Epidemiology and prevalence of
Chronic cystitis in women is more common than in men due to some peculiarity of their anatomical structure( short urethra) .Men are much less likely to get sick of this disease and they usually combine with other inflammatory diseases of the urogenital system. Chronic inflammation of the walls of the bladder is one of the most common pathologies among inflammatory urological diseases.
Causes of chronic cystitis
Among the causes of chronic cystitis are the following:
- microbiological( bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, including sexually transmitted infections);
- physical( thermal, mechanical, radioactive);
- chemical( poisons, toxins, various medicinal substances, etc.).
In addition, there are factors that predispose to the development of this pathology:
- hypothermia;
- bladder stones;
- infectious-inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs( prostatitis, pyelonephritis);
- foci of chronic infection of the body( caries, chronic abscesses and others);
- long sedentary work;
- spicy, salty, smoked and fried food;
- non-compliance with personal hygiene;
- excessive sexual activity;
- prolonged constipation;
- medical manipulations on pelvic organs( for example, cystoscopy, catheterization of the bladder and others);
- incorrect treatment of acute cystitis;
- decreased immunological strength of the body due to various causes.
Classification of chronic cystitis
 Chronic cystitis is a collective concept of many similar pathological conditions associated with inflammatory pathology of the bladder. In order to make it easier to differentiate them from each other and designate an appropriate regimen for the treatment of chronic cystitis, various classifications have been devised.
Chronic cystitis is a collective concept of many similar pathological conditions associated with inflammatory pathology of the bladder. In order to make it easier to differentiate them from each other and designate an appropriate regimen for the treatment of chronic cystitis, various classifications have been devised.
Due to the cause of cystitis:
- is infectious;
- is parasitic;
- is traumatic;
- chemical;
- is allergic;
- exchange;
- cystitis in diabetes mellitus;
- dyshormonal;
- beam;
- in spinal patients;
- cystitis in children;
- cystitis in pregnant women;
- is a neurogenic;
- is a yaterogenic;
- postoperative.
Apparently, the reasons leading to cystitis are many. Therefore, it is such a common disease.
Cystitis is divided downstream:
- acute;
- is chronic.
Acute cystitis occurs no more than once a year and is characterized by a sharp bout of pain in the lower abdomen with dysuric phenomena and urinary syndrome. If this attack is repeated 2 or more times a year, then we are already talking about exacerbation of chronic cystitis. In fact, this means that the wall of the bladder is already so changed, and the bacteria are so firmly entrenched in it that it takes a lot of time and effort to completely cure this disease, both from the medical staff and from the patient himself .Therefore, it is so important to correctly treat acute cystitis, so that it does not become chronic.
In relation to other diseases of the urinary system, cystitis can be:
- primary;
- secondary.
Primary cystitis occurs as an independent disease, the secondary one is a consequence of another disease.
 By localization of inflammation in the bladder itself, cystitis can be:
By localization of inflammation in the bladder itself, cystitis can be:
- neck;
- diffuse;
- trigonitis( inflammation is localized at the junction of the urethra with the bladder).
In the clinical picture, chronic cystitis is divided into:
- chronic latent cystitis:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- with a stable latent flow;
- with rare exacerbations;
- with frequent exacerbations;
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- persistent chronic cystitis;
- interstitial chronic cystitis.
With chronic latent cystitis , depending on its form, clinical symptoms may be completely absent or manifest as exacerbations with varying frequency.
With persistent chronic cystitis , there appear distinct phases of exacerbations and remissions, as well as relevant laboratory and endoscopic features.
In interstitial chronic cystitis , there is a persistent pain syndrome and other severe symptoms. This is the most severe form of chronic cystitis.
According to morphological changes in the wall of the bladder, the following types of cystitis are distinguished:
- catarrhal;
- hemorrhagic;
- ulcerative( necrotic);
- follicular;
- fibrous;
- bullous;
- polyposis;
- cystic;
- inlaying.
With catarrhal chronic cystitis, the inflammation appears as a congestion and swelling of the mucous membrane.
With hemorrhagic chronic cystitis, sites of mucosal damage are found with their bleeding. In this cystitis in the urine will be found a large number of red blood cells, and urine can thus acquire a dark or red color( macrohematuria).
With ulcerative( necrotic) chronic cystitis on the mucous membrane of the bladder, deep defects of the mucosa up to the muscular membrane are found.
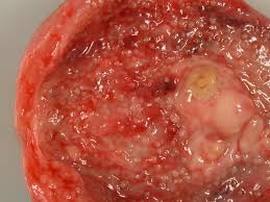 When follicular chronic cystitis in the submucosal layer, there are tubercles( follicles) that raise the mucosa itself, making it bumpy. And the mucous membrane itself is not changed.
