What is it?
Acute and chronic pyelonephritis is an inflammatory lesion of the kidney caused by pathogenic microorganisms. Inflammatory process involves cups, pelvis and parenchyma of the kidney.
This disease can develop at any age. In prevalence, it takes second place, second only to acute infections of the respiratory tract.
About the causes of acute pyelonephritis
Acute renal pyelonephritis is always associated with infectious agents that are its immediate cause. The most common pathogens are bacteria that normally live in the large intestine. These are:
- Intestinal bacillus( found in 90% of cases);
- Klebsiella;
- Enterobacteria;
- Staphylococci;
- Enterococci;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- Proteus.
Other possible pathogens are: tuberculous mycobacteria, candida, viruses.
Microorganisms can enter the kidney in various ways:
- Ascending is the most common way. It implies the initial multiplication of microorganisms at the outer orifice of the urethra and their subsequent penetration into the bladder.
- Hematogenous, which occurs when bacteremia occurs when bacteria are present in the blood, from which they enter the kidney.
- Contact - microbes spread to the kidney from a number of located organs in which the inflammatory process has already developed.
An increased risk of pyelonephritis exists in people with predisposing factors:
- Urine retention in the background of obstruction of the urinary tract;
- Diabetes mellitus( significantly increases the risk of purulent forms of the disease);
- Polycystic kidney disease;
- Anomalies in the development of urinary and genital organs;
- Urolithiasis;
- Catheterization of the bladder.
According to epidemiological studies, there are three periods of increased incidence of pyelonephritis, depending on age:
- The period of early childhood, when the incidence of girls is 8 times higher than that of boys.
- Reproductive age under 35 years - the incidence of women prevails over the incidence of men( 7 times).
- Age is over 60 when men are more vulnerable than women( this is due to the frequent development of prostate tumors in older men).
Content
- 1 Symptoms of acute pyelonephritis
- 2 Symptoms of acute pyelonephritis
- 3 diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis
- 4 Treatment of acute pyelonephritis, antibiotics
- 4.1 Diet in disease
- 4.2 Complications of pyelonephritis
- 4.3 prevention of acute pyelonephritis
Symptoms of acute pyelonephritis
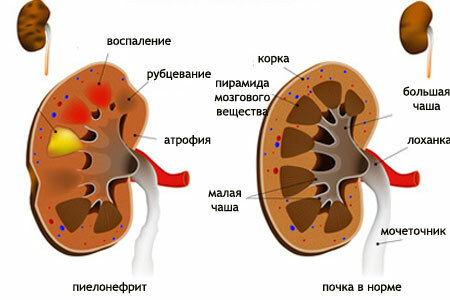
forms of acute pyelonephritis determine the nature of the clinical symptoms. The higher the activity of the inflammatory process, the more severe the disease and the more diverse the clinical picture.
The main forms of acute pyelonephritis are:
- Serous, representing the initial stage of inflammation, in which a purulent infiltrate in the kidneys does not yet exist;
- Purulent - the next stage of serous inflammation;
- Apostematous - in the kidneys multiple small foci of purulent exudate are formed;
- Carbuncle - the fusion of several purulent foci into one;
- Abscess - formation in the renal parenchyma of the purulent cavity, which is preceded by ischemia and necrosis followed by the addition of pyogenic bacteria.
Symptoms of acute pyelonephritis

Uncomplicated acute pyelonephritis has a vivid clinical symptomatology. It consists of a general intoxication syndrome and a local inflammatory syndrome:
- The patient's condition is moderate or severe.
- Weakness, increased sweating.
- Fever up to 40 ° C with chills.
- Nausea accompanied by vomiting.
- Headache.
- Increased urination( unlike cystitis, it is painless).
- Pain in lumbar region of aching or cramping.
Against the background of the depressed state of immunity, acute pyelonephritis can occur in an atypical form that simulates lesions of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis
The diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis is made on the basis of the results of 2 main analyzes:
- General clinical study of urine( sometimes requires Nechiporenko analysis with targeted count of leukocytes).
- Bacteriological study of urine with the determination of sensitivity to antibiotics of isolated microorganisms.
Urine analysis for acute pyelonephritis will be reliable and informative only if the rules for its collection are observed. These include:
- Collecting the average urine stream( the first 10 ml is the urine from the urethra, and the rest is the urine from the bladder, filtered in the kidneys).
- A man must take out the foreskin and rinse the head of the penis thoroughly.
- A woman should thoroughly wash her genitals, then close the vagina with a cotton ball to avoid getting into the urine of microorganisms.
