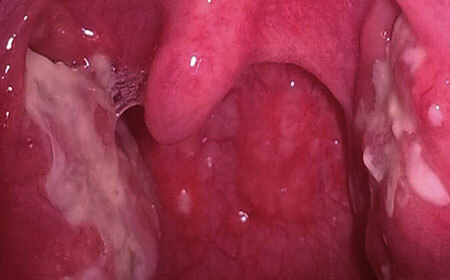
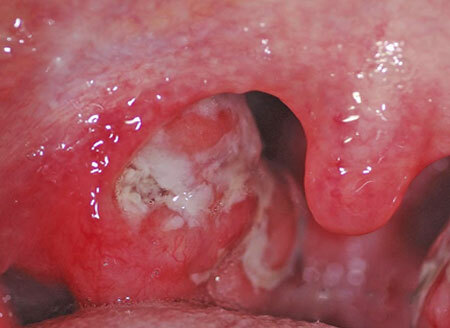
In the ENT pathology, the leading place among pediatric diseases is laryngitis in children. It is caused by inflammatory reactions in the mucous layer of the laryngeal membrane and in the structure of the elastic tissue of the vocal cords. The most prone to the disease are toddlers and preschoolers.
Almost 35% of small patients( before 2 years of age) have cold catarrhal pathology accompanied by laryngitis. It rarely occurs independently and, as a rule, manifests itself in tandem with an infectious tracheitis or inflammation of the bronchi. But more often, with that and another at the same time - laryngotraheronhitis.
Contents
- 1 Causes of laryngitis in children
- 2 Genesis of the disease
- 3 Acute form of laryngitis in children
- 4 Symptoms of laryngitis in children
- 4.1 Features of the manifestation of the disease in infants up to the year
- 5 Diagnosis examination
- 6 Treatment of laryngitis in children
- 7 Prophylaxis and prognosis
Causes of laryngitis in children

often the cause of the disease is caused by the influence on the body of various forms of viruses - influenza and parainfluenza viruses, adenoviruses, resverator-syncytial and measles, herpes and hell virusesovirusami.
The disease of bacterial genesis strikes babies rarely, but if it happens - proceeds in severe form. To provoke bacterial laryngotracheitis can:
- a hemophilic infection( Afanasyev-Pfeiffer's stick);
- representatives of coccal infections( staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus and pneumococcus);
- causative agent of pertussis - Bordetella pertussis. A number of factors serve as a stimulus to development:
- hypothermia( hypothermia);
- nasal congestion;
- vitamin deficiency;
- weakening of immune functions;
- exacerbation of ENT diseases.
Maximum susceptibility to laryngitis, in children under one year of age, they are children suffering from lymphatic diathesis. The most common is the allergic form of the disease.
The development of laryngitis of allergic genesis, in infants and older children, is often provoked:
- chemicals are components of household chemicals;
- paint and varnish pairs;
- dust and wool of pets;
- uncontrolled use of medicinal sprays and aerosols for the treatment of the nasopharynx;
- a strong cry and choral lessons in the school, causing overstrain of the vocal cords;
- effect of food allergens;
- spasms of the larynx as a result of severe shock, trauma, aspiration, or acidic environment of the stomach as a result of gastroesophageal reflux( food reflux).
The genesis of the disease
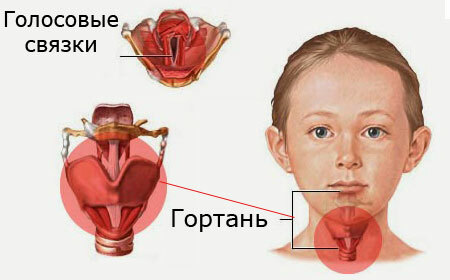
The genesis of the disease is caused by the anatomical peculiarity of the structure of the children's respiratory apparatus - a narrow lumen, funnel-shaped, rather than cylindrical, as in adults, the form of the respiratory tube( larynx), the mucosal looseness and tissues of the internal environment( connective), their predisposition to swelling, innervation ability, incompetence of respiratory muscular muscles.
It is these physiological properties of the child's body that explains the frequent development of obstructive processes and ODN syndrome( acute respiratory failure), with laryngitis.
For example, if the puffiness caused by the disease leads to a thickening of the upper mucosal layer for at least one millimeter, the child's respiratory glow will decrease by exactly half, which will create certain difficulties with breathing.
In the genesis of the obstructive syndrome, a certain role is due to the genetic factor - predisposition to reflex muscle spasm or mechanical causes, blockage of the laryngeal cavity by foreign bodies, or inflamed mucus. Abnormal cavity constriction of the respiratory tube and malfunction in the respiration usually occur at night, due to changes in the processes of blood and lymph circulation.
