 Hyperostosis is considered a fairly rare disease of bone tissue. Serious statistical studies on the prevalence of this pathology was not conducted.
Hyperostosis is considered a fairly rare disease of bone tissue. Serious statistical studies on the prevalence of this pathology was not conducted.
In the International Classification of Diseases( ICD-10), hyperostosis is included in the class of bone and connective tissue diseases with code M 85 "other bone density and structure disorders".
The content of the article
- What is the essence of the disease?
- Pathogenesis
- main reasons
- Varieties and classification
- Clinical manifestations
- ossificans periostoz or syndrome Marie-Bamberger
- syndrome Morgagni-Styuarat-Morel
- syndrome Kaffee-Silver- or infaltivny hyperostosis
- cortical hyperostosis
- disease Camurati-Engelmann
- disease Forestier
- ApproachDiagnosis
- Approach to therapy
- Complications of the disease
What is the essence of the disease?
The definitions of the disease are different for different authors. Some consider it a pathological growth of normal bone tissue within the unchanged bone size, others equate to complication of periostitis, thirdly - they claim that this is a variant of tumor growth.
Opinions agree that the disease can occur on its own or as a result of a severe course of other diseases.
Features of the pathogenesis of
Pathology develops rapidly or gradually. Tubular bones are most often affected. Bone tissues grow and form a new bone in the periosteum.
It sprouts into the trabeculae, into the cortical layer, into the brain area. It is important that the calcium content in the blood is not disturbed( excluding the process of osteopetrosis with the formation of calcified cartilage sites).
Possible growth variants:
- affects all bones of the body, the bone structure is broken, bone marrow is atrophied and replaced by a connective tissue;
- is limited to only spongy substance with the formation of sclerosis sites.
The main causes of
Until now, scientists can not clearly answer the question "Why does hyperostosis arise?"But the main factors of the disease, leading to an impaired process of bone tissue growth, are sufficiently studied.
These include:
- pathology of the endocrine system with acromegaly( anterior pituitary disease), increased function of parathyroid
 glands, decreased activity of thyroid hormones;
glands, decreased activity of thyroid hormones; - is a consequence of chronic poisoning with poisonous substances containing compounds of phosphorus, arsenic, fluorine, lead, bismuth;
- hypervitaminosis of vitamins A, D;
- excessive physical activity;
- exposure to penetrating radiation or an excessive dose of radiation exposure;
- response to chronic inflammatory processes, long-term infectious diseases, acute viral infection;
- kidney pathology that hinders the process of removing excess phosphate through the tubules;
- blood diseases( myeloma, lymphogranulomatosis, leukemia, sickle cell anemia);
- cancers;
- Paget's disease in the last stage of sclerosing;
- manifestation of neurofibromatosis;
- consequence of diseases( echinococcosis, cirrhosis of the liver).
Varieties and classification of
The general classification principle suggests dividing the disease into:
- local, local forms of - when one bone is affected, for example, frontal hyperostosis develops in women with menopause, in men with obesity;
- general or generalized process - is found in infants in infancy, with a disturbance in the balance of sex hormones, as a result of genetic mutations.
Restriction of hyperostosis only tubular bones is called a periostosis. The disease affects the lower leg, forearm, the deformation of the fingers is detected.
Clinical manifestations of
Symptoms and clinical signs of hyperostosis were described by various doctors and received their names in the names. They are rooted in medical practice in the form of syndromes with characteristic manifestations.
Therefore, it is better to view the clinic from a posidrome approach.
Ossifying periostosis or Marie-Bamberger syndrome
Bone changes are located on multiple sites on both sides in the forearms, lower legs, metacarpal and plural bones.
Symptoms:
- fingers look like "drumsticks";
- nails become flat and wide like "watch glass";
- is a pain in the joints and bones;
- increased sweating;
- discoloration of the skin from pallor to redness;
- possible growth of the nose and the appearance of excess skin on the forehead.
Simultaneously, patients suffer from relapses of arthritis of the joints of the hands, feet.