Laboratory signs of acute pyelonephritis are:
- Increased number of leukocytes in the urinary sediment.
- Detection of bacteria.
- A small amount of erythrocytes, indicative of necrosis and stones in the urinary tract.
N.B.Leukocyturia and bacteriuria are not always detected in patients with pyelonephritis. Therefore, the absence of these signs does not exclude this diagnosis. The most common situation is observed with apostematous pyelonephritis and abscess, when purulent foci are located in the upper layers of the cortical substance of the kidney.
Diagnostic criterion of pyelonephritis during bacteriological examination is the titer of microbes more than 104 cfu / ml. If the indices are lower than this value, then the infection in the urinary tract is absent.
Ultrasound examination is additional to the above. It is carried out to study the structure of the kidneys and exclude in them local pathological processes( purulent foci and cysts) and anomalies. With his help, you can determine the presence of obstruction of the urinary tract.
In difficult diagnostic cases, it is required to resort to radiography and computed tomography.
Treatment of acute pyelonephritis, antibiotics
Treatment of acute pyelonephritis is carried out with mandatory patient compliance with bed rest. The first line of therapy is the mandatory prescription of antibiotics for a period of 1 to 2 weeks.
The group of choice is fluoroquinolones, since the E. coli( as the most frequent pathogen) shows them hypersensitivity. In some cases, protected penicillins can also be prescribed.
In severe conditions, antibiotic treatment begins with an injection. And after clinical and laboratory improvement, they switch to tablet forms.
The second direction in the treatment is the use of antispasmodics and anti-inflammatory drugs. The latter not only stop the inflammatory reaction in the kidneys, but also reduce the elevated body temperature, normalizing well-being.
In some cases, patients may require surgical treatment. Indications for him are:
- The destruction of the renal parenchyma( purulent inflammation).
- Discharge of urine outflow.
With purulent foci, depending on their size, complete removal of the kidney( nephrectomy) or drainage of the abscess through the skin under ultrasound control can be performed. Disrupted urodynamics( outflow of urine) suggests catheterization of the ureter.
Diet with
DiseaseThe diet for acute pyelonephritis( diet number 7) plays an important role in the early and most complete restoration of kidney function. It implies the restriction of protein products and the complete elimination of salt, while the amount of fats and carbohydrates remains within normal limits.
The daily volume of the liquid should not exceed 800 ml. Extractive substances are forbidden.
Patients with pyelonephritis are allowed:
- Protein-free and cut-off bread;
- Soups, but on the second broth;
- Low-fat meat( the first 14 days of the disease, its amount in the diet should be reduced, and then you can increase the daily portion);
- Low-fat fish;
- Eggs( not more than 2 per week);
- Dairy products and milk( in moderation);
- Vegetables and fruits;
- Low-fat and unsalted varieties of cheese;
- Coffee and tea.
It should be excluded from the diet:
- Black and wheat bread;
- Pickles;
- Broths based on meat, fish and mushrooms;
- Fatty meat, incl.and sausages;
- Pulses and mushrooms;
- Onion and garlic;
- Strong coffee and chocolate;
- Any kinds of alcohol;
- Mineral water enriched with sodium.
In the framework of diet number 7, cooking can be different - boiling, baking and steaming. The frying is also allowed. The temperature of the food does not matter.
Complications of pyelonephritis
Acute pyelonephritis, which occurs without complications, very quickly "responds" to ongoing antibiotic therapy. Residual lesions of the renal parenchyma are minimal or nonexistent, especially when the disease is in childhood( all changes are reversible).
Repeated episodes of the disease are rare.
However, after acute pyelonephritis, in rare cases, unfavorable outcomes may develop:
- Nephrosclerosis - the formation of scarring on the kidney, leading to a decrease in their function.
- Acute kidney failure( timely onset of treatment contributes to a safe resolution).
- Septic syndrome( its development predisposes the presence of diabetes in the patient)
A very rare complication with aggressive course is xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis. It is characterized by the presence of a large number of lymphocytes and macrophages in the renal parenchyma, stimulating the formation of lipid inclusions and uncontrolled multiplication of cells.
These signs bring together xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis with a malignant tumor. Therefore, in determining the diagnosis, a major role is assigned to literate histological research.
Prevention of acute pyelonephritis
Preventative measures will help prevent the development of acute pyelonephritis in patients at risk. They are recommended:
- Timely treatment of carious teeth and other diseases of the oral cavity, pathology of ENT organs.
- Regular urination, excluding urine stagnation.
- Hardening and strengthening of immunity.
- Observing the hygiene of the genitals.