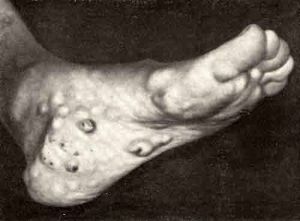
 Bone cancer is a general definition for a number of diseases with benign and malignant neoplasms.
Bone cancer is a general definition for a number of diseases with benign and malignant neoplasms.
Depending on the type of tumor, the stage of the disease, the symptoms can be very weak and the patient does not pay attention to them.
Bone lesion develops in two ways: directly from bone tissue or by metastasizing from other organs.
Contents of the article
- Chondrosarcoma - what is it?
- Causes and Risk Factors
- Degrees of Malignant Process
- What indicates the likelihood of developing a tumor?
- Diagnostic Techniques
- Therapy: Challenges and Opportunities
- Prognosis for Patient Survival
- Preventive Measures
Chondrosarcoma - what is it?
In primary cancer, cells randomly and chaotically divide and begin to grow where they should not be - in healthy bone tissue. One of the most common varieties of the tumor is chondrosarcoma - a malignant neoplasm of the cartilaginous tissue.
This is the second most common tumor skeletal disease, which accounts for about 20% of the total sarcoma about
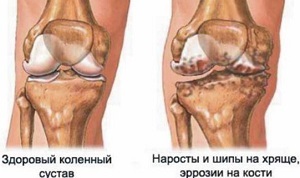
.It appears as a dense build-up, adjacent to the outer layer of the bone and capable of germinating at different depths.Can develop in any bones, but more often it focuses in the pelvic and humeral girdle, ribs, less often in the limbs and spine.
Most often, the tumor is detected in people of middle age and the elderly from 30 to 60 years, with predominantly in the strong half - women are sick less than twice. According to statistics, the earliest case of the disease was fixed at 6 years, and the latest in 90.
Causes and risk factors
The cause of development of primary malignant cartilage formations has not yet been identified.
There are several factors that contribute to the malignancy of the chondroma:
- bone marrow skeleton chondromatosis - Ollier-Muffucci syndrome;
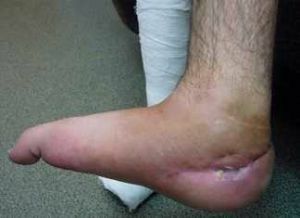
In the photo, the secondary chondrosarcoma
- is a hereditary factor, especially in chondrodysplasia with angiomatosis;
- malignant neoplasms in the kidney - Wilms disease;
- abnormal growth and impaired bone composition - Paget's disease;
- incorrect or untimely started treatment, for example, only partial removal of bone-cartilaginous exostosis.
Degrees of malignant process
Chondrosarcoma is classified into three degrees of malignancy, which can be identified during a histological examination:
- I degree - characterized by the presence of chondocytes with small dense nuclei not exceeding 8 mm in diameter. Multi-nuclear cells are practically not found, there are no mitotic figures;
- II degree - the intercellular substance is predominantly myxoid, the cells are much larger than at the I degree. Especially a large number of cells accumulate in the peripheral part of the lobules. The figures of mitosis are single, the nuclei of chondrocytes are already enlarged, there are zones of necrosis( destruction).
- III degree - intercellular substance is almost everywhere myxoid. The cells are arranged in groups or strands and have an irregular shape. There are many extensive necrotic areas. The nucleus is 5-10 times greater than that of a healthy analogue.
For a full understanding of the stage of the disease, several tumor-shaped pieces and sections are studied. The most malignant processes are detected in hemorrhagic and soft myxoid areas.
What indicates the probability of developing a tumor?
The first symptoms of chondrosarcoma appear late. The whole point is that the latent period of the degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant tumor can last several years and the patient consults a doctor when a persistent pain syndrome has appeared and the tumor has grown significantly in size.
Metastasis usually occurs by hematogenous route( along the bloodstream) to the liver, brain, lungs, regional lymph nodes.
