What is it, ovulation?
For the conception of a child, not every day of the menstrual cycle is suitable. Only within one day a woman will be able to become pregnant, and if this does not happen, then after 10-14 days, menstruation will come. In order for fertilization to take place, a fusion of the spermatozoon and the mature egg is necessary.
However, the body of a woman is not adapted to the isolation of the female germ cell in a short time. It should mature in the follicle of one of the ovaries, and then - go outside.
The process of rupturing a follicle capsule and the subsequent appearance of an ovum is called ovulation. In simple words, ovulation is the only day in the menstrual cycle when a woman is able to become pregnant.
Contents
- 1 Hormones required for ovulation
- 2 When does ovulation occur?
- 3 Methods for determining ovulation
- 4 How does the ovulation process occur?
- 5 Signs, symptoms, sensations of ovulation
- 6 On what day after ovulation can I do a pregnancy test?
- 7 What if I do not have ovulation?
Hormones required for ovulation
One of the main causes of female infertility is a hormonal failure, in which the egg in the ovary either does not ripen, or the capsule of the dominant follicle does not erupt, and it continues to grow, forming a follicular cyst. Favorable conditions for the appearance of ovulation suggest the presence of a normal concentration in the body of the woman following hormones:
- Estradiol - responsible for the growth of the dominant follicle and endometrium. If this hormone is not enough, then the mass of antral follicles will not be dominant.
- Luteinizing hormone( LH) - has the property to increase by the time of maturation of the follicle. As a result, the LH peak ruptures its capsule and the egg has the opportunity to go outside and fall into the fallopian tube.
- Follicle-stimulating hormone( FSH) - responsible for the process of maturation of the follicle, like estradiol. Hormones of FSH and LH are complementary, so determining their concentration in isolation from each other will not be informative.
- Testosterone - an overabundance of this hormone prevents both the maturation of the egg and the rupture of the capsule of the dominant follicle.
Sometimes a woman is diagnosed with such abnormalities of the endocrine system, which permanently interfere with the onset of ovulation and which can not be cured completely. In such cases, doctors try at least temporarily to bring the state of hormones back to normal, so that a conception occurs.
When does the day of ovulation occur?
Despite the fact that a woman is ready to conceive a child all day, the main question remains on what day after the monthly ovulation occurs? If we look at the medical literature, then the answer to this is very unambiguous: ideally, the release of the egg from the ovary should occur in the middle of the cycle.
But every woman's body is individual, so early and late ovulation can be observed. The cause of these abnormalities is hormonal imbalance:
- For early ovulation, an elevated concentration of estradiol and FSH, as well as testosterone values close to the lower limit of the norm, are characteristic.
- Late ovulation is characterized by a low concentration of estradiol and high testosterone.
Absolutely accurate in advance to calculate the day of ovulation is impossible. However, there are special surveys that allow the most reliable prediction of the timing of the release of the egg from the dominant follicle.
Methods for determining ovulation
If a woman knows what time period in her cycle is most conducive to conception, then she can use it for both pregnancy planning and contraceptive purposes.
Graph of BT - the moment of ovulation is displayed on it by a sharp one-day drop in temperature by 0.3-0.4 degrees. The next day, the temperature rises to 0.2 degrees and holds for about two days approximately at this value, after which it rises to a mark of 37 degrees and above.
As a result, a step is formed on the graph between the lowest temperature value and the subsequent increase. This step means the day of ovulation.
The problem with tracking the output of the egg with the help of graphs is that a woman can only learn about the ovulation that is scheduled a day before( at the time of the temperature drop).
Ovulation Tests - the approach of a fertile day is displayed on the test with two bright strips. This means that for the next 36 hours the capsule of the follicle breaks, the egg will fall into the fallopian tube and within 24 hours will be suitable for fertilization.
One package contains several test systems - this allows you to observe how the color of the test strip becomes brighter.
Question: in the ovulation test is a weak second stripe, what does it mean?
If the second test strip for ovulation is weak, this either means that the LH concentration has not yet increased and the dominant follicle is not ripe, or indicates that ovulation has already passed. However, this method of determining ovulation has one significant drawback.
The fact that the reagent in the test system becomes active only if the body increases the concentration of LH.But it can happen that the dominant follicle in a woman is not ripe and does not exceed 9 mm in diameter, and the peak of LH still occurred.
Thus, the test will produce a false positive result.
USID-folliculometry - is the most accurate way to predict the day of ovulation. In the first phase of the cycle, the doctor can observe the growth of the dominant follicle and conclude that when his capsule breaks through.
After the day of supposed ovulation, it is necessary to visit the ultrasound room once again to make sure that it has taken place: characteristic features in the first 2-3 days will be the presence of a yellow body and fluid in the anterior space.
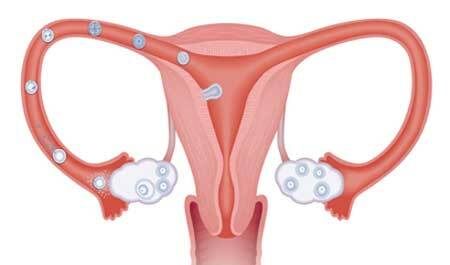
How does the ovulation process occur?
When the dominant follicle reaches a size of 18 - 22 mm in diameter - this means that the egg in it is fully ripe and ready to go. The whole process of ovulation can be considered sequentially:
- In the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland, a signal is produced that causes this department of the brain to intensively produce luteinizing hormone. After a few hours, the LH reaches a peak equal to 17-77 mU / ml.
- The maturing follicle forms a tubercle on the surface of the ovary. Along with the increase in LH, there is a rapid increase in estradiol, as a result of which the dimensions of the dominant follicle reach 22 mm.
- After the onset of increased LH secretion, the uterine signal from the brain is delivered to the tube that is closest to the ovary that is about to ovulate. The funnel of the oviduct is located above the ovary in such a way that the mother tube has the opportunity to grab the egg.
- Under the influence of the LH peak, the wall of the dominant follicle closest to the abdominal cavity becomes thin, and its integrity is impaired.
- The egg leaves the follicle along with a follicular fluid that will nourish the female germ cell until it is fertilized.
- The Fallopian tube uses the cilia to grab an egg and carry it inside its cavity, where it will meet with spermatozoa.
All these processes occur within 24 - 36 hours and for most women are completely invisible. As a rule, only the signs of a subsequent increase in progesterone are noticeable: increased appetite, tenderness of the chest, etc.
Signs, symptoms, sensations of ovulation

