Dysarthria, if viewed from a purely medical point of view - this is a violation in the work of the speech apparatus.
Dysarthria, if viewed from a purely medical point of view - this is a violation in the work of the speech apparatus.
The specific disease is caused by the presence of neurological injuries, including - and the cortex of the human brain.
This disturbance is based on the blocking( partial paralysis) of the muscles of the speech apparatus.
Let's look at what is a mild dysarthria, symptoms and methods of treatment of the first degree pseudobulbar form of the disorder, which is often referred to as erased.
Contents
- Terminology - forms and stages of disruption
- Reasons and early detection
- Clinical picture features
- Conditional classification of patients
- Diagnostic criteria and procedures
- Correction and treatment
- Medication
- Preventative measures
Terminology - forms and stages of violation
There are several mainforms of children's dysarthria, depending on the location of the source of the existing disorder:
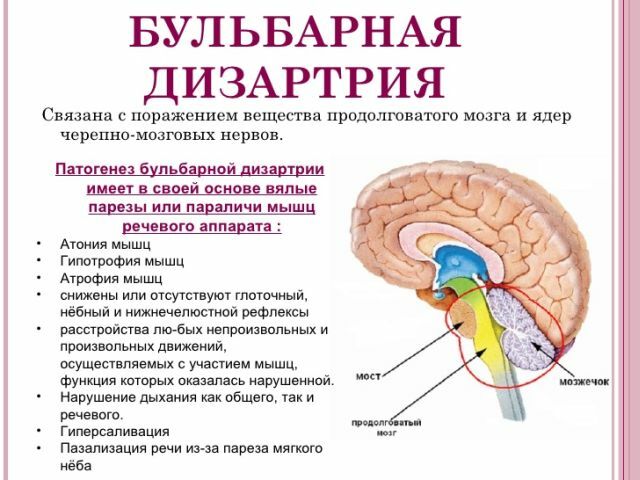
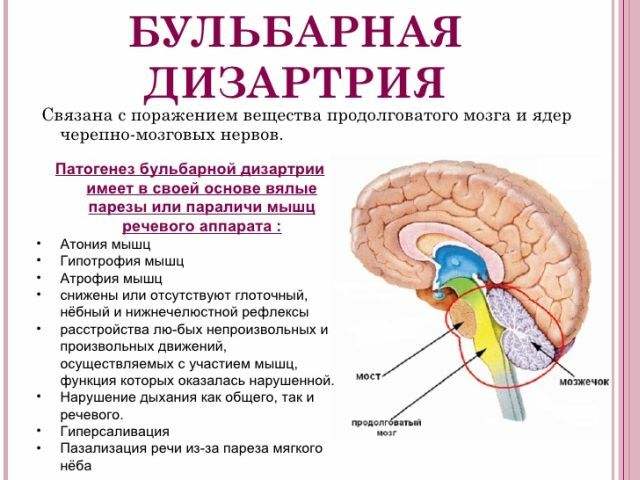
- Bulldog .The defeat of a large number of nerve endings, which in turn leads to the fettering of certain muscle groups that respond and affect directly the articulation. Features - violation of facial expressions.
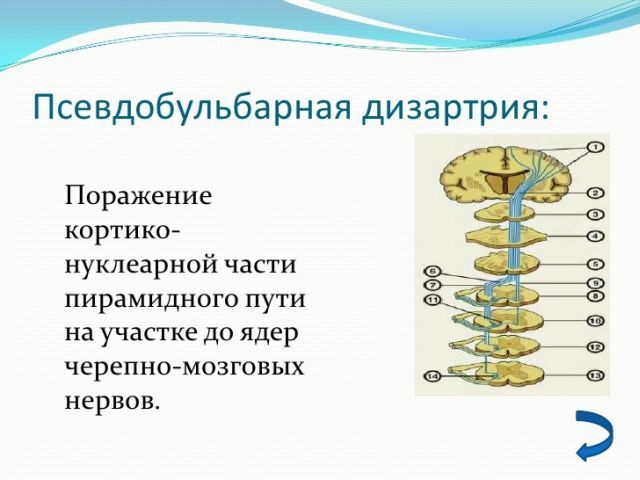
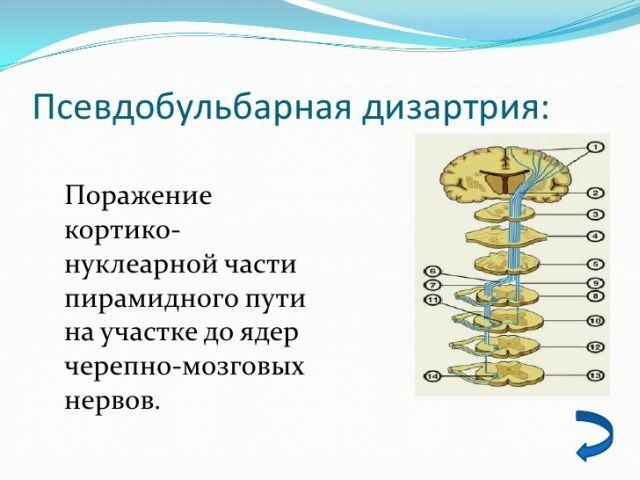
- Pseudobulbar .Damage and dysfunction of some parts of the brain, which leads to paralysis of the speech apparatus. A characteristic feature is the monotony of the pronunciation.
