Today, there are a number of orphan( rare) diseases that modern medicine can not cope with. The possibility is only to support such patients, to some extent improving their quality of life, but the disease does not succeed.
Today, there are a number of orphan( rare) diseases that modern medicine can not cope with. The possibility is only to support such patients, to some extent improving their quality of life, but the disease does not succeed.
Pompe disease( generalized glycogenesis) is not currently considered a list of these diseases, although science has not yet found ways to cure this ailment. However, Russian patients have the opportunity to be treated in their country and, subject to certain conditions, receive assistance from the state, public organizations and charitable foundations.
Contents
General
- Inheritance
General characteristics of
Pompe syndrome affects the nerve and muscle cells of the body. This is due to the lack of alpha-glycosides, which is the result of mutational changes at the gene level.
If the patient does not receive proper treatment, then the structure of the muscle tissue changes, after which it is no longer able to function normally. The process progresses over time, the lesion spreads to other muscle groups, which is accompanied by severe pain.
In a severe stage, patients lose the ability to move independently, and by damaging the muscles in the respiratory system may become dependent on devices for artificial ventilation.

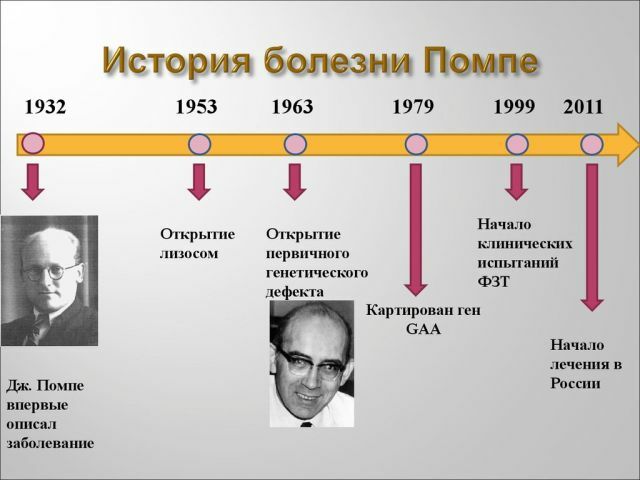
Historical background and statistics
This disease was discovered relatively recently - in the 30s of the last century. For the first time it was described by a scientist from Holland, I. Pompe.
The disease is equally likely to affect the faces of both sexes, it is not predominantly masculine or feminine. In the early form, the disease occurs in 1 case per 140,000 children born, and among the adult population, Pompe's disease affects 1 in 60,000 people.
In 2006, a method was developed in the United States to support such patients, and by 2013, effective methods were found by Russian scientists. But, unfortunately, not every patient can afford to be treated, as the cost of therapy is very high.
Causes and mechanism of development of
The disease develops due to the deposits of glycogen in skeletal muscles and myocardium. This process is due to mutations in the gene GAA, due to which and affects muscle tissue, heart muscle, nervous system and liver. The process progresses, and in the cells there are various kinds of damage, including a dystrophic nature.
Pompe disease is generalized and muscular. In the first case, there are changes in organs such as the liver and kidneys, and the muscular system is also affected. In addition, manifestations of heart failure and violation of the swallowing reflex are not uncommon.
In muscle form, the symptoms are not so severe, and the disease manifests itself by a decreased tonus of muscle tissue and impaired posture. With this kind of ailment, patients calmly live to old age.
Inheritance of
Pompe disease is considered hereditary and is transmitted by an autosomal recessive type. A child whose parents are carriers of a mutational gene inherits the disease. 
The probability that such parents may have a child with Pompe syndrome is 25%.However, there are great chances to give birth to healthy children.
Science already knows what is happening in the body of a person suffering from the syndrome, but it was not possible to find out the cause yet.
As follows from the foregoing, individuals who have blood diseases among people with a similar disease are at risk, and the closer the relationship, the higher the risk.
Modern classification of
Pompe disease is conventionally divided into 4 groups depending on the age in which the primary symptomatology was manifested:
- Early infantile type .The most severe form of the disease, which manifests itself from the first months of life, affecting the liver and heart. As a rule, children do not live up to a year, dying of cardiac or respiratory insufficiency.

- Late infantile type .It manifests itself in the first 3 years of life and develops not so rapidly. Patients die closer to adolescence, and the cause is most often heart failure.
- Juvenile type .The first symptoms appear from 6 to 10 years, and the lethal outcome comes closer to 20 years.
- Adult type of illness .It manifests itself from 20 to 40 years, develops slowly, and the patient has enough chances to live to a very old age.
To study the disease in more detail is quite difficult, because it is considered relatively rare.
Symptomatology and clinic depending on age
At different ages, the disease manifests itself with various symptoms. The most severe and fleeting is the early infantile type of disease.
Symptoms of the disease in the first months of life:
- muscle weakness;
- low motor activity;
- delayed physical development;
- excitability and frequent crying for no apparent reason;
- disorders in the respiratory system;
- enlargement of the liver and proliferation of cardiac muscles;
- violation of swallowing and sucking reflexes, an increase in the tongue.

