What is phlegmon?
Phlegmon is called an acute purulent inflammatory process that occurs in fatty tissue and spreads to surrounding tissues, including tendons and muscles.
The disease occurs at any age, equally common in men and women. The inflammatory process can develop by itself or is a complication of other purulent processes - carbuncles, furuncles, abscesses and others.
Where does phlegmon occur?
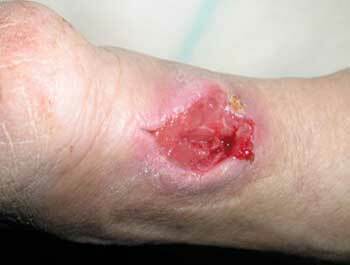
Phlegmon, abscess cleaning, photos
Inflammation of fatty tissue can occur as a result of violation of the integrity of the skin when penetrating into the wound of pathogens.
However, as practice shows, the disease most often develops where there were no injuries or injuries. The favorite places of localization of the pathological process are:
- Breast;
- Anterior abdominal wall;
- Back;
- Hips;
- Buttocks.
Face and neck phlegmon are quite common.
Contents of
The causes of phlegmon
- 5 Complications of phlegmon
- 6 Prophylaxis
- 7 Phlegmon - code on μb 10
Causes of phlegmon formation
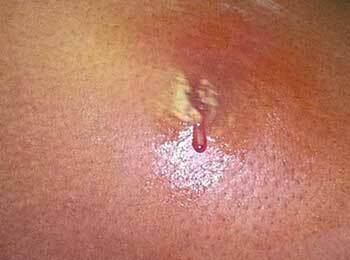
If the skin is damaged, the cause of acute inflammation is obvious - penetration from outside of bacteria. With the formation of phlegmon "on an equal place" its exact causes are not established by medical science.
However, it is believed that the chronic foci of infections in the body or weak immunity can cause the development of an inflammatory process.
Predisposing factors are:
- Diabetes mellitus or other disorders in the work of the endocrine system;
- Depletion of the body, for example, in cancer patients;
- Taking medications that are detrimental to the immune system;
- Immunodeficiency conditions;
- Severe intoxication of the body.
Forms of the disease
There are several forms of the disease:
Serous phlegmon - inflammation is caused by the accumulation of pathological fluid( fluid).The cellulose becomes turbid in appearance as a result of the accumulation of its accumulated fluid.
The boundaries of the pathological focus and non-infected tissues are practically not noticeable.
Purulent phlegmon - the surrounding pathological focus of the tissue begins to melt, resulting in a large amount of pus. With this form of inflammation, fistulas or ulcers often form near the lesion, from which a green-yellow liquid is released.
As the phlegmon progresses, the disease spreads to the muscles and fascia, resulting in a gray cloth and pus.
Putrefactive - at this stage, the structure of tissues breaks down and the formation of gases, as a result of the neoplasm exudes an unpleasant smell of rot.
The site of localization of the pathological process and located near the tissue acquire a mushy shape of a dark color. This condition leads to a strong intoxication of the whole body.
Necrotic form - necrotic foci( dead skin) are formed on the surface of the neoplasm, which are subsequently rejected by the body, and bleeding wound surfaces remain in their place.
Often after necrotic phlegmons abscesses are formed, the treatment of which is carried out( mainly) by an operative route.
Anaerobic - an inflammatory process spreads to large areas of fatty tissue, causing the formation of necrotic foci with the release of gas. Affected tissues acquire an earthy tint and an intolerable unpleasant odor.
When probing, crunches are clearly heard( crepitation), which is due to the accumulation of gases. The tissues around the anaerobic phlegmon resemble boiled meat.
Symptoms of phlegmon, photo
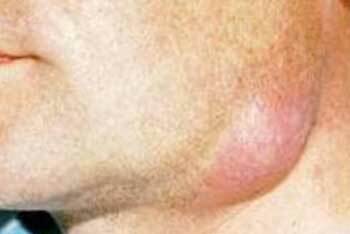
Manifestations of phlegmon of face and neck, photo 3
The clinical picture of the disease is acute. At the initial stage the site of localization of the inflammatory process is sharply painful, hot to the touch, edematous. The softened areas of the neoplasm indicate the accumulation of pus under the skin.
