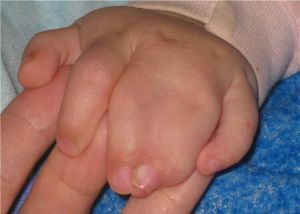
 Syndactyly - abnormal development of fingers due to disruption of their division in the embryonic stage. The disorder constitutes about 50% of all congenital injuries of the hands and occurs at a frequency of 1: 2000.
Syndactyly - abnormal development of fingers due to disruption of their division in the embryonic stage. The disorder constitutes about 50% of all congenital injuries of the hands and occurs at a frequency of 1: 2000.
May be an independent disorder or be accompanied by other lesions: polyphalangeia and underdevelopment of fingers, brachidactyly, ectrodactyly, splitting the brush, etc. In 60% of children with this deviation there is an additional anomaly of the musculoskeletal system.
The content of the article
- The causes of the pathology
- The causes of the pathology
- The classification of the disease
- The clinical picture in the pathology
- Diagnostic techniques
- The treatment of the disease
- The prognosis and complications
The causes of the pathology
The causes of the syndactyly of the toes and the hand lie in the field of genetics. More than 20% of severe forms have genetic character .
In the absence of this factor, it is necessary to assume a violation of separation of the fetal limbs under the influence of negative conditions. The brush is placed on the 5th week of development;at this stage the fetus is naturally endowed with natural syndactyly.
At standard development on 8 week fingers are laid. In case of violation of the appearance of partitions, fingers are not divided, ie, there is syndactyly.
Among the causes of the pathology may be harmful effects on the future mother, X-ray, infection during pregnancy. Often the reasons for the appearance of such a baby are unknown.
Less often, the acquired lesion occurs due to brush burns.
 Another genetic disease of ectrodactyly of the extremities is the causes and possibilities of treatment of pathology.
Another genetic disease of ectrodactyly of the extremities is the causes and possibilities of treatment of pathology.
How effective is the treatment of osteomyelitis with antibiotics in combination with other techniques. You can learn more about the treatment of the disease by reading our material.
Classification of the disease
In medicine, the deviation is divided by species, the length of the joint and the condition of the fingers.
By type of soldering:
- soft-cloth type;
- bone appearance.
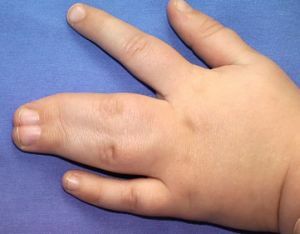
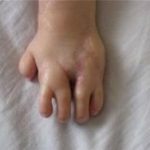
In the photo of syndactyly in the full form of
In the length, depending on the number of fused parts of the fingers, the is identified as a complete and incomplete form of .Full - fusion, covering the nail parts. Incomplete - fusion of the phalanx joints. This form is divided into an incomplete basal form and a terminal form.
The state of the connected fingers is simple and complex. With a simple violation there is a connection of normal fingers, with a complex - changed fingers. Among other things, the hereditary types of the disease are distinguished:
- Type I - webbed connection of 3 and 4 fingers;2 and 3 toes. There are webs between other fingers.
- Type II - connection of 3 and 4 fingers with doubling 4 fingers, connection of 4 and 5 toes with a doubling of 5 fingers.
- Type III - double-sided connection of 4 and 5 fingers;The little finger is shortened. Basically, the feet are not affected.
- Type IV - bilateral skin lesion, the shape of the brush is spoon-like. The defeat of the feet is not observed.
- Type V is a lesion with a union of the bones of the pastern and the metatarsus. On the hands - skin connection of 3-4 fingers, on the legs - 2-3 fingers.
Unilateral deviation is observed more often than bilateral;the connection of the fingers more often than the toes.
Clinical picture in the pathology of
When the hands are injured, the middle and ring fingers are connected;feet -2 and 3 fingers. Rarely connected are the ring finger and little finger, thumb and index finger, all fingers. With bilateral lesions, the connection is symmetrical.
Unshared fingers can be normal or underdeveloped. Sometimes there is a decrease in the number of phalanges.
With a basal lesion, the working capacity of the brush hardly suffers. But syndactyly in children inhibits the overall development of the child.
Diagnostic techniques
 Violation is determined immediately after the appearance of the baby neonatologist. Follow-up examination and follow-up is performed by a pediatric surgeon or orthopedist. To exclude hereditary problems, a child with a violation should be consulted by a geneticist.
Violation is determined immediately after the appearance of the baby neonatologist. Follow-up examination and follow-up is performed by a pediatric surgeon or orthopedist. To exclude hereditary problems, a child with a violation should be consulted by a geneticist.
The diagnosis can be made during a visual examination, but research is needed to determine the type and development of the treatment algorithm.
X-ray of the hands and feet helps assess joints, bone density, bone presence and length. rheovasography, UZDG, angiography, electrothermometry is performed to determine the subtleties of the structure of the vessels of the connected parts.
Treatment of a disease
Treatment of the syndactyly of fingers is carried out only in an operative way. If the diagnosis of the syndactyly of the toes is made, then the operation is not assigned if the disturbance does not interfere with walking.
The timing and the appropriate method of the procedure is selected based on the form and nature of the lesion.
The purpose of the intervention is to eliminate the external flaw and restore the brush.
The optimal age for the procedure is 4-5 years. At an end lesion, an earlier operation is needed to help prevent unequal growth and secondary finger changes.
Approaches to treatment are divided into groups:
- division of the membrane without plastic;
- division of connected fingers with skin plasty by local tissues;
- finger dissection with free skin plasty;
- separation of fingers with combined plastic;
- multi-stage interventions with skin, tendon, muscle and bone plastic.
After the operation for immobilization of the fingers on the limb, a plaster is applied for 4 months.
Prognosis and complications of
The applied methods of treatment give positive results. With a timely operation, the structure and work of the brush are restored.
The indicators of the effectiveness of treatment are the absence of deformation and constricting scars, the total volume of movements in the interphalangeal joints, and the good sensitivity of the fingers.
If the treatment is not implemented, the deviation adversely affects the growth and development of the limb.