Problems with the digestive system - a scourge of modern society. First of all, it is connected with gastronomic habits( fried food, fast food, etc.) and the disturbed diet, frequent stresses and bad habits.
One of the most common diseases of the digestive tract, reflux esophagitis, is registered in almost half of the population. However, often patients hesitate to consult a doctor when symptoms of reflux esophagitis appear, and the treatment is delayed or requires more radical measures because of total esophageal damage and complications.
Contents
- 1 Reflux esophagitis - what is it?
- 2 Reflux disease stages
- 3 Symptoms of reflux esophagitis by disease forms
- 4 Treatment regimen for reflux esophagitis, drugs
- 4.1 Dietary food
- 4.2 Surgical treatment
- 4.3 Forecast
Reflux esophagitis - what is it?
Reflux esophagitis is an inflammatory process that affects the esophageal mucosa as a result of regular throws of the contents of the stomach and duodenum into the esophagus. Let us consider in more detail what it is.
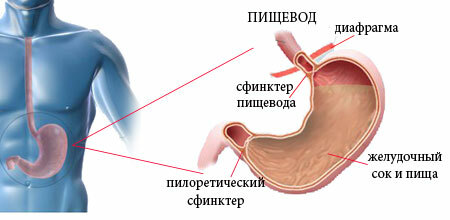
Reflux-esophagitis, in medicine called gastroesophageal reflux disease( GERD), develops in the distal esophagus. Beginning with catarrhal inflammation, the disease passes into the erosive stage with subsequent scarring. A heavier variant of GERD flow is necrosis and perforation of ulcerative foci.
Reflux disease is chronic and is caused by the following disorders: disturbed evacuation of food from the stomach and increased intra-abdominal pressure. However, the following conditions are necessary for the development of the disease:
- decrease in the tone of the circular muscle( lower sphincter) of the esophagus;
- aggressive properties of the stomach contents thrown into the esophagus;
- reduced regenerative capacity of the esophagus mucosa due to circulatory disorders.
The causes of reflux esophagitis include both organic pathology and external factors:
- diaphragmatic hernia of the esophagus;
- congenital pyloric stenosis and acquired pylorospasm;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- gastritis( especially with reproduction in the stomach of Helicobacter pylori);
- systemic scleroderma;
- operations on the esophagus and stomach;
- smoking, alcohol abuse;
- long-term use of medications that reduce the tone of the esophageal sphincter( Metoprolol, Nitroglycerin).
The risk of developing reflux-esophagitis significantly increases obesity and pregnancy, eating spicy foods, coffee and undiluted fruit juices.
Stages of reflux disease
Symptoms of GERD - their severity and impact on the general condition of the patient - directly depend on the degree of damage to the esophagus mucosa.
The following stages of reflux esophagitis are distinguished:
- Stage 1 - minimal damage to the esophageal mucosa, the diameter of the inflammation focus is less than 5 mm, limited to one fold;
- 2nd stage - single or multiple foci, in a size exceeding 5 mm;
- Stage 3 - spread of inflammation to 2 or more folds, a total of less than 75% of the circumference of the esophagus is damaged;
- Stage 4 - large, confluent foci, the circumference of the lesion is greater than 75%.
Symptoms of reflux esophagitis by forms of the disease
Symptoms of reflux esophagitis are manifested not only characteristic of the damage to the digestive signs, but also, at first glance, not associated with damage to the esophagus. Typically, the ongoing reflux disease can be suspected for the following regularly recurring symptoms:
- Heartburn and burning soreness behind the sternum - the patient often indicates their appearance after eating, especially after coffee, fatty / hot food, alcohol;
- Belching with sour or air, nausea;
- Lump in the throat and difficulty in swallowing food;
- Pain after eating - occur 1-1.5 hours after a meal, indicate a pronounced inflammatory process.
Symptoms of reflux esophagitis are particularly exacerbated if the patient lies in bed( assuming a horizontal position) after eating.
Often the disease occurs in an erased form. In typical signs, the severity of which can vary significantly( possibly asymptomatic course, the disease is detected during the exercise of EGF), uncharacteristic reflux-esophagitis symptoms are attached.