Symptoms of late infantile and juvenile form( from 3 to 10 years):
- decreased muscle tone in the lower limbs with a gradual transition to other muscles;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- problems on the part of the respiratory system;
- lack of weight;
- increase in heart, spleen and liver size.
Symptoms of an adult or late form of the disease( from 20 years):
- insomnia or increased drowsiness;
- frequent headaches;
- muscle weakness and severe shortness of breath;
- scoliosis.
This form of the disease is considered to be the least dangerous, and the mortality rate is much lower here than with the development of the disease in childhood.

Diagnostic search stages
 The detection of the disease is carried out in several stages.
The detection of the disease is carried out in several stages.
First, the main diagnostic methods follow, and then additional studies can be assigned depending on the type and stage of the disease.
The main methods for detecting type 2 glycogenosis include:
- anamnesis;
- laboratory tests of blood serum;
- assessment of clinical symptoms;
- MRI of the muscles of the lower limbs and other parts of the body;
- ECG and EchoCG chest X-ray.
After conducting the main diagnostic activities, 
- is assigned to study DNA for genetic defects;
- biopsy and microscopic analysis of muscle tissue;
- blood test to determine the level of activity of alpha-glucosidase.
When it comes to the late form of the disease, then apply such methods:
- polysomnography;
- determination of lung capacity;
- electromyography of skeletal muscles.
Based on the results of the conducted studies and assessment of the general condition of the patient, treatment is prescribed.
What to do when the diagnosis is made
So, a disappointing diagnosis is put and there is no doubt. What to do next? In this case it is necessary to follow the following algorithm of actions:
- prepare a package of the following documents: an extract from the medical card, which should contain information about the diagnosis, the recommended drugs and the mode of their introduction;protocols of medical commissions;referral for disability;
- to transfer the indicated list to the attending physician for the preparation of the application for treatment;
- visit health authorities with an application for the purchase of necessary drugs;
- write an application to a public organization for assistance;
- if the application was rejected, it is necessary to notify the Ministry of Health and seek legal assistance.
What modern medicine can offer
 As mentioned above, it is impossible to cure Pompe disease. However, science has been dealing with this problem for several years and certain achievements have been made. Today, you can slow down the process and ease the patient's condition. What does modern medicine offer in Russia?
As mentioned above, it is impossible to cure Pompe disease. However, science has been dealing with this problem for several years and certain achievements have been made. Today, you can slow down the process and ease the patient's condition. What does modern medicine offer in Russia?
The only drug available to Russian citizens is Mayozaim for intravenous administration. This is a lifelong remedy, its action is aimed at restoring the functions of organs and systems that were affected by the disease.
The drug can be used at any age and in all forms of the disease. The following positive effects are noted as a result of its use:
- improves the condition of bones and muscles;
- stabilizes the work of the respiratory system;
- increases motor activity.
Application of Mayozeim reduces the risk of death by 99%, and improved the work of the respiratory system by 92%.However, in some patients, the following side effects of the drug can be observed:
- vomiting and nausea;
- allergic manifestations on the skin;
- shortness of breath and tachycardia.
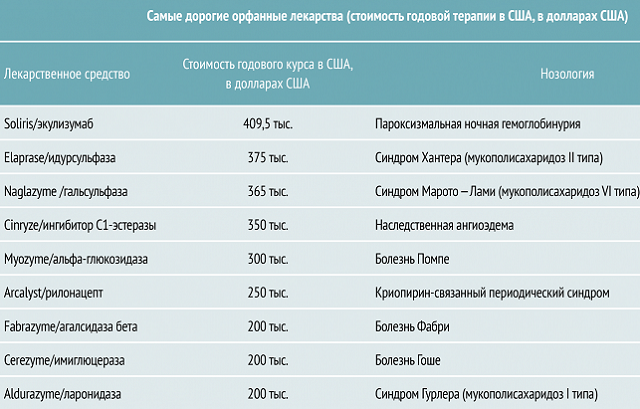
The disadvantage of the drug is its high price. If there is no possibility to carry out treatment with it, doctors correct the patient's condition with the help of cheaper and less effective drugs.
Prognosis and prevention of
The prognosis for Pompe disease depends on the form of the disease. In the early infantile type, children die before they reach the age of one year. The cause of death is heart failure.
The late infantile and juvenile form will allow the patient to reach the age of 20 years. Death occurs as a result of cardiopulmonary insufficiency.
The most favorable prognosis for those with whom the disease was diagnosed after 20 years. These people can live up to old age, but almost everyone has a disability.
As for prevention, it does not exist. This is a genetic disease, and there is no guarantee that a healthy child is born in a family where there have been similar cases of illness. You can only determine the degree of probability of the birth of a sick baby by going through an appropriate examination.