 Anopia( anopia) is a visual defect or a complete absence of it.
Anopia( anopia) is a visual defect or a complete absence of it.
As a rule, it occurs due to the cessation of the activity of the optic nerves and in the presence of diseases of the retina of the eye.
Violation threatens complete blindness.
Consequence of neurological problems of
This visual defect arises against the background of the death of the optic nerve. This is accompanied by a condition in which the nervous tissue feels an acute shortage of nutrient components. Because of this, the tissue ceases to perform its functions, as a result of which neurons begin to die off a little.
Over time, atrophy extends to a large number of cells, and in neglected cases on the entire nerve trunk.
This pathology can not occur on its own, as a rule, this occurs against a background of other neurological problems:
- The presence of edema of the initial portion of the nerve trunk .Occurs in any pathological conditions, with the development of which increases intracranial pressure( meningitis, hydrocephalus, trauma in the area of the skull, etc.).
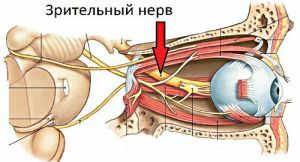
- Development of growths around the nerve or tissues located near it .At the same time, neuronal tissue proliferation occurs, which leads to neuronal contraction.
- Poisonous nerve damage .It arises as a result of the influence on the body of poisonous elements, which provokes the disintegration of nerve cells. The following substances can exert a toxic effect: methanol, industrial waste( lead and carbon disulfide), alcohol and tobacco in excessive quantities, medicines( Digoxin, Sulfanilamide, Sulfalen, etc.).
- Intrabulbar and retrobulbar neuritis .It manifests itself as an infectious process that affects neurons in the cavity of the eyeball or behind it.
Other provoking factors
The main causes of aninopsy are the modification of the structure of the eyeball and the hemostasis of its internal environment. Also, the development of pathology leads to damage to the visual crossover and the course of age-related degenerative reactions. Anopia also occurs against the background of the following diseases:
- cataract;
- closed angle glaucoma;
- aneurysm of cerebral vessels;
- effect of ionizing radiation;
- the presence of chronic diseases, as a result of which the structures of the eye are affected( diabetes mellitus);
- hemodynamic disorder in the system of the middle and posterior cerebral arteries;
- benign and malignant formations in the tissues of the pituitary and brain.
Classification of violation
Anxia can be partial and absolute( complete blindness).As for partial defects, they can be of the following types: 
- hemianopia - bilateral blindness of the half of the visual field occurs as a result of disturbance of the visual system at the level of the optical tracts or visual cortex of the brain;
- quadrantanopia - blindness of a quarter of the visual field, develops against a background of damage to the occipital part;
- upper and lower hemianopia - atrophy of the upper or lower segment of the optical field;
- bitemporal hemianopia - incomplete blindness, in which loss of perception of the temporal half of the right and left fields of vision occurs;
- Binasal hemianopia - incomplete blindness, in which the perception of the nasal halves of the right and left visual fields is lost.
There is a special type of anomie - scotoma, which is characterized by the presence of a dark blind spot against the background of a stable and explicit image.
 The scotoma has various shapes( oval, round, arc-shaped, sectoral and annular) and appears in any area of the optical field.
The scotoma has various shapes( oval, round, arc-shaped, sectoral and annular) and appears in any area of the optical field.
Due to aninopsy, a concomitant disorder develops, such as amblyopia( decreased visual acuity).This pathology has several levels of severity( mild, moderate, severe and blind) and occurs in all patients with an anopy without exception. The disorder arises spontaneously and consistently increases. In untimely treatment, irreversible blindness can occur.
Features of the
The main symptom of the disease is temporary or permanent blindness. When the fields of vision fall out as a result of an acute vascular catastrophe, visual hallucinations are observed in the form of fire, geometric figures, certain images and forms. In some cases, there is a reconstruction of explicit visual fields in blind areas. These phenomena occur as the optical analyzer becomes accustomed to the existing defects.
In general, the symptoms manifested depend on the type of vision defect. If this is an incomplete atrophy, then the symptoms may not appear at all, or the loss of the visual field at one of the eyes is noted. At full atrophy the visual organ completely ceases to see. This is accompanied by an involution of the right or left optical fields in both eyes.
Diagnostic methods
For diagnostics, the examination of the fundus is carried out first. With its help, you can check the primary department of the nerve trunk.
In addition to the examination, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- Laser tomography of the eye disc .The application of this method allows us to consider the transformation of the nerve trunk by the appearance of
 atrophy.
atrophy. - CT and MRI of the brain .When it is used, the cause of the disease( tumor, cyst, etc.) is established.
- Fluorescent angiography of .The symptoms of tissue damage and scarcity of blood supply are determined.
- Opto-coherent tomography of the optic disc .
Features of therapy
Since anaphylaxis is not an isolated disease but a sign of any pathological process, the treatment consists in arresting the underlying pathology. For the regeneration of eye functions, the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- antihypoxants and antioxidants reduce the activity of destructive reactions and eliminate oxygen starvation of the nerve;
- nootropics accelerate the regeneration of neurocytes and stimulate their blood flow;
- microcirculation correctors promote the improvement of metabolic processes in nerve cells;
- drugs that reduce the capacity of vessels perform protection of the optic nerve from subsequent lesions.
 In addition to the above, new methods are used to restore the eye using peptide bioregulators. In certain cases, surgical methods of treatment are applied, which improve visual functions.
In addition to the above, new methods are used to restore the eye using peptide bioregulators. In certain cases, surgical methods of treatment are applied, which improve visual functions.
The most severe consequence of aninopsy is the complete loss of vision. The prevention of this pathology depends on the success of the therapy of the disease, which provoked blindness.
Prevention is the maintenance of a correct lifestyle, exercise and systematic monitoring of blood sugar levels. It is also necessary to regularly check with an ophthalmologist.