- Pulmonary form of GERD
Combines dyspeptic symptoms( eructations, heartburn) and signs of obstruction of the bronchi: prolonged coughing, shortness of breath, attacks of suffocation at night.
The process of casting acidic contents from the esophagus into the bronchi is often diagnosed as bronchitis, but its treatment does not bring the desired recovery. Also reflux-esophagitis in the pulmonary form can provoke bronchial asthma.
- Cardiac form of reflux disease
Anatomically close arrangement of the nerve plexuses causes the frequent occurrence of symptoms that mimic angina. However, always painful attacks occur after a nutritional error: overeating, acute and sour food, fatty and fried.
- Otorhinolaryngological form of reflux esophagitis
Often, on the background of heartburn and belching, the patient notes perspiration and sore throat( pharyngitis simulation), the appearance of nasal congestion and the secretion of clear mucus( rhinitis due to irritation by an acid cast in the nasal passages and edema of the nasal mucosa).
- Dental form of reflux inflammation of the esophagus
Sour contents of the stomach, bypassing the esophagus and getting into the oral cavity, destroys the tooth enamel. The patient can mark total caries.
Reflux-esophagitis without timely treatment occurs over the years with a gradual increase in symptoms and can lead to irreversible changes in the mucosa of the esophagus - scarring.
Treatment regimen for reflux esophagitis, drugs
 The curative scheme of reflux disease includes a complex effect aimed at eliminating its cause and symptoms. For a complete cure, long-term compliance with all the items of the treatment regimen is necessary:
The curative scheme of reflux disease includes a complex effect aimed at eliminating its cause and symptoms. For a complete cure, long-term compliance with all the items of the treatment regimen is necessary:
Drug therapy
Treatment of reflux esophagitis with drugs is prescribed only by a qualified gastroenterologist and includes:
- Antacids, antacids( Almagel, Maalox, Fosfalugel, Rennie), antisecretory PPI( omeprazole, Rabeprazole, Pantoprazole);
- Means for healing erosions - Solcoseryl, Actovegin, Drotaverin, Pantothenic acid, sea buckthorn oil;
- Medications that eliminate nausea and eructation due to increased motility of the gastrointestinal tract, Motilium, Cerucal, Raglan.
Mode events
A strict mode will not only accelerate the recovery, but also will prevent the occurrence of exacerbations. The habit should include:
- Education of stress resistance.
- Sleep 7-8 hours. The head should be raised by 25-30 degrees.
- Discarding corsets and pulling underwear.
- Do not lift weights.
- Euphyllin, nitrates, β-blockers, hypnotics and sedatives increase the course of reflux esophagitis and make it difficult to treat. Their reception is possible to exclude.
Dietary food
The diet with reflux-esophagitis eliminates all products that can increase the acidity of the stomach and cause bloating. What you can not eat when you are sick:
- drinks - spirits, strong tea, lemonades, coffee;
- pickles, smoked products, all canned products;
- beans, black bread;
- mushrooms, fresh / sauerkraut;
- fast food, chips;
- fried and spicy dishes;
- sauces - ketchup, mayonnaise;
- chewing gum.
The menu for reflux esophagitis should be made up of the following products:
- milk, low-fat cottage cheese and sour cream;
- chicken, soft-boiled eggs;
- cereals welded on water;
- dried white bread;
- lean meat, steamed, in the oven;
- cooked vegetables;
- boiled lean fish;
- compotes, sweet fruit jelly.
Surgical treatment of
Surgery for reflux disease is performed with ineffectiveness of conservative therapy, development of Barrett's esophagus, bleeding, marked adhesion of the esophagus.
The pronounced hypothyroid of the esophageal sphincter, which does not recover for 6 months of the complex treatment of reflux esophagitis, also requires the intervention of surgeons.
However, even a successful operation, the patient should regularly repeat preventive courses of taking proton pump inhibitors( omeprazole, etc.).
Forecast
Although conservative treatment of reflux esophagitis is quite successful, any violation of the diet can cause an exacerbation. Each patient should remember: after a course of drug therapy, usually lasting 2 weeks, reflux disease is not eliminated!
Only the treatment of regular medication courses, lifelong diet and exclusion of provoking factors can prevent the development of recurrences of the disease and its complications in the form of perforation of ulcerous areas and bleeding, adhesions.