 To date, a large number of hereditary diseases affecting the dorsal, brain and peripheral nerve fibers are known due to genetic mutations transmitted in generations along the vertical.
To date, a large number of hereditary diseases affecting the dorsal, brain and peripheral nerve fibers are known due to genetic mutations transmitted in generations along the vertical.
The human nervous system is extremely complex and vulnerable. Any adverse effects on the fetus, especially on genes responsible for different structures of the nervous system, can trigger the appearance of severe pathologies.
For example, disruption of the normal development of leaflets of ectoderm and mesoderm in the embryo leads to damage to the nervous tissue, skin, eyes, vessels and internal organs. Such multisystem is characteristic for phakomatoses. What kind of pathology is this? Let's try to figure it out.
Features of the
Disease Group For the first time, phacomatoses have been described as a large group of hereditary diseases in the 20s of the last century. This group combines pathological conditions associated with changes in the skin in combination with damage to the organs of vision, different parts of the nervous system and internal organs( more than 50 nosological forms).
Clinically, phacomatoses are detected at an early age or immediately after birth, usually a dermatological manifestation. At the same time, neurologic symptoms can appear much later - in adolescence and adulthood. In contrast to congenital malformations, this pathology has a steadily progressing course.
At the heart of all types of disease is a mutation of genes responsible for producing a suppressor( tumor suppression factor) of tumors. 
Inheritance of pathology occurs vertically from parents to children in an autosomal dominant type( half of the children will receive an abnormal gene from the mother or father).
These diseases are highly heterogeneous - along with severe prognostically unfavorable forms, erased monosymptomatic variants are observed.
Common to all types of phakomatosis is the presence of multiple tumor growths - these are hemangiomas, fibromas, papillomas, telangiectasias and pigment spots on the skin. At the same time, each nosological form has specific features.
Classification of diseases
The term "phakomatosis" can not be used as a diagnosis, it refers to the ratio of pathology to a certain group of neurocausal diseases, there is a classification from which the most common forms among them are:
- Recklinghausen's disease ( type 1 neurofibromatosis) is an incurable progressive pathology with a large number of nodular growths( neurofibroma), pigment spots on the skin of the coffee color, nervous system tumors and abnormalities of the musculoskeletal system;
- neurofibromatosis type 2 - characterized by multiple more active tumors, in particular bilateral symmetrical neurinoma of the auditory nerve;
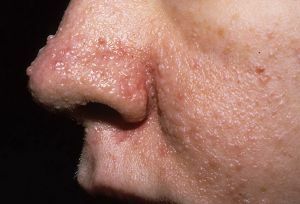
Tuberous sclerosis
- Burneville disease ( tuberous sclerosis) - characterized by benign tumors in many organs, epileptic seizures, adenomas of the sebaceous glands, mental retardation in children;
- Sturge or Sturge-Weber Syndrome ( encephalotrigeminal hemangioblastosis) is a congenital nevus of cherry on the face, vascular tumors of the retina and brain, secondary glaucoma;
- Klippel-Trinone syndrome ( hypertrophic hemangiectasia) - a flame nevus in the limb region, varicose veins, partial gigantism of the affected part of the body due to the proliferation of arteriovenous anastomoses and excessive vascularization;
- Louis-Bar syndrome - a combination of cerebral ataxia and telangiectasia, congenital immunodeficiency;
- Rendu-Osler disease - telangiectasia of the skin and mucous membranes, vascular pathology in internal organs, bleeding and chronic anemia;
- Hippel-Lindau syndrome - multiple hemangiomas in the brain and spinal cord, retina, internal organs;
- Bone-Deshome-Blanc disease ( neuroretinal hemangiomatosis) - excessive vascular proliferation and retinal damage, but without secondary glaucoma;
- Bloch-Sulzberg melanoblastosis - in female representatives, hyperpigmentation and inflammation of the skin in combination with damage to the nervous system, anomalies of the eyes, skeleton and internal organs( male fetus perishes);
- hypothelanosis Ito - skin pigmentation spots in combination with epileptic seizures, musculoskeletal and cerebral anomalies.
Clinical manifestations of
For all phakomatoses, a pronounced polymorphism of cutaneous manifestations, lesion of various structures of the nervous system and visceral organs is typical. Characteristically, at an early age, mainly dermatological symptoms are detected, and neurological and others are detected later.
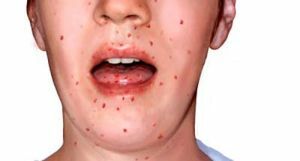 In some cases, phacomatosis is combined with a congenital immune deficit( Louis-Bar's disease), premature aging and( or) risk of malignancy of tumors.
