. Suppressors prohibit cell attack, helpers - allow. In fact, this is a specific database that allows an attack without recognizing such a cell in the body, or prohibits it by recognizing such a cell known earlier.
- If T-helpers allow an attack, the release of the cells attacking the gland and macrophages begins. Attack involves contact with the cell, including with the help of interferons, active oxygen and interleukins.
- B-lymphocyte is involved in the production of antibodies. Antibodies, in contrast to active oxygen and other attacking agents, are specific formations directed and developed to attack a particular type of cell.
- Once the antibodies are bound to antigens-the attacked cells-an aggressive immunity system called the complement system is launched.
Speaking specifically about autoimmune thyroiditis, scientists came to the conclusion that the disease is associated with a malfunction of the macrophage when the protein is recognized. The protein of the gland cells is recognized as foreign, and the process described above is triggered.
The violation of such recognizability can be genetically inherent, and may be represented by low activity of suppressors designed to stop aggressive immunity systems.
Antibodies that produce a B-lymphocyte attack thyroperoxidase, microsomes and thyroglobulin. These antibodies are subjects of laboratory research when the patient passes the diagnosis of the disease. The gland cells become unable to produce hormones and the hormone deficiency is formed.
Symptoms of
The chronic form of autoimmune thyroiditis may not exhibit symptoms for a long time. The first symptoms of the disease look like this:
- Feeling of a lump in the throat during breathing, swallowing;
- Discomfort in the throat, neck;
- Slight pain in palpation of the thyroid gland;
- Weakness.
At the next stage of the disease, more severe symptoms appear. It is these symptoms that push the endocrinologist to suspect a patient of an autoimmune thyroiditis:
- Tremor of the hands, feet, fingers;
- Rapid heart rate, high blood pressure;
- Increased sweating, which is more often noted at night;
- Anxiety, anxiety, insomnia.

In the first years of the disease, hyperthyroidism may appear, the symptoms of which are similar. In the future, the thyroid gland can normalize or the amount of hormones will be slightly reduced.
Hypothyroidism is observed during the first ten years from the onset of pathological processes, and its severity is enhanced by severe physical or psychological stress and injuries, upper respiratory tract diseases and other risk factors mentioned above.
Forms of the disease
Thyroiditis is distinguished by the severity of symptoms and the physical state of the thyroid itself.
- Hypertrophic form - there is an increase in the organ, possibly a local or general enlargement of the gland. Local magnifications are called nodes. This form often begins with thyrotoxicosis, but in the future, with adequate treatment, the organ function can be restored.
- Atrophic form - gland does not increase in size, but its function is significantly reduced, leading to hypothyroidism. This type occurs with prolonged exposure to radioactive radiation in low doses, as well as in the elderly and children.
By and large, the form of the disease does not greatly affect how the disease will be treated. Fears can only be caused by nodal formations. If a node is found, oncologist's consultation is necessary to prevent the degeneration of the node's cells into malignant ones.
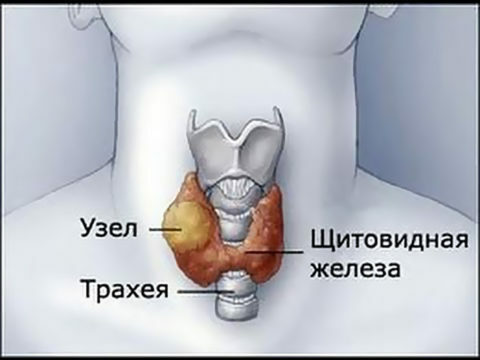
Otherwise, the nodal connections in most cases do not need to be removed unless a malignant nature is revealed, and the treatment can be medicated, without surgical intervention, if there are no other bases for the operation.
Diagnostic methods
First of all, the therapist will send the patient to receive not only an endocrinologist, but also a neurologist, and a cardiologist. This is necessary for the reason that the symptoms of thyroiditis are non-specific and can easily be mistakenly attributed to other diseases. To exclude pathologies from other body systems, consultations are scheduled with several doctors.
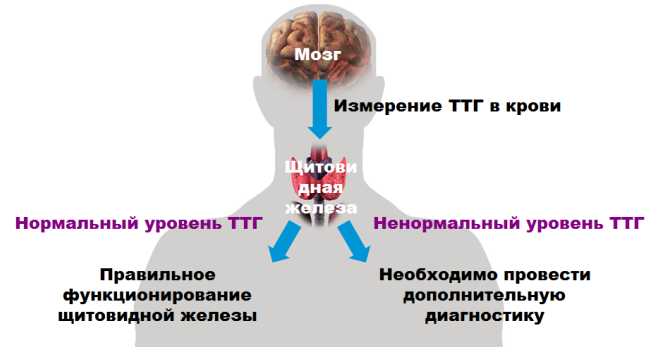
The endocrinologist necessarily conducts a palpation of a thyroid gland and directs on laboratory diagnostics. The patient donates blood to the number of thyroid hormones, namely, T4, T3, TSH - thyroid-stimulating hormone, AT-TPO - antibodies to thyroid peroxidase. By the ratio of these hormones in the results of the analysis, the endocrinologist makes a conclusion about the form and stage of the disease.