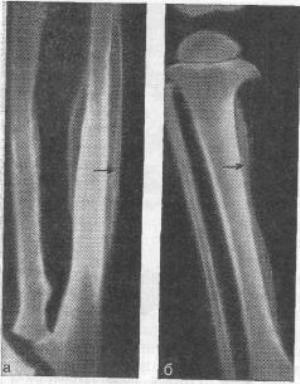
Radiograms determine the symmetrical thickening of bone tissue in the diaphysis of the tubular bones, lamination in periosteal areas.
Morganyi-Stuarat-Morel Syndrome
Frontal or frontal hyperostosis is found in menopausal women.
Symptoms:
On the photo hyperostosis of the frontal bone
- severe headaches;
- obesity;
- manifestation of male sexual characteristics( hair on face and body);
- insomnia, irritability;
- is a disorder of the menstrual cycle.
Often accompanied by diabetes and hypertension.
Radiographically determined: thickening of the frontal bone, proliferation of bone tissue in the area of the Turkish saddle, lesions of the vertebrae.
In blood tests: elevated levels of somatotropic and adrenocorticotropic hormones.
Cuffy-Silverman syndrome or infectious hyperostosis
This form is characteristic of young children. Begins as an infectious disease: loss of appetite, fever, the baby becomes restless.
Typical manifestations:
- on the arms and legs, the face develops limited swelling, rarely painful( no signs of inflammation);
- , when changes occur in the area of the lower jaw, the face becomes "moon-shaped."
X-ray is determined by the compacted bone tissue in the zone of clavicles, tubular bones, lower jaw, curvature of the tibia.
In blood tests: acceleration of ESR, leukocytosis.
Cortical hyperostosis
The disease is hereditary, the lesion is generalized.
Symptoms:
- violation of innervation of facial muscles in the facial nerve zone;
- exophthalmos( bulging eyes);
- decreased vision and hearing;
- chin increase;
- thickening of clavicles.
The disease manifests itself in adolescents. X-ray: compaction of bones in the cortical zone.
Kamurati-Engelman disease
The disease is congenital in nature.
The zones of diaphysis of the humerus, femoral and tibia bones are affected.
Symptoms appear in childhood:
- in a child stiffness and soreness in the joints;
- poorly developed muscles;
- formed a "duck" gait.
Forestier disease

Hyperostosis Forestier manifested by back pain
Forestier disease differs from other species by the simultaneous damage of the ligamentous apparatus of the joints and the development of immobility.
Most often affects the thoracic and lumbar spine.
Mostly men are ill after 50 years.
It is noted that muscular people with excess weight are most susceptible.
Symptoms:
- pain in the spine, often in the morning after sleep, prolonged position without movement, physical exertion;
- inability to bend over, turn the torso to the side;
- patients feel bad by the end of the working day.
On the roentgenogram in a direct and lateral projection the signs of ossification of the bodies of the vertebrae and tendons are determined.
Approach to diagnosis
It is impossible to diagnose only external symptoms and complaints of the patient.
For the final diagnosis, methods are used:
- radiography,
- computed tomography,
- , a radionuclide study is rarely performed.
Approach to therapy
If pathology is a complication of another disease, then a basic disease is needed.
The result comes with the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, hormonal drugs that eliminate the effect of somatotropin, antibiotics for chronic pneumonia.
In the treatment of primary disease,
- uses high doses of corticosteroid hormones;

- is undergoing general restorative treatment;
- recommended nutrition with sufficient protein and vitamins;
- with the help of massage and physiotherapy joints are developed.
In most cases, early diagnosis can achieve good results after several months of treatment. The prognosis of hyperostosis is favorable.
Treatment of Forestier's disease requires a special approach:
- for pain relief - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, it is possible to use spinal blockages;
- group of chondroprotectors is assigned to strengthen intervertebral discs;
- pentoxifylline is used to improve blood circulation in the area of the spinal cord and spine;
- are recommended for wearing special orthopedic bandages supporting the spinal column.
Complications of the disease
Running cases with ineffective treatment cause stiffness of bones and joints, with some forms complete immobility.
In childhood, the disease can be suspected by the pediatrician when the baby is examined or the parents. If the family already had such cases it is necessary to tell the doctor about this for targeted control.
Endocrinologists in the territorial polyclinic are engaged in treatment and clinical examination.