When follicular chronic cystitis in the submucosal layer, there are tubercles( follicles) that raise the mucosa itself, making it bumpy. And the mucous membrane itself is not changed.
With fibrotic chronic mucosal cystitis, white or dark purple films( fibrin and pus) can be detected. The mucosa itself becomes folded, compacted.
When bullous chronic cystitis macroscopically observed pronounced congestive hyperemia and severe edema of the mucous membrane of the bladder.
With polyposis chronic cystitis, prolonged inflammation results in the appearance of polypous growths in the mucosa. The most common polyps are found in the neck of the bladder.
Cystic chronic cystitis is characterized by the presence of cysts under the mucous membrane. These cysts can be single, and can be arranged in groups. These cysts are filled with a lymphoid tissue and are surrounded by a modified epithelium.
Inrush( alkaline) chronic cystitis differs from others in that the bacteria that are in the bladder have the ability to metabolize urea and form alkali. The latter, in turn, leads to the formation of calcium phosphate salts, which are deposited in the wall of the bladder. This cystitis is characterized by the duration of the flow and in treatment requires, in addition to antibacterial treatment, measures aimed at acidifying urine.
Chronic cystitis and pregnancy
If the patient had chronic cystitis before pregnancy, then during pregnancy, the probability of exacerbation of the disease is high. This is because during pregnancy, the defenses of the body decrease and there is pressure on the bladder from the side of the fetus. When treating this condition, it is necessary to select such drugs from chronic cystitis, which do not have a teratogenic effect.
Symptoms of chronic cystitis
Symptoms of chronic cystitis in women and men do not fundamentally differ. This pathology is characterized by the fact that in its clinic there are periods of exacerbations and remissions. These periods can alternate with different frequencies. There are no clinical signs of chronic cystitis during the periods of remission, and during the exacerbations the following symptoms are possible:
- dysuric phenomena( painful and frequent urination);
- pain in the lower abdomen, in the lower back;
- a change in the color of urine( possibly finding in the urine of blood or pus);
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- over time, it is possible to develop depressive and anxious conditions.
Over time, the symptoms of chronic cystitis may worsen, especially if its treatment is not given proper attention.
What should I do for chronic cystitis?
The actions for chronic cystitis depend on its stage. During periods of remission, it is necessary to prevent this disease in order to avoid exacerbation. In the case of the onset of this exacerbation, it must be treated promptly and correctly.
How to treat chronic cystitis?
 Treatment of chronic cystitis is a complex task and requires a lot of work both from doctors and the patient. One should include the appropriate regimen, diet, etiotropic, pathogenetic, symptomatic and general restorative therapy. How to cure chronic cystitis by all the rules and laws in a specific clinical situation, only the competent doctor in this matter( urologist or gynecologist) knows. All other doctors can be consultants and "advisors" in this matter.
Treatment of chronic cystitis is a complex task and requires a lot of work both from doctors and the patient. One should include the appropriate regimen, diet, etiotropic, pathogenetic, symptomatic and general restorative therapy. How to cure chronic cystitis by all the rules and laws in a specific clinical situation, only the competent doctor in this matter( urologist or gynecologist) knows. All other doctors can be consultants and "advisors" in this matter.
Treatment of chronic cystitis in women and men is not fundamentally different. The only difference is that women have more predisposing factors to the development of cystitis, so her treatment requires a little more attention.
Treatment for chronic cystitis. During the exacerbation, bed rest should be observed. This will reduce the unnecessary effects on the bladder of various factors( mechanical, thermal and other).
Diet for chronic cystitis. This issue should be given special attention. First of all, it is necessary to maintain the optimum water load, that is, to drink 2-2.5 liters of liquid per day. A large volume of urine will mechanically wash out bacteria and products of inflammatory reactions from the bladder, thereby preventing stagnant phenomena in it.
In order to reduce the harmful effects of various substances irritating the mucous membrane of the bladder, the excess diet, spicy, smoked and fried foods should be excluded from the diet. Categorically it is not recommended to take alcoholic beverages as during an exacerbation of a chronic cystitis, and during remission.
In addition, the features of the diet will depend on the type of chronic cystitis and the presence of concomitant pathology. So with alkaline cystitis, it is advisable to consume more foods that acidify urine( foods rich in vitamin C).In other cases, it is recommended to adhere to the milky-vegetable diet, which alkalinizes urine.
With diabetes it is necessary to monitor the level of carbohydrates in the diet and the level of sugar in the blood. In this case, high blood sugar will negatively affect the treatment of cystitis itself.
For other metabolic diseases, the corresponding diets should be observed.
Etiotropic treatment of chronic cystitis
 For effective treatment of chronic cystitis, it is necessary to eliminate the cause, which is detrimental to the bladder mucosa. In most cases, this is caused by infectious agents( bacteria).In this case, etiotropic treatment will be the use of appropriate antibacterial drugs.
