Despite the opinion of many, bettolepsy( cough and cerebral syndrome, cough syndrome) has nothing to do with epilepsy, it is worth paying attention to this part of the word: -lepsy in translation from ancient Greek means "grip", or "fight".
Despite the opinion of many, bettolepsy( cough and cerebral syndrome, cough syndrome) has nothing to do with epilepsy, it is worth paying attention to this part of the word: -lepsy in translation from ancient Greek means "grip", or "fight".
But is not the brain having to fight, unclosing the tight embrace of hypoxia? Deadly embrace in a deadly battle, where is life at stake? And in both cases?
Therefore, before repeating what others have said, you should think twice.
The true causes and provoking factors
To hypoxia - oxygen starvation of tissues, in this particular case of the brain, leads to any relatively long-term existing state, accompanied by:
- or mechanical obstruction to breathing - oxygen supply;
- or caused by lack of oxygen in the blood for another reason( defect of red blood cells with some anemia, for example).
In the variant of bettoleptic, these two factors of hypoxia development are combined. This is the mechanical obstruction of the respiratory tract, damaged by acute or chronic pathology, and the prolonged time of circulation of oxygen-poor blood.
Time in minutes. Time that can be enough for the onset of irreversible changes in the brain.
We will admit to this basis that developed by the age of 40-50, and at an earlier age does not develop cough fainting, - atherosclerotic vascular degeneration, which in itself is the cause of chronic hypoxia. And also the episodes of excess  arterial pressure associated with it. And even arrhythmia - moments of a permanent nature.
arterial pressure associated with it. And even arrhythmia - moments of a permanent nature.
It is worth adding to the canvas two more smears, adding to the causes of bettolepsy the following:
- endocrine pathology in the face of sugar sickness;
- is a chronic allergy to everything that has developed, including, as a result of an exorbitant infatuation with taking medication.
The risk of developing cough epilepsy is unusually high in all these treasured treasures.
But. .. not everyone coughs into coughing! And only 2% of adults from experiencing different types of paroxysmal conditions! And children do not suffer from this disease( exception - cases where the background is whooping cough).
Why?
For the development of cough fainting, one more condition is necessary - the presence of pathological impulse from the reflexogenic zones:
- respiratory system;
- of the larynx( in particular, the activity of the upper-nerve nerve);
- of the carotid sinus, of the jaundiced veins, of the aorta;
- venous sinus brain.
The reaction from the pressoreceptors located in these reflexogenic zones is a necessary link that closes the fatal chain - pathological impulse from them leads to an increase in the activity of the vagus nerve, contributes to the onset of bradycardia and the manifestation of a dangerous condition - the Morgani-Edams-Stokes syndrome.
The hand of fate, or who falls ill inevitably
Accordingly, the causes of the development of bettolepsy include states with phenomena of increased intrathoracic pressure, as well as hypoxia of the brain, leading to disorders in the activity of the nervous system. Other provoking disorders, diseases and conditions:
- respiratory system diseases in the face of bronchial asthma, chronic bronchitis with asthmatic component and outcome in the emphysema
 of lung, fibrous-cavernous forms of pulmonary tuberculosis, laryngitis, whooping cough;
of lung, fibrous-cavernous forms of pulmonary tuberculosis, laryngitis, whooping cough; - status that occurs when aspirating small objects into the larynx, trachea;
- neovralgia of the overlying nerve;
- pathology of the cerebral arteries and veins in the face of vascular anomalies, compression of the vertebral arteries with osteochondrosis or atherosclerotic deposits;
- household chronic poisoning - drug addiction and alcoholism.
To the provoking cough syndrome factors should also be attributed some habits and household features in the form:
- wearing tight-fitting clothing;
- habits to rapid change of posture( with a sharp jumping after a long sitting);
- "passive smoking";
- propensity to anxious-hypochondriac, "suffocating psyche," states.
Why it is possible to lose consciousness:
Symptomatology and clinic
 A typical picture that predicts a cough syndrome is the redness of the facial skin and visible parts of the upper half of the victim's body at the peak of a coughing fit, swelling with congestive blood resulting from a vein strain, followed by cyanosis.
A typical picture that predicts a cough syndrome is the redness of the facial skin and visible parts of the upper half of the victim's body at the peak of a coughing fit, swelling with congestive blood resulting from a vein strain, followed by cyanosis.
Then comes a faint - the body without any "preliminary explanation" falls to the floor.
The future fate of a person depends on the length of time of fainting. But in any case, the skin of the victim pales, in an unconscious state, suffocation stops with a cough.
Depending on the depth of the developed hypoxia of the brain, the following may occur:
- rapid return to consciousness of ( with fainting from seconds to minutes);
- return to consciousness longer, with the development of short-term tonic convulsions in the form of twitching of limbs and a decrease in the tone of the pelvic organs with incontinence of feces and urine.
Consequences of cough fainting depend on the severity of somatic pathology predisposing to the development of bettopepsia - with deeply-entered changes, it is possible to damage the fine brain structures that are particularly sensitive to hypoxia and fluctuations in the level of blood pressure and CSF in the corresponding systems.
Diagnostic criteria and methods of research
Since it is possible to smoothly flow a fit of betolpsia into a small epileptic fit, the treating neurologist needs to know exactly which pathology he is dealing with. 
Therefore, the important diagnostic criteria is the onset of cough syncope:
- without precursors;
- during a cough fit - at the first minute;
- no biting of the tongue and discharge from the mouth of foamed saliva, and also characteristic of epilepsy of subsequent falling asleep.
For the establishment of a true diagnosis, the preceding actions of the sufferer are significant - in the form of eating, defecating, excessive laughter-geloplexy, and also the influence of cold air and tobacco smoke on it. Important is his age( mature or even older), as well as the presence of respiratory and vascular disorders.
In addition to carrying out the Valsalva trial, it should be noted the effect of using instrumental methods to study the state of the nervous system and the body as a whole:
- EEG;
- ECG, echocardiography and Holter monitoring;
- monitoring of blood pressure;
- X-ray and other methods of detecting respiratory pathology.
If necessary, in-patient examination is carried out, including in case of difficult cases - in the epileptologic center.
Need help with cough fainting
Usually, treatment of betolapsy as such is not performed, it only helps at the time of the attack. However, everything depends on the patient's previous condition and the depth of his fainting.
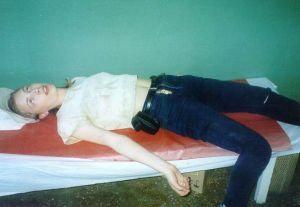
Those present at a seizure for quickest man's re-enactment can apply rubbing with ammonia spirits of temples and take measures to inhale fainting of his vapors;with the same success, another sharply smelling substance( vinegar) can be used.
Ensure the supply of fresh air, as well as taking measures to remove a foreign body stuck in the throat.

If necessary, the method of forced ventilation of the lungs is used - the artificial respiration method.
The rest is the task for the "emergency aid" team, at the beginning of the seizure it must be called immediately. For, after getting to know the situation, only her employees can be injected with cardiotonic and vasoconstrictors: Ephedrine, Mezaton, and with bradycardia - Atropine sulfate.
In all cases of the first attack of bettalesia, hospitalization is required with a diagnostic purpose, and further treatment of the underlying pathology is necessary under the supervision of the treating specialist: therapist, neurologist, cardiologist.