In some cases, phacomatosis is combined with a congenital immune deficit( Louis-Bar's disease), premature aging and( or) risk of malignancy of tumors.
The defeat of the central nervous system in this pathology morphologically looks like the growth in the membranes and brain tissue of nodules, cystic cavities, neurofibromatous formations, demyelination sites, atrophy and calcification, congenital vascular anomalies such as aneurysms, hemangiomas.
The clinic has a picture of a convulsive syndrome with different flow patterns. In children, epileptic seizures often occur, as a result of which phacomatosis is often accompanied by a delay in neuropsychic development, oligophrenia, and antisocial behavior. The degree of severity of mental retardation is directly proportional to the severity and frequency of epileptic seizures.
For a group of diseases, lesions of different pairs of cranial nerves are characteristic with the development of oculomotor, auditory disorders, paresis and other symptoms.
Pyramidal insufficiency( more often of a unilateral nature), extrapyramidal disorders( brady- and oligokinesia, hyperkinesia, tonic muscle spasms), cerebellar dysfunction( impaired coordination), sleep disorders may be present.
Dermatological manifestations are usually detected in the first weeks or months of life. Elements of rashes are single or common, of different color and size, more often asymmetric.
Typical are pigmented spots of different shades of brown, areas of reduced pigmentation, nodular elements, neurofibromas, papillomas, shagreen skin with plaques, hemangiomas.
In some cases, phacomatosis occurs with endocrine disorders such as obesity, diabetes insipidus, disruption of normal sexual development. There are symptoms of a vegetative-trophic character( hair loss, brittle nails, dryness and peeling of the skin).
Often there is eye damage, which manifests itself early enough after the birth of the child. Upon examination, hemangiomatosis of the retina, persistent pathological expansion of the conjunctival vessels is revealed. Perhaps asymptomatic flow and manifestation only in the form of reduced visual acuity.
Lesions of internal organs are structurally and functionally caused by tumors developing in them, which are more often benign in nature, but are prone to frequent recurrence and progression.
In addition, reduced immunity in children with phacomatosis contributes to a tendency to join various infections that worsen the course of the underlying ailment.
Diagnosis and therapy
Any suspicion of phacomatosis requires consultation of specialists from different branches of medicine - pediatrics, genetics, neurology,  endocrinology, psychiatry, dermatology, ophthalmology.
endocrinology, psychiatry, dermatology, ophthalmology.
Genealogical and DNA analysis, blood and urine biochemistry, a wide range of instrumental and neuropsychological studies - EEG, brain and internal organs echography, MRI, CT, angiography, X-ray studies of the kidneys, stomach and intestines are carried out from the surveys. If necessary, other types of examinations are appointed to clarify the diagnosis.
There is no specific treatment for phakomatosis. Only symptomatic therapy is performed according to the indications for each patient with a specific form of the disease. The following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- anticonvulsant ( Carbamazepine, Topaleptsin, Epitropil and others);
- diuretics ( eg, Diakarb);
- neurometabolic ( vitamins B12, B6, Nootropil, Encephabol, Aminolone).
 In case of ineffectiveness of conservative therapy, surgical removal of neoplasms is carried out, which is especially indicated in case of suspected malignancy of the tumor, with a sharp progression of clinical symptoms, development of the brain compression syndrome.
In case of ineffectiveness of conservative therapy, surgical removal of neoplasms is carried out, which is especially indicated in case of suspected malignancy of the tumor, with a sharp progression of clinical symptoms, development of the brain compression syndrome.
Along with medicines in the treatment of phakomatosis, a major role is played by psycho-corrective measures aimed at restoring or developing the disturbed intellectual abilities of the child, coping with identified mental abnormalities, learning and social adaptation. The complex psychological help to families is practiced.
Do not need to hang a nose
In most cases, phacomatoses have an unfavorable prognosis, which directly depends on the type of pathology, the age of debility of the disease and the severity of the course, and the presence of immunodeficiency, the injuries received.
The worst forecast for the early onset of the disease, severe episyndrome, a deep degree of oligophrenia, the appearance of malignant neoplasms.
The main means of prevention is counseling couples planning to conceive a child, a specialist in the field of medical genetics. The possibility of procreation should be determined individually in each case.
Difficulties in diagnosing diseases from the phakomatosis group are associated with a significant polymorphism of clinical manifestations and the dependence of the debut of symptoms on the patient's age.
Patients with this pathology throughout life are observed by doctors of many specialties. That is why the great awareness of this disease matters. The choice of the right way and tactics of patient management is possible only with the concerted action of different specialists.