 The most common problem with knee injuries is the anterior cruciate ligament rupture( PKC).
The most common problem with knee injuries is the anterior cruciate ligament rupture( PKC).
In order to understand the mechanism of injury, as well as its causes, it is necessary to understand the anatomical features of the knee, which is one of the most complex structures of the musculoskeletal system.
Content of the article
- Anatomical educational program
- Causes of trauma
- Mechanism of development of rupture
- Varieties of injury
- How will the ligament rupture manifest itself?
- Diagnostic methods
- First aid
- Further actions in the medical institution
- Surgery
- Rehabilitation activities
- Complications and prevention
Anatomical educational program
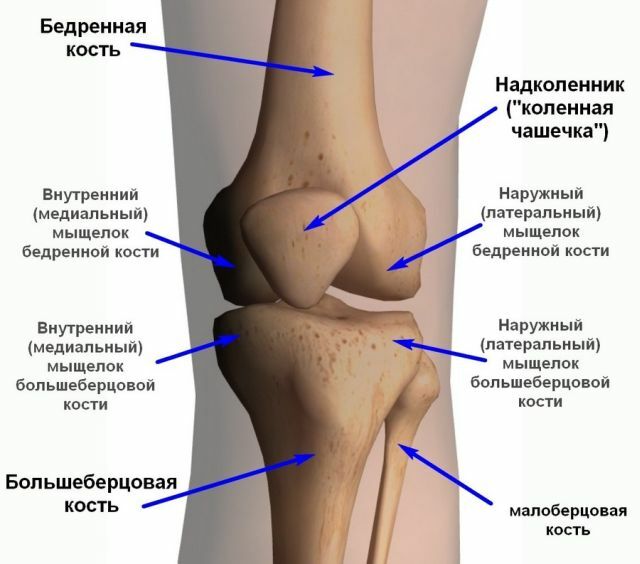
The knee is made up of three bones:
- tibia;
- femoral;
- knee cap.
And in order for the knee to function normally, these three bones are joined by five entire ligaments: a patellar ligament, internal and external collateral ligaments, anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments.
The structure and anatomy of the knee
A bunch is a strong enough connective tissue that provides the knee work in a certain range. If you go beyond it, at least, you can earn stretching or ligament rupture.
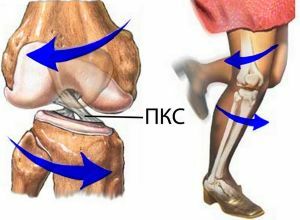
The anterior cruciate ligament( PKC) is located in the middle of the knee joint and connects two bones: the shin and thigh. Supporting the knee joint, the ligament does not allow the tibia to move forward.
As for the posterior cruciate ligament, it lies slightly behind the anterior and, if viewed from the front, they form a cross( hence the name of the ligament).
Bundle is provided with a huge number of nerve fibers, receptors, but practically has no blood vessels.
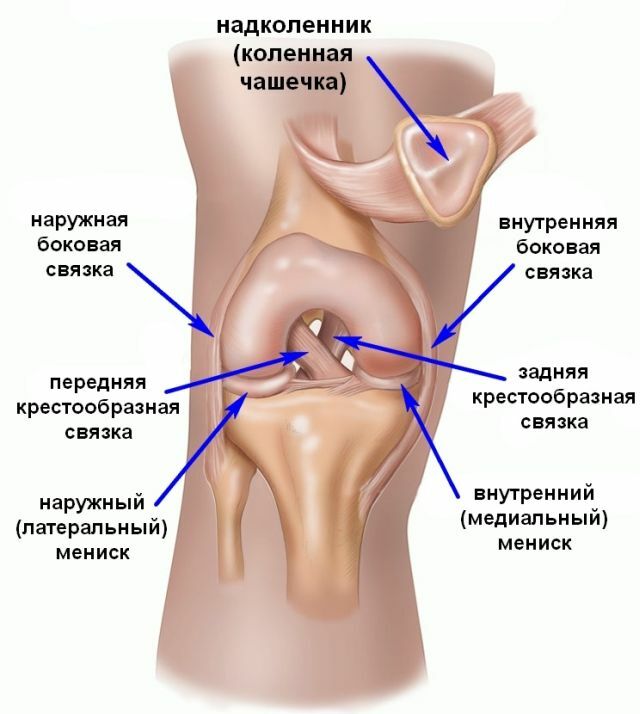
Knee ligament location
Causes of injury
The rupture of the cruciate ligament of the knee joint is risked by athletes and is associated with sports injuries. In addition, other factors can cause the gap:
- hit the knee area;
- traffic accident;
- sharp movements in the knee: fast running, followed by an unexpected stop, jumps, squats, flexion-extension;
- falling from height;
- stumbling;
- degenerative and inflammatory processes in the corresponding ligaments;
- landing on legs straight;
- sharp turns.