- Cortical .Unilateral damage to the cerebral cortex, with violation of certain structures. The main symptom is a violation of pronunciation of a part of syllables, and the general structure of speech is preserved.
- Cerebellar .Speech disorders due to damage to the cerebellum. Characterized by the instability of the structure of the child's speech - tonality and loudness are constantly changing.
- Subcortical .The part of the brain responsible for the normal formation of speech is affected. Feature - slurred and blurred pronunciation.
- Mixed .It is a consequence of various injuries of a child of the age group up to 2 years. As a feature - the addition of several factors that affect the formation of dysarthria.
There are four degrees of dysarthria pathology that are divided according to severity and severity of speech impairment:
- Degree I is an erased dysarthria. Often detected at 5 years of age. The main symptoms may be similar to the symptoms of other diseases of the nervous system. Especially noticeable is the confusion of sounds and the substitution of some by others. Most children omit part of the sounds when pronouncing long words.
- Degree II .It can be characterized by a fairly clear speech, but pronunciation defects are especially obvious. Perception of the child's words requires some effort.
- Degree III .The aggravation of speech comes to the point that outsiders can not practically perceive the meaning of the words pronounced by the child.
- Degree IV .Distortion of speech reaches the limits that even close relatives can not perceive what they say at the first time. Among other things, speech may be absent altogether.
Rubbed dysarthria is a turning point in the development of a specific type of neurological pathology. It is the easiest form of  pseudobulbar dysarthria, the timely detection of which guarantees complete cure and the ability of the child to continue to lead a normal life style.
pseudobulbar dysarthria, the timely detection of which guarantees complete cure and the ability of the child to continue to lead a normal life style.
The specific term "erased dysarthria" was first proposed by Dr. Tokareva, who clearly characterized manifestations of the first degree of dysarthria, as "erased, in her own manifestation, symptoms of pseudobulbar dysarthria."
Differs a special difficulty in overcoming the problems with pronunciation. Children suffering from a specific type of disease say the overwhelming part of the sounds correctly, but the child's speech flow is poorly automated and there is no clearness of the differentiation of sounds.
Reasons and early detection
Factors that provoke the appearance and progress of the disease, arise even at the stage of embryonic development in the womb and at birth. Often, they are:
- lack of oxygen in the developing fetus;
- severe toxicosis and gestosis;
- Neuropathy or kidney damage;
- viral diseases I-II trimester;
- birth injury;
- weakness or excessive activity of the mother's labor;
- of neuroinfections.
It is important to notice the manifestation of an erased dysarthria at the earliest possible age, since a successful and complete cure is possible only if detected up to 5 years.
Treatment for detection at a more mature age is complicated by the already formed perception and some additional impairments in the child's mental development. Complexities also arise because the body is partially formed and the most active stage of its growth is completed.
Features of the clinical picture
 The causes of the emergence of a specific form of dysarthria is the defeat of the sublingual nerve, which determines the clarity of the pronunciation and, as a consequence, the further progress of the disease and the defeat of the cerebral cortex.
The causes of the emergence of a specific form of dysarthria is the defeat of the sublingual nerve, which determines the clarity of the pronunciation and, as a consequence, the further progress of the disease and the defeat of the cerebral cortex.
With an erased form of dysarthria, disturbances can touch the nerves of the oculomotor system, which leads to a secondary sign in the form of strabismus.
The erased dysarthria in children is manifested by the following main symptoms:
- speech sluggishness due to partial blockade of the speech device, the lips and tongue of the patient are practically immobile, while performing exercises related to articulation shows a weakness of expression;
- noticeable jitter of voice and language in hypercrisis, which are manifested due to the strain of the facial muscles;
- there is a distortion of the lips, which prevents the correct performance of exercises;
- tonus of facial muscles is weakened, and control is understated, as a consequence - excess saliva.
