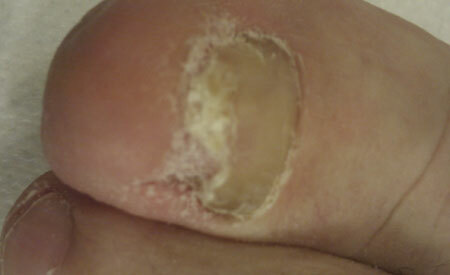
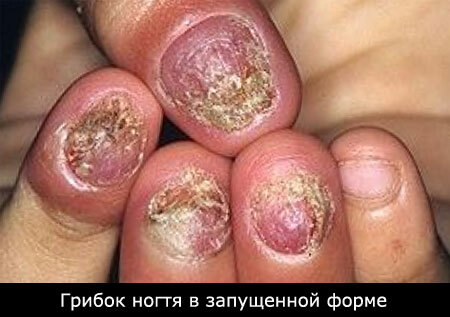
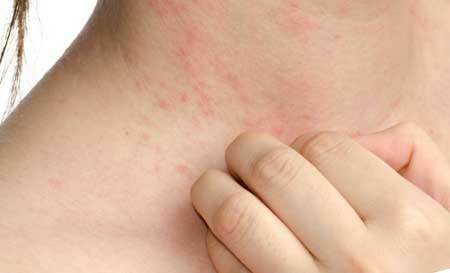
Human skin is susceptible to a variety of infectious lesions caused by various fungi that are capable of causing the disease itself( pathogenic) or causing the disease due to certain conditions( conditionally pathogenic). All of them are united in the general classification - dermatomycosis. Inguinal epidermophytosis is one of the representatives of this class.
According to statistics, the frequency of isolated infection of the skin and its appendages with fungi in the system of parasitic dermatomycosis reaches 10%.
When the inguinal form of the epidermophyte, the fungus affects large skin folds that can retain moisture and heat for a long time. More often men are ill. In women, inguinal epidermophyte is much less common.
The disease manifests itself as pustular( pustular) eruptions, scaly foci, pustular pyoderma or erythema spots:
- with localization in the groin folds and between the gluteal region;
- on the inner thigh surface;
- in the folds of the soft tissue of the perineum;
- in the pranal zone( on the tissues surrounding the anus).
Infection of these areas can be isolated, but as a result of primary infection, or transfer, any skin areas are exposed to infection: fovea of the armpits and popliteal zones, elbows, under the breast, on the scalp in the hair.
Contents
- 1 Genesis of development
- 2 Clinical signs and symptoms of inguinal dermatomycosis
- 3 Treatment of inguinal epidermophytosis in males and females, photo
- 4 Prevention of epidermophytia
- 5 Inguinal epidermophytia, ICD code 10
Genesis of development
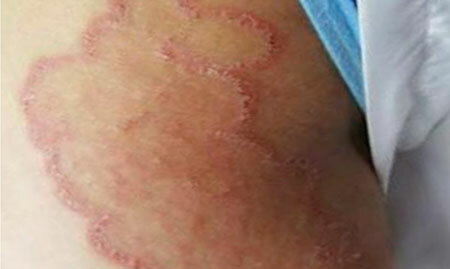
Inguinal epidermophytia, photos in women
The causative factor of inguinal epidermophytia is caused by intensive developmentand parasitizing the human skin of mold and yeast filamentous fungal parasites of the family Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Epidermophyton floccosum, Trichophyton rubrum. These are the mushrooms that "eat us", and do not coexist peacefully.
The risk of infection increases with the creation of certain conditions for the fungus pathogen, which contribute to the proliferation of associations of microorganisms that have a destructive effect on the organic intercellular substances of the skin. Such conditions can be caused by:
- high pathogenicity of the pathogen;
- a certain indicator of friability( maceration) of the skin and the presence of micro-traumas;
- by a general decrease in the adaptive-compensatory capacity of the organism( reactivity);
- with unsanitary conditions;
- high humidity and change the acidity of the skin.
Getting on the skin of a person, fungi receive everything that is necessary for their development and life: fatty sebaceous glands, sweat, epithelium. Detection of a fungal parasite in a man or a woman always indicates a particular problem.
Promote the development of epidermophytia in women:
- problems in autonomic dysfunction( VSD);
- disturbances in metabolic processes;
- endocrine pathology;
- deficiency in the body of vitamins;
- insufficiency of the immune system;
- hot climatic conditions;
- increased sweating.
Transmission of infection occurs through contact, through personal belongings of the patient or not observing basic hygiene.
Clinical signs and symptoms of inguinal dermatomycosis
The initial manifestation of clinical symptoms of inguinal epidermophytosis in women depends on the type of fungus pathogen.