The main symptoms of the disease include:
- severe pain with irradiation in the thigh or back( swelling squeezes the sciatic nerve);
- unilateral edema over the site of localization of the neoplasm;
- restriction of joint motion;
- difficulty in urinating( if the build-up pressure on the bladder).
Diagnostic techniques
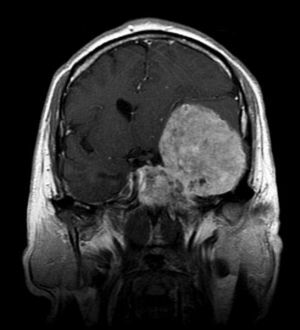
Intracranial tumor
The leading diagnostic method is X-ray. In the case of confirmation of chondrosarcoma, the sites show irregularly shaped lesions that contrast sharply against the background of soft tissues.
Specialists distinguish peripheral and central foci( on the surface or inside the bone).
With peripheral chondrosarcoma at the site where the tumor is adjacent to the bone, eroded surfaces of the cortical layer are identified.
On the edges of the neoplasm are visible deposits of calcium salts, in the hearth there is also calcification, which is expressed in the mottle of the picture.
If the tumor is found in the tubular bones, then in the picture the lesions are also spotted with speckles of calcification. The lesions appear as spindle-shaped thickenings.
The central hodrosarcoma of the bone is more often diagnosed, peripheral malignant neoplasms are usually secondary.
To confirm the diagnosis, as well as to check the spread of the tumor to other parts of the body, experts prescribe a more serious clinical examination:
- MRI or computed tomography of the affected bone;
- chest x-ray;
- MRI of the brain;
- open or penetrating needle bone biopsy;
- osteoscintigraphy - scanning of the bone system, in which any abnormal manifestations are detected.
Therapy: Complexities and possibilities of
The type of treatment for bone cancer depends on many factors: the degree of tumor development, its location, the prevalence of the other organs, the size and overall well-being of the patient.
The main method of treatment is surgery with the complete removal of a cancerous tumor and part of a healthy tissue. If the disease is in stage III, then limb amputation is possible.
In some cases, the operation is categorically contraindicated, then radiotherapy, chemotherapy and palliative therapy are prescribed.
However, most chondrosarcom do not respond to such treatment, so surgical intervention remains the most effective.
Some patients require complex treatment, combining several techniques at the same time:
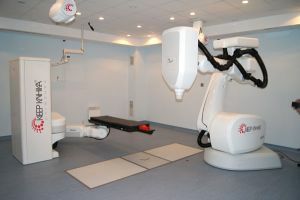
Cyberknife
- radiosurgical system Cyber-Knife;Chemotherapy and radiotherapy
- .
Tumors of I and II degrees are favorably cured by by the Cyber-Knife radiosurgery system for 1 -5 sessions of .Advantages of this method are obvious - it is not required to perform an operation that leads to disability of the patient.
In the last stages of treatment is considered only as a palliative.
Prognosis of patient survival
Successful treatment and recovery is completely dependent on the size and biological activity of the tumor, as well as the degree of development of the disease.
Neoplasms of the 1st stage do not give metastasis to other organs, and dissemination of the foci of the third degree is almost 70%.
After the operation, the survival rate of patients:
- with the I stage of the disease is about 90%;
- at the II degree - up to 60%;
- and with III - only 30%.
Preventative measures
There are no specific preventive measures for this disease, as the causes of the emergence and further development of malignant tumors have not been identified.
Specialists advise representatives from the risk zone to undergo annual medical examinations, with the slightest signs of ailment to seek help in medical institutions, to lead a healthy lifestyle.
Patients who have been treated for two years are recommended to undergo on-site examinations every three months.
In the fifth year after the treatment, the examinations are carried out every six months, then every year.
Early detection of the disease and timely treatment starts reduces the risk of developing a malignant tumor. At early stages of neoplasm detection, a complete cure is possible. In the case when the disease is badly started, the life expectancy is significantly reduced.