Manifestations that accompany the erased dysarthria, you can specify:
- violation of fine motor skills;
- increased causeless fatigue;
- imbalance;
- inability to imitate elementary exercises;
- complexity of orientation in space.
Conditional classification of patients
Conditionally all children with a confirmed diagnosis erased dysarthria can be divided into three groups, based on - which function is broken:
- children who are unable to clearly separate sounds and reproduce intonations, the only true in this or that situation. It is accompanied by violations of spatial perception;
- patients with impaired perception of sound moments and inability to clearly separate sounds and reproduce the required intonations. In the speech there may be grammatical and lexical errors;
- polymorphic disorders with separate pronunciation and perception of sounds, intonations, there are also difficulties in adding words and word forms.

Diagnostic criteria and methodologies
It is rather difficult to determine the presence of the disease. Most of the success in determining the erased form of the violation depends on the responsibility and observation of the parents who need to notice any irregularities in time and go with the child to the speech therapist. The speech therapist will conduct some checks.
A doctor's examination consists of the following steps:
- examination and verification of present speech disorders;
- revealing pathologies not associated with articulation;
- check the performance of the muscles of the face, in particular - mimic;
- check the written abilities of children over 5 years old, based on: calligraphy, spelling and other.
Having detected some defects related to neurological diseases, the speech therapist sends the parents and the child to an appointment with a pediatric neurologist who is involved in the preliminary diagnosis.
In order to accurately identify the disease and the stage, a complex of medical measures is carried out. In diagnosis, the neurologist directs the patient to such ancillary research:
- electroencephalography;
- MRI of the brain;
- CT of the brain;
- study of the conductivity of nerve impulses.
Based on the findings and based on the results of additional checks, the neurologist makes a specific treatment plan and makes the final diagnosis.
Treatment and treatment
Treatment is based on the diagnosis, in the case of an erased dysarthria, with adequate correction methods,  usually has a favorable prognosis, but it is required to determine whether there are any other neuralgic diseases and disorders.
usually has a favorable prognosis, but it is required to determine whether there are any other neuralgic diseases and disorders.
Mandatory methods of its correction with erased dysarthria:
- training in physiologically correct breathing;
- respiratory gymnastics aimed at speech development and strengthening of vocal cords;
- massage of the muscles of the speech apparatus and additional exercises to develop the colloquial skill;
- appointment of exercises aimed at developing fine motor skills, children with a similar disease often have problems with calligraphy;
- pronunciation adjustment and the development of expressive speech;
- increased conversational activity;
- doing exercises to develop memory and attention.
Drug treatment
As additional prescriptions, some groups of drugs and vitamins are sometimes used, the main effect of which is to stimulate brain activity, improve memory and increase the level of attention. 
In medicamentous treatment with mild form of dysarthria the following drugs are included:
- relieving vascular spasms - Pantogam;
- nootropics - Encephabol, Pantokaltsin, others;
- metabolic - Actovegin, Cerebrolysin, other;
- sedative - Tenoten, Novo-Passit.
Preventive measures
 As preventive measures to prevent a particular disease, it is necessary to pay close attention to the period of pregnancy and the process of delivery.
As preventive measures to prevent a particular disease, it is necessary to pay close attention to the period of pregnancy and the process of delivery.
If timely prevent fetal hypoxia and protect the child from damage to the head in the process of birth, and also - in the first years after, then dysarthria is unlikely.
To completely eliminate an erased dysarthria, parents are required to:
- regularly visit with a child speech therapist - if at the age of the year there is no "agukanya" if in two years does not speak at all if up to 3 years the vocabulary is too poor or not pronounced simplesounds, if in 3-5 years there is no clarity of pronunciation or speech is very different from the speech of peers - this is the reason for an urgent visit to the speech therapist;
- talk to the child and instill in him an interest in the conversation;
- together with the child to train speech - to learn tongue twisters;
- protect the child from contact and ingestion of toxic substances ;
- to conduct prophylaxis of neuroinfections - a cap in the cold period is mandatory, timely treatment of colds and ENT diseases, regular visits and dental treatment.
In case of initial symptoms of dysarthria, it is necessary to visit a doctor, without postponing a visit to the hospital for later. In the case of timely treatment, all prescriptions and therapy can be limited to a short course of drug treatment of the root cause, that is - violations in the brain, and referral to a special group of children in the kindergarten. Usually, in such groups all necessary training and correction of speech is conducted.