Acute onset of the disease with characteristic clinical symptoms and active hyperemia causes fungi of the family Trichophyton mentagrophytes.
The action of the fungal pathogen of the genus Trichophyton rubrum and Epidermophyton floccosum causes lubricated symptoms with a slow chronic pattern of epidermophytosis, with alternating acute course and remission.
The onset of the disease is characterized by the formation on the skin of small red itchy and flaky spots( up to a centimeter in diameter).
Sometimes there is a growth that causes a merger. Erythematous spots spread to the pubic area, affect the lower abdomen and perineum, pass into the zone between the gluteal folds and popliteal pits.
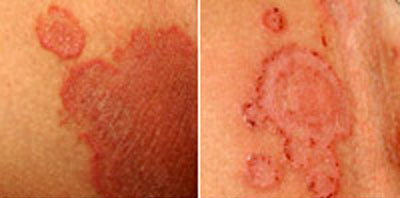
photos of symptoms of inguinal dermatomycosis
The gradual growth of plaques increases their diameter by a factor of 10.A characteristic feature of epidermophytosis is the clear boundaries of the spots. Their scalloped edges are surrounded by an inflamed roller, covered with a multitude of bubbles and pustules filled with turbid fluid. The roller protrudes above the surface of the skin, and the central inflamed part of the spot, slightly sticks into the surface.
Over time, the inflammation passes, the skin becomes light, the plaque becomes a reddened circle. At the peak of the development of the disease there are:
- itching symptoms;
- burning in affected areas;
- touching clothes causes soreness, movement - discomfort.
When inguinal epidermophyte in women, lack of competent treatment in the acute period, promotes the transition of the disease to the stage of chronic course, which means that new lesions can occur over many years.
In addition, improper treatment, or none at all, can contribute to the development of various complications:
- lead to lymphatic vascular disease( lymphangitis);
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- joining secondary infections.
Consultative reception and examination at the dermatologist will answer all questions, than to treat inguinal epidermophyte in men, what to do first of all for women, and what preventive measures are needed.
Treatment of inguinal epidermophytia in men and women, photo
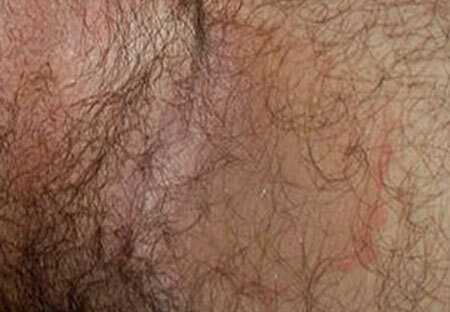
Treatment of inguinal epidermophytosis in men, photo of inguinal region
Diagnosis of epidermophyte is based on localization of skin lesions and manifestations of clinical symptoms. The conclusion is based on the results of microscopic and cultural examination of scrapings from the skin.
Treatment of inguinal epidermophytosis with tablets or other pharmacological agents in men and women is based on a specific criterion providing effective local therapy with:
- A broad spectrum of antimycotic and fungicidal action;
- Additional anti-inflammatory effect and antibacterial efficacy;
- The minimum multiplicity of use;
- Short application period.
Complex treatment consists of:
1) Ointments and creams of antifungal action - Lamizila and Mikoseptin, Oksiconazole, Econazole, Clotrimazole or Ketoconazole, etc.
2) Anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed during the period of acute manifestation of the disease.
Hormonal external agents( glucocorticosteroids) - Mazipredon, Isoconazole, Diflucortolone or, Triderm, resorcinol and silver solutions. They are applied before the end of inflammatory reactions, with the further use of only antifungal external agents.
3) Antihistamine therapy - is prescribed for severe itching symptoms, includes drugs of Tavegil, Suprastin or Zirtek and their derivatives.
The use of lotions from the decoction and oak bark, compresses from cloves, fir, fig or geranium oils at an early stage of the disease, can generally exclude the use of medications.
Prevention of epidermophytia
 The basis of prevention is daily personal hygiene, regular drying of wet areas of the body, using only personal hygiene items.
The basis of prevention is daily personal hygiene, regular drying of wet areas of the body, using only personal hygiene items.
At the end of the treatment course, it is necessary to conduct a thorough and thorough disinfection of the things and objects with which the patient was in contact. After treatment, in the next two weeks, it is necessary to wipe the former lesions with a weak( 2%) iodine solution( every other day).Injury epidermophytia, ICD code 10
In the ICD 10, the disease is( from the classifier's start):
Class I. Some infectious and parasitic diseases( A00-B99)
B35-B49 - Mycoses
B35 - Dermatophytosis
- B35.6 - Epidermophytosis inguinal