There are also risk factors that increase the likelihood of this injury:
- weak hips;
- weak hamstring, quadriceps;
- wrong tactic of performing physical exercises;
- female gender;
- classes in sports that require sharp stops, turns, movements: basketball, football, skiing.
Gap development mechanism
Knowing the mechanism of injury development is important not only to medical specialists, but also to athletes, in order to avoid the causes of the rupture. 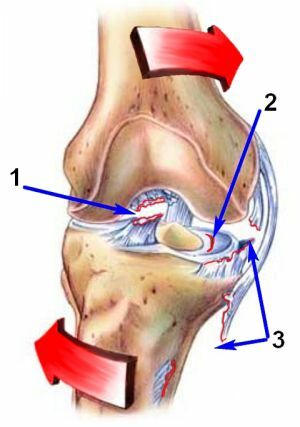
Knowledge will help and far from sports people to avoid injury PKS:
- leg deviation( valgus) and its simultaneous rotation to the outside;
- rotation of the lower leg to the outside, and hips inward( most often manifested in football, basketball, where it is necessary to make jumps);
- contact damage: direct shock to the knee area;
- damage to skiers, called "ghostly foot": at the time of the fall, one ski breaks away from the ground, touching only the back part, thus rotating the tibia relatively femur;
- hit the knee, in the thigh or calf area.
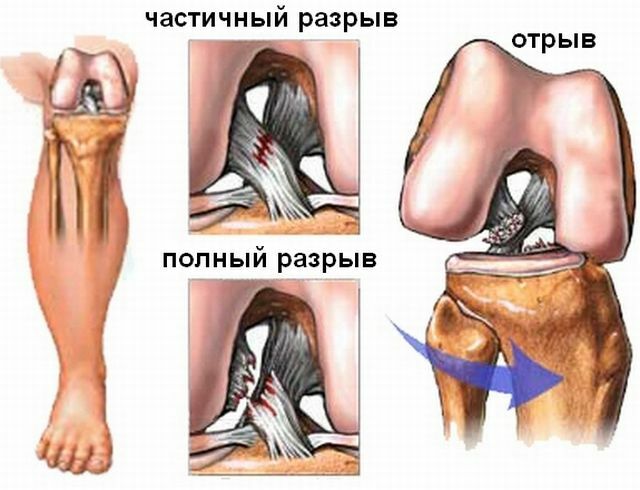
Variety of injury
The rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee joint is:
- Partial .In this situation, the unstable position of the shank may not occur, since the surviving part will stabilize the movement of the joint. In this situation, painful sensations are present, up to 50% of the fibers are broken. Complex treatment is also used. In the case of athletes, surgery is mandatory.
- Microdischarge is characterized by minor damage, for which conservative methods are applied. Surgery is not required. There are no special complications.
- The complete rupture of the provides for exceptional surgical intervention, in view of the complete rupture of the ligament and the loss of the supporting function of the foot.
How will the rupture of a bundle manifest itself?
Understand that a person has had an anterior knee ligament rupture, knowing its symptoms:
- severe pain in the knee area at the time of injury;
- crural dislocations, which have a periodic character;
- edema in the knee region;
- permanent pain in the knee in all movements;
- redness at the site of injury, bruises and scratches;
- temperature in the area of injury;
- bleeding into the cavity of the knee joint;
- characteristic sound( crash) while getting injured.
About whether a person has a PKC rupture or not, a traumatologist can ascertain, relying on the symptomatology and mechanism of trauma formation. After anesthetizing the place of traumatization, he will begin to examine and then he will answer: Is there a gap and what is his degree.
Diagnostic methods
After examination, the specialist will most likely be assigned other special diagnostic methods: 
- Arthroscopy .Minor surgical intervention, as a result of which a special device for studying the joint condition is introduced into the rupture area. This method can also serve as a correction.
- X-ray examination is a method that can not directly enlighten and show the sheaf and its condition, but can exclude other variants of the appearance of pain, such as arthrosis, patellar fracture, etc.
- MRI is the most accurate method not only for examining the condition of the anterior cruciate ligament, but also for other possible problems. Most accurately shows even the place of the gap.
- US will show the presence of fluid in the joint cavity, can visualize the state of the damage itself.