For effective treatment of chronic cystitis, it is necessary to eliminate the cause, which is detrimental to the bladder mucosa. In most cases, this is caused by infectious agents( bacteria).In this case, etiotropic treatment will be the use of appropriate antibacterial drugs.
In chronic cystitis antibiotics of the group of fluoroquinolones( ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, norfloxacin) and cephalosporins of 3 and 4 generations are used.
But before using a particular drug, it is necessary to carry out a bacteriological analysis of urine on the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics. This analysis will show which of the antibiotics is best suited for this clinical situation. But, unfortunately, bacteriological research lasts a whole week, and treatment should be prescribed as soon as possible. Therefore, before the result of the analysis of the bacteriological examination, doctors use antibiotics, relying on their own experience in this matter.
Treatment with antibiotics is carried out for a course of one to two weeks to kill all pathogens. Otherwise, bacteria may have time to "get used to" this antibiotic and next time do not respond to it.
But the cause of chronic cystitis can be not only bacteria .If the cause is viruses or fungi, then the treatment will be different. With radiation cystitis, it is necessary to exclude the effect of radiation on the patient's body, while toxic - to exclude the effect of toxin and so on.
Pathogenetic treatment of
The pathogenetic treatment includes surgical treatment. It is advisable when cystitis is caused by some anatomical features of the urinary system, in which urine stagnation occurs in the urinary tract. Surgical correction is able to correct these defects and normalize urodynamics.
Symptomatic treatment of
The need for this type of therapy occurs with severe pain and high body temperature. For symptomatic treatment of chronic cystitis, drugs such as antispasmodics( papaverine, drotaverin), NSAIDs( ibuprofen, ketoprofen, etc.), paracetamol and others are used.
As a topical treatment, instillations( washing) of the bladder with solutions of antiseptics are used.
How to get rid of chronic cystitis?
Is chronic cystitis treated? Still as it is treated! However, it must be understood that a chronic disease implies under itself such changes in the affected organ, in which their reverse development is almost impossible. With prolonged inflammatory processes in the tissues of an organ, functional tissue is replaced by a coarse connective tissue. Figuratively speaking, a scar( scar) forms on the mucous membrane of the bladder. And the scars at this stage of the development of medicine can be cured by stem cells or by the transplantation of a healthy organ.
Therefore, the question - "Can I cure chronic cystitis?" - You can answer positively. However, not every patient is able to provide such treatment.
Speaking about the treatment of chronic cystitis, they mean not complete cure as such and full-fledged rejuvenation of the cells of the bladder, but the achievement of a phase of stable and prolonged remission. This remission can last a lifetime of the patient, provided that he observes therapeutic and preventive recommendations.
Treatment of chronic cystitis with folk methods
 Folk remedies for chronic cystitis can help both in treatment and in the prevention of this disease. However, it should be remembered that self-medication is fraught with certain consequences. Therefore, it is better to coordinate this treatment with your doctor.
Folk remedies for chronic cystitis can help both in treatment and in the prevention of this disease. However, it should be remembered that self-medication is fraught with certain consequences. Therefore, it is better to coordinate this treatment with your doctor.
Any decoction of herbs and other beverages that have a diuretic m, will have a therapeutic effect on the urinary system with its chronic inflammation. Also, as a diuretic, you can use sweet tea with milk.
Cowberry juice, berries and decoction of cowberry leaves is a natural uroseptic, that is able to kill bacteria in the urinary tract. Therefore, if possible, it should be included in your diet.
Cranberries also impair the ability of bacteria to penetrate the bladder's mucosa.
In pharmacies there are so-called kidney fees, which you need to brew and take half a glass twice a day( morning and night).
To preserve and improve the body's immunological strength, it is recommended to use decoction of echinacea( 3 tablespoons per 1 liter of water). This decoction is taken 100 ml three times a day for 1 month. After a break of 2 weeks, treatment can be repeated.
When taking a bath, you can add to it a variety of antiseptic agents, such as a decoction of chamomile, baking soda and manganese.
Consequences of chronic cystitis
- Infection from the bladder may rise higher( pyelonephritis) or fall lower( urethritis).
- Long-term painful and dysuric phenomena in cystitis can lead to depressive and neurotic states.
- Possible incontinence development.
- Chronic cystitis can be the basis for the development of tumor processes of the bladder( cancer).
Video: Cystitis in women. Prevention and treatment of cystitis.
 Chronic cystitis is a disease in which the clinical manifestations of acute cystitis( exacerbation) occur 2 or more times in 12 months.
Chronic cystitis is a disease in which the clinical manifestations of acute cystitis( exacerbation) occur 2 or more times in 12 months.