Given the nature of the clinical manifestations of the disease, it can manifest as acute course, chronic, complicated and uncomplicated condition.
Among the many varieties of manifestation, endoscopic classification, children are prone to catarrhal and hypertrophic laryngitis. If the catarrhal manifestation of the disease is noted only by inflammatory reactions in the upper( mucous) layer of the laryngeal tube, the hypertrophic variant is characterized by hyperplasia and overgrowth of the basal layer.
According to the prevalence of inflammatory reactions, laryngitis can be - laryngitis subchordalis( sublingus, habitual name - false croup), diffuse( diffuse), or manifest laryngotraheobronchitis.
Acute form of laryngitis in children
Clinic of acute course appears in infants on the third day of the presence of colds. According to statistics, boys are more likely to be from 3 to 5 years old. At this age, the disease, rapidly progressing, is accompanied by the development of acute inflammatory processes in the mucous structure of the larynx and trachea( laryngotracheitis).
Disturbances in the child's condition are marked by characteristic symptoms:
- hoarseness and hoarseness of voice;
- with unpleasant tickling( tickling) in the throat and difficulty swallowing;
- swelling and narrowing of the respiratory tract, which provokes shortness of breath;
- by the spread of inflammatory reactions to the tissues of the vocal cords, in many cases there is a loss of voice;
- barking cough worries the baby;
- appetite worsens and temperature values increase( 38.0 ° C and higher);
Heavy breathing is accompanied by a whistle. Delay in the treatment of the disease, with its acute manifestation, can be complicated by a sharp violation of breathing and lead to choking( laryngospasm).Usually such attacks are noted at night.
It can be easily noticed that auxiliary, skeletal muscles are included in the respiration process - a sure sign of lack of oxygen.
In this case, the retraction of the intercostal and supraclavicular muscles is noted. Self-medication in such cases is unacceptable. Calling the ambulance and treating laryngitis in children with a symptom of laryngospasm should be immediate.
In uncomplicated form of the disease, the symptoms of the disease take place within one, two weeks.
The chronic form is inherent in older children.
Shown:
- with a stable or periodic loss of voice( dysphonia);
- rapid fatigue and weak voice;
- sullen and unpleasant tickling in the throat;
- with dry cough.
Symptoms of laryngitis in children

In acute process, the disease develops within a couple of hours, depending on the intensity of inflammatory reactions, is due to the four stages of development.
The first stage. At the first stage of the genesis of laryngitis in children, the symptomatology is manifested in mild and poorly expressed form, against the background of the disturbing state of the little man or his natural activity.
Breathing becomes rapid and noisy, with inspiration, shortness of breath - this indicates a normal level of carbon dioxide in the blood and no violation of blood composition. The duration of the first stage of the disease is up to two days.
The second stage. Characterized by increased symptoms. To noisy breathing signs of dyspnoea in a state of rest and constant manifestation by inhalation are added.
Only the quickened work of the muscles of breathing compensates for the lack of oxygen. In the chest zone there is a retraction of the soft tissues, which is strengthened by the tension of the sternum. At the same time:
- kids are restless, sleep is disturbed;
- on the background of pale skin a bluish aureole around the lips is clearly visible;
- heartbeat is rapid.
Such signs may be permanent or periodic for 5 days. Treatment should be stationary.
In the third stage of the , the cough intensifies, becomes coarse, subsequently superficial. Dyspnoea manifests itself in any breath. It is constantly changing. That noisy, rapid and irregular, then quiet and superficial.
Deterioration of metabolic processes and blood circulation causes increased work of the respiratory muscles. The condition is characterized as severe, marked:
- restless state, retardation and drowsiness;
- by reducing the sound of the voice and its hoarseness;
- signs of retraction of the abdomen during breathing;
- by falling of a BP and a malfunction of a warm rhythm.
The last stage. Very serious and dangerous condition - asphyxiation. Characterized by:
- convulsive manifestations;
- by the decrease of temperature indicators;
- possible development of coma;
- with rapid breathing or total absence of breath;
- slowed heart rate;
- by changing the gas component of blood to critical norms;
- by the addition of toxicosis and other complications.
Symptoms speak for themselves, therefore urgent medical intervention is required, even if the condition of the child does not cause anxiety in the parents. Do not wait for the increase in symptoms and bring the baby to a loss of consciousness.
Features of the manifestation of the disease in infants up to the year

From the age of 3 months old babies can be laryngitis-prone. This is due to the fact that it is very difficult for a small organism, not quite adapted to the external environment, to prevent the penetration of microbial infection to such a depth.
In older children, the respiratory system is more developed and they often suffer from rhinitis or sore throats, and are less likely to undergo inflammatory processes in the laryngeal tube and the tissues of the vocal cords.