First aid
First aid measures for suspected rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament are common to any joint or ligament damage:
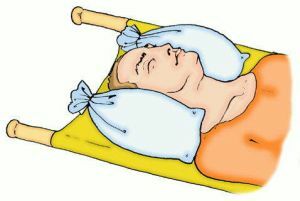
- the leg must be immobilized and placed on a hill;

- in any case not allow support for a damaged leg: lay the injured person;
- joint should be fixed with elastic bandage;
- should be cold for 15-20 minutes, repeat the procedure in an hour;
- always give an anesthetic( tablet, injection) and immediately seek medical help;
- with hemarthrosis, the doctor will prescribe a procedure for pumping blood from the joint region;
- in most cases can be superimposed with gypsum lingeta to eliminate knee mobility.
Further actions in the medical institution
 The main goal of treatment for rupturing the anterior cruciate ligament is the removal of inflammation, the elimination of pain and the restoration of ligament and knee joint function.
The main goal of treatment for rupturing the anterior cruciate ligament is the removal of inflammation, the elimination of pain and the restoration of ligament and knee joint function.
Various methods are used for treatment and conservative ones are the first ones. This is the first medical aid that must be urgently given to the victim, ensuring peace, anesthesia and elimination of knee mobility.
If all these rules have been met, but the blood has collected in the joint cavity, the doctor prescribes a special procedure for removing it.
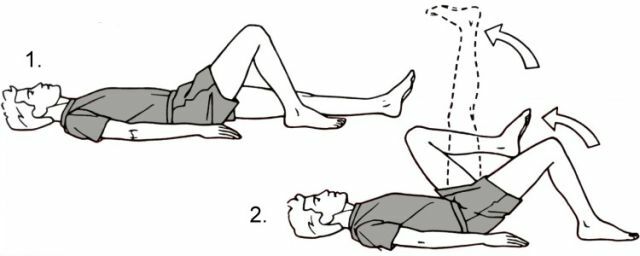
If the trauma does not require surgical intervention, the specialist appoints a special physical training.
Performing these exercises the patient can strengthen the work of the muscles and, accordingly, pump them, not giving rise to atrophy, which often happens after prolonged treatment of ligaments and neglect of physical exertion.
Performing a set of exercises will restore strength to the muscles, and in addition, will strengthen the joints themselves, so that they do not stop moving in all directions.
Inseparable components of therapy are massage, use of orthopedic devices supporting the knee, treatment in sanatoria.
Operative intervention
If a complete ligament rupture has been established, it can not be avoided without surgery, and it is a reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament, which is performed using special transplants that mimic certain human tissues( in our case a ligament).
The use of an autograft from the patellar ligament is used, which is cut off from the tibia, the patella, along with the enzymes and fixed in the bone channel, so it completely replaces the ligament after it has ruptured.
Otherwise, the graft is cut from the hamstrings of the hamstrings, which, after receiving, are sewn in half and positioned, as in the previous case.
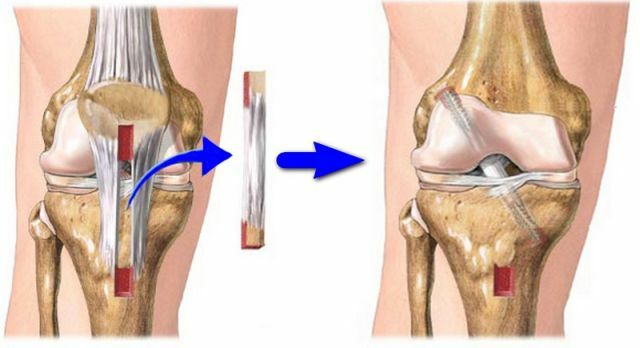
Anterior cruciate ligament repair with
graft Rehabilitation measures
If no surgical intervention was used to treat the trauma, it will take approximately 6-8 weeks for rehabilitation and it will consist of applying cold to the damaged area, massage, physiotherapy, physical exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles, joints and ligaments, in order to avoid their atrophy.
If there is an operative intervention, the rehabilitation time will increase to 6 months:
- So in the first month of is the main task - to remove puffiness, pain, to allow passive movement in the joint. The program is maximum - to walk without crutches.
- The second stage of the - up to 10 weeks: improve the performance of the previous stage and achieve walking without special control.
- The third stage of the is the achievement of muscle endurance and strength with the help of exercises( pay special attention to squats, lunges).
- The fourth stage of the is the maximum range of movements, as well as endurance, activity.
- The fifth stage of is the consolidation of the achieved result.
Complications and prophylaxis of
The main complications after the received trauma and improper treatment can be: 
- limitation of range of movements;
- after surgery, non-observance of the rules and rehabilitation can lead to the detachment of the transplant and its migration from the bone channels;
- patellofemoral arthrosis.
On average, after the treatment, traumatized people in 90% of cases continue to engage in sports with a break for about six months.
With regard to the prevention of rupture of PKC - it is strict adherence to the rules in training, avoiding jerks, sudden stops after running and injuries of the knee, hip, shin.