As the disease progresses, general symptoms are also added:
- Increased body temperature( up to 39.0-40.0 degrees);
- Fever;
- Increasing weakness;
- Increased thirst( often with phlegmon patients complain of severe dry mouth);
- Shortness of breath, palpitations;
- Severe headaches
- Pale skin and lowering blood pressure.
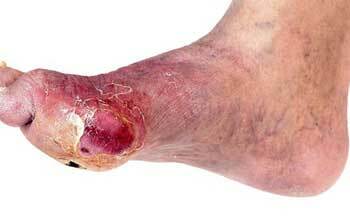
Against the background of general intoxication of the body, the patient may experience vomiting, anuria( or oliguria), a weak threadlike pulse.
Treatment of phlegmon
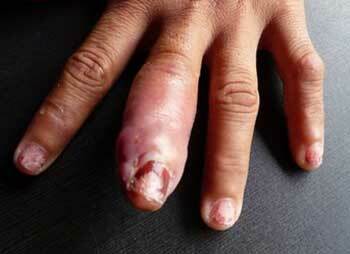
Phlegmon of the finger, photo 5
When diagnosing phlegmon, hospitalization in the surgery department is required. In an acute period, a strict bed rest is shown. If there is pus at the site of infiltration, it should be immediately removed by operative opening and draining.
If the disease is detected at the stage of infiltrate formation, that is, before tissue softening and pus accumulation, treatment of the inflammatory process is carried out by conservative methods - using thermal procedures, ultraviolet radiation, mercury ointment.
With the formation of condensation and high body temperature, the patient is assigned phlegmon surgery to ensure a qualitative outflow of pus.
After the removal of pus, the cavity is washed and inserted into special tubes. A sterile gauze dressing moistened with 10% sodium chloride solution is applied to the wound.
Without fail, patients with acute inflammation of fatty tissue are prescribed antibiotics of a wide spectrum of action, as well as concomitantly fortifying preparations and vitamins.
To eliminate the pain syndrome, it is advisable to prescribe analgesics, to remove heat - antipyretic drugs.
To accelerate the rejection of dead tissue areas, ointment Iruksol or other local products containing enzymes are prescribed.
For the early healing of open wounds, ointment Troxevasin or Metilitacil ointment is prescribed.
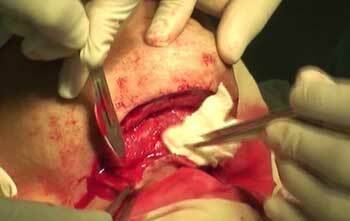
Operation phlegmon photo 4
Recovery after phlegmon surgery requires several months, and the patient must strictly follow the doctor's recommendations so that there is no recurrence and transition of the disease to a chronic form. Complications of phlegmon
Complication is the spread of infection through the body with blood or lymph flow, which is fraught with general intoxication of the body and the development of sepsis or lymphadenitis.
Phlegmon and abscesses in the maxillofacial area can lead to the spread of infection on the brain tissue, which leads to the development of meningitis or purulent meningoencephalitis.
The phlegmon of the neck can lead to suffocation, and the involvement of the nearby arteries in the inflammatory process and subsequent destruction of the vessel walls causes massive arterial bleeding and death.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of phlegmon development will help strengthen the patient's immune system, timely and adequate treatment of furuncles and carbuncles, normalization of metabolism and eradication of chronic bacterial foci in the body.
Which doctors should be treated with phlegmon?
If you identify the first symptoms of phlegmon, the patient is recommended to consult a surgeon.
Treatment of neoplasm of the maxillofacial area is performed by dental surgeons, with the development of the disease as a result of a fracture or other trauma - traumatologists.
Phlegmon - code for μb 10
In the international classifier of phlegmon diseases is in class XII( L00-L99)
L00-L99 - Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue
- ( L00-L08) Infections of the skin and subcutaneous tissue
( L03) Phlegmon
- L03.0)
- ( L03.1) Flegmon of other parts of the limbs
- ( L03.2) Facial phlegmon
- ( L03.3) Tissue phlegmon
- ( L03.8) Other phlegmon localizations
- ( L03.9)Phlegmon, unspecified