The organism of breast babies is untenable in the fight against such pathology, therefore it is not recommended to neglect medical help under any circumstances. Especially when the temperature rolls over and there is a barking barking character. This may be a sign of the rapidly developing puffiness of the larynx and provoke the death of the baby.
What should alert parents?
- Anxious babies and a strange wheezing sound when breathing.
- Unexplained snoring, frequent or shortness of breath.
- The presence of blue in the nasolabial area, especially in the morning.
- Appearance of barking dry cough and spitting out.
- Signs of swelling and congestion of the larynx.
- Frequent crying that can talk about pain in the throat or in the head.
- Increased temperature, as a consequence of the inflammatory process.
Diagnostic examination
In many cases, the pathology is diagnosed in the physical examination of the patient and familiarity with his anamnesis and clinical signs. Special otolaryngological examinations include:
- Methods of pharyngoscopy, otoscopy and rhinoscopy.
- Palpable assessment of the condition of the cervical lymph nodes.
- Laryngoscopy as the main instrumental diagnostic method, which allows to detect flushing, swelling, see the state of the vessels, possible hemorrhages in the laryngeal vascular lining, thickening of their folds, changes in the ligament of the ligamentous apparatus, and tests for voice formation( phonation).
- PRC examination of secretion from the larynx for the detection of bacterial or viral pathogens.
- Study of voice functions with the involvement of a phoniatrist and speech therapist.
Treatment of laryngitis in children
Treatment of laryngitis in children is helped by a triad of basic measures - clinical recommendations, methods of medicamental and physiotherapy. Clinical recommendations are based on the necessary measures, the observance of which must be rigorous.
- Restriction of the baby's motor activity during a period of elevated temperature, if possible - bed rest( although it is difficult to limit this).
- Switch to silent mode. As much as possible to unload the vocal cords. Do not even talk in a whisper. Take an interesting baby, show your imagination.
- Provide the baby with a warm, non-irritating drink( milk with honey and butter, not acidic fruit drinks and compotes).
- Exclude from the diet acidic, salty and astringent foods and beverages.
- When swelling of the larynx, restrict fluid intake.
Medication Therapy
The treatment with medications is aimed at relief of symptoms and the elimination of infection.
With the development of complications in the form of a false croup( may occur in children under 6 years of age), the following are prescribed:
- Diuretics that help to relieve swelling( Furosemide and analogs).
- Spasmolytics, for stopping the guttural spasticity - Papaverin, No-Shpa, etc.
- Antihistamines, which eliminate allergic reactions that provoke swelling of the respiratory tube - Tavegil, Suprastin and many others.
With an uncomplicated version of laryngitis it is prescribed:
- Antibacterial or antiviral medication, depending on the pathogen.
- Taking antibiotics with laryngitis in children is justified in the presence of a bacterial pathogen, with purulent sputum, rapid increase in temperature or febrile state. Preparations for cephalosporins and penicillin group are prescribed for a week.
- Drugs that impair or suppress the cough reflex.
- Means that promote the withdrawal of mucus and sputum from the respiratory system - "Bromgeksin" or "Lazolvan".
- Antiseptic topical products in the form of aerosols or absorbable tablets.
If necessary, drugs can be administered by the endolaryngeal route.
Physiotherapeutic measures
Methods of physiotherapy are aimed at ensuring the outflow of blood from sites of inflammation and to speed up the removal of puffiness.
This can be achieved:
- by nebulization therapy;
- microwave and UFO therapy;
- UHF, electrophoresis and phonophoresis;
- with antiseptic treatment of mucous cover;
- mustard applique on the feet and calves of the feet;
- with hot foot baths;
- rubbing feet with alcohol-containing solutions.
As an inhalation, with laryngitis in children,
- soda solutions( 0.5 liters of warm water and 1 tablespoon of soda food) are used;
- steam inhalation for 10-15 minutes, every 3 hours;
- for children 4-5 years old can be prepared herbal infusion for rinsing.
All these manipulations are carried out only in the absence of an elevated temperature.
Prophylaxis and prognosis of
In the process of neurulation( maturation of the central nervous system), a number of changes occur in the children's body, in particular, due to structural changes in the laryngeal tube - the friability of its submucosa disappears, which allows successfully "grow" the development of laryngotracheitis. To overcome this pathology in early childhood, it follows:
- to prevent the action of allergenic pathogens;
- in time to sanitize infections;
- stimulate the immune system with immunomodulating medications that prevent the manifestation of infections;
- vaccinate children's infections.
The prognosis of uncomplicated laryngotracheitis is favorable. Reduction in the incidence is noted already in the school age group of children. In complicated forms, accompanied by the manifestation of a false groin, it all depends on the adequacy and timeliness of the help of parents and doctors, because the critical stenosis of the respiratory passage can cause asphyxia and lead to death.