The immunogram and ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland is also prescribed. During the examination, an increase in the size of the gland or an uneven increase in nodular thyroiditis is found.
To exclude the malignant form of the nodes in autoimmune thyroiditis, a biopsy is appointed - a study of a piece of the gland tissue. Thyroiditis is characterized by a high concentration of lymphocytes in the thyroid gland cells.
With a clear clinical picture of thyroiditis, the possibility of malignant neoplasms in the gland increases, but often the thyroiditis proceeds in a benign manner. Lymphoma of the gland is, rather, an exception than the rule.
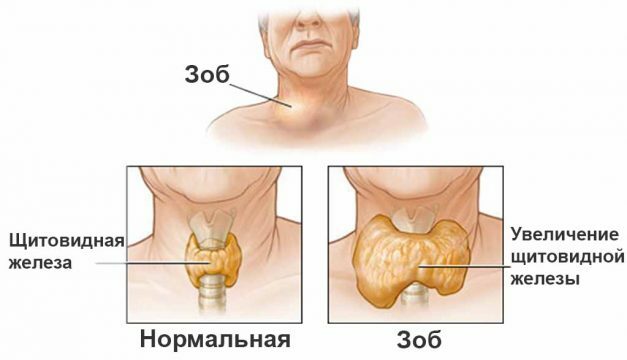
As the increase in the size of the gland is characteristic not only of autoimmune thyroiditis, but also of diffuse toxic goiter, ultrasound alone can not serve as a basis for establishing a diagnosis.
Substitution therapy
Treatment of chronic autoimmune thyroiditis depends on the course of the disease. Often when hypothyroidism - a deficiency of thyroid hormones - is prescribed replacement therapy with synthetic analogues of thyroid hormones.
These drugs are:
- Levothyroxine;
- Alosteen;
- Antistrum;
- Veprena;
- Iodalance;
- Iodomarine;
- Calcitonin;
- MicroROID;
- Propitsil;
- Thiamazole;
- Thiro-4;
- Tyrosol;
- Triiodothyronine;
- Eutiroks.
In patients with cardiovascular diseases, as well as in old age, it is necessary to start substitution therapy with small doses of drugs and observe the reaction of the body, undergoing laboratory diagnostics every two months. Correction of the treatment scheme is carried out by an endocrinologist.
When combined autoimmune and subacute form of thyroiditis, glucocorticoids are prescribed, in particular, prednisolone. For example, women with a chronic form of the disease during pregnancy experienced a remission of thyroiditis, in other cases in the postpartum period, on the contrary, hypothyroidism was actively developing. It is at these critical moments that glucocorticoids are needed.
Hyperfunction of the gland
When diagnosing the hypertrophic form of autoimmune thyroiditis, as well as with significant compression and discomfort of breathing due to an increase in the thyroid gland, surgery is indicated. Similarly, the problem is solved if the prolonged enlarged state of the gland has moved and the organ has started to grow rapidly.
In thyrotoxicosis - increased function of the thyroid gland - are prescribed thyrostatics and beta-blockers. These include Mercazolilum and Thiamazole, which are prescribed most often.
To stop the production of specific antibodies to thyreperoxidase and thyroid gland in general, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed: Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, Voltaren.

Also shown are preparations for immunostimulation, vitamin-mineral complexes and adaptogenes. With a decrease in the function of the gland, repeated courses of substitution therapy are prescribed.
Forecast
The disease progresses rather slowly. For fifteen years, on average, the patient feels sufficient performance and the state of the body. Under the influence of risk factors, relapses can develop, which are easily stopped by the course of drugs.
Exacerbation of thyroiditis may be accompanied by both hypothyroidism and thyrotoxicosis. Moreover, most often hypothyroidism as a consequence of thyroiditis in the phase of exacerbation, occurs in the postpartum period in women. In other patients, thyrotoxicosis predominates.
Treatment with hormones is not always life-long. Such a prognosis is possible only with congenital abnormalities of the thyroid gland. In other cases, timely-started courses of replacement therapy with synthetic hormones are sufficient to eventually reduce the dose of hormones and completely stop taking them.
Conclusion
The decision to take hormonal drugs is made only by an endocrinologist on the basis of laboratory diagnosis and ultrasound results. In no case can you engage in self-medication of endocrine diseases, since hormone imbalances, supported from the outside, can lead to a coma.
With timely detection, the prognosis of treatment is favorable, and remissions can last for years with short-term rare exacerbations, which are easily eliminated by the course of drugs.