A small part of the fair sex feels when the period is favorable for conception, let's describe the possible signs, symptoms and sensations on the day of ovulation. First of all it is:
- Tingling in the lower abdomen on the left or right - may be a symptom of the maximally increased dominant follicle, the shell of which will break in the near future.
- A sudden increase in appetite - may indicate not only an increase in progesterone, but also hormonal changes that occur during ovulation.
- Bloody discharge - a few drops of light brown color indicate that the release of the egg from the follicle took place 3-4 hours ago. However, only a small number of women have such a symptom. And if intermenstrual bleeding is present, then you need to make sure that they are provoked by ovulation.
- Strengthening of sexual desire - is associated with the restructuring of hormones and with a change in the phases of the menstrual cycle.
- The appearance of translucent transparent excretions. In consistence they look like raw egg white. During the period of ovulation, the "thread" of such secretions can be stretched to 5-7 cm in length.

stretching discharge, a sign of ovulation, photo
If you plan to have sexual intercourse as ovulation symptoms appear, these attempts may not lead to pregnancy. The fact is that most of the signs appear when ovulation is either about to begin, or has already occurred.
During this period of time, sperm can not reach the fallopian tube( for this they need several hours, and the egg lives only 12 to 24 hours).
On what day after ovulation can I do a pregnancy test?
There are various reasons that cause the woman's desire to learn about her pregnancy as early as possible: from banal impatience, to the need for special medications to support the life of the embryo.
When the question arises on what day after ovulation you can do a pregnancy test, you need to consider that it all depends on the time when the implantation of a fertilized egg into the uterus occurred.
- Early implantation, 3 to 5 days after ovulation. The test will show a weak second strip already on day 9.
- The most common time for implantation is on the 6th-8th day. In this case, the test will show a weak second strip on the 11th day after ovulation.
- Late implantation, on day 9 - 12.The test will begin to show a weak second strip, starting from 13 - 14 days after ovulation.
However, it is almost impossible to determine the day of implantation. The only exceptions are cases when this process is displayed on the graph of BT by a one-day drop in temperature by 0.3-0.4 degrees( implantation of the west).
But far from all women the basal temperature reacts to the attachment of the fetal egg.
What if I do not have ovulation?

Normally, a woman can have 1-2 anovulatory cycles per year. If ovulation is not present for several months, it signals that it is necessary to take tests for hormones and show results to the doctor.
As an additional examination, you can make ultrasound of the uterus and appendages, as well as a picture of the Turkish saddle. Among the reasons why there is no ovulation, you can list the following:
Violation of the endocrine glands - the dominant follicle either does not mature, or does not burst in time, growing into a cyst. Inability to conceive due to improper functioning of the endocrine system is quite common and difficult to correct.
As a rule, the development of not one hormone is broken, but several - this complicates the process of treatment.
Overweight or dystrophy - any serious body weight deviations from the norm provoke the body to work for wear. The body instinctively feels that the conditions for conception are unfavorable, so the brain month after month can not send impulses to the pituitary gland and hypothalamus to adequately produce the necessary hormones.
Increased stress stress - the suspension of reproductive functions occurs for the same reason as serious body weight deviations from normal. The body begins to actively combat stress and regards the environment as unfavorable for the bearing of a child.
Excessive stresses - physical stress can be accompanied not only by the absence of ovulation, but also by the absence of monthly ones. Reproductive functions are returned when the woman refuses excessive loads and for several months changes her way of life to a calmer one.
Most of the causes of inability to conceive are due to improper hormone production. Therefore, in addition to a gynecologist, you can also visit the endocrinologist, who examines in more detail the hormonal background and the work of the endocrine system.
If ovulation is not present for several months - this is an excuse to go to the hospital and not engage in self-medication. First, it can further exacerbate hormonal failure, and secondly, it will take away precious time, which is better spent on an adequate course of treatment.