What is it? Infection of blood is a condition in which pathogenic microorganisms enter the blood, rapidly multiplying and spreading throughout the body. The role of causative agents can be bacteria, viruses and fungus flora.
However, not every entry of a microorganism into the blood leads to its infection - a combination of several factors is necessary:
- simultaneous intake of a large number of pathogens into the blood;
- deficiency of immune resources in the body, which can stop the growth and reproduction of microorganisms.
Therefore, the probability of infection of the blood is greatest in the following cases:
1. If there is a foci of infection in the body of , which has a close connection with the blood or lymphatic vessel. This situation is observed with:
- pyelonephritis;
- dental infections;
- pathology of ENT organs, etc.
2. In case of suppression of the immune system:
- HIV infection
- treatment with cytostatics or steroids( these drugs neutralize antibodies, reduce their production and suppress the activity of cytotoxic cells, ie they inhibit both cellular and humoral immunity)
- spleen removal
- lymphogranulomatosis and other leukemias( tumors of the hematopoietic system)
- is a tumor of any organ( cancer diseases are always combined with an oppressed state of immunity, TBE root causes tumors)
- prolonged excessive sun exposure( sun rays are able to detrimental impact on immune organs - the thymus, bone marrow, lymph nodes).
3. When combined chronic infection and depressed immunity( this is the most difficult case).
The nature of the course of blood infection can be from acute( fulminant) to chronic. In the latter case, with various concomitant diseases accompanied by immunodeficiency, there is an exacerbation. The early onset of antibiotic treatment results in complete cure.
This is reflected in the nature of the course of infection, which has now changed significantly( the number of lightning-fast forms has decreased).Without treatment, blood poisoning always leads to death.
Contents of
Main causes of blood poisoning
- 3 Treatment of blood poisoning
- 3.1 Consequences of
- 4 Answers to frequent questions about blood infection
The main causes of infection of blood
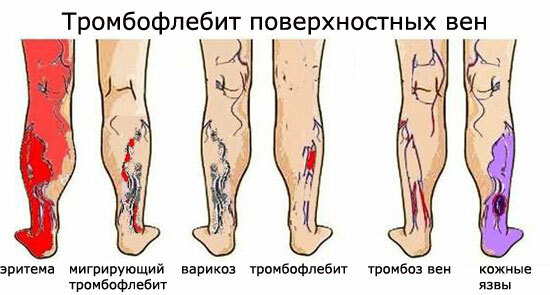
The ways of blood infection in all cases are associated with any( even the slightest) possibilitydirect contact of the pathogen with the blood, where it immediately enters. These can be:
- extensive festering wounds;
- boils;
- postoperative wounds.
In some cases, the cause of blood infection may be infection of a blood clot that has fallen into the filter of the inferior vena cava or in the aortic aneurysm.
Similarly, infection occurs with intravascular catheters. Especially dangerous, they become, if installed for a long time. Therefore, the optimal time between changing catheters is 72 hours. Risks of venous catheters have a dual mechanism:
- Immediate possibility of contact of blood and microorganisms living in the environment;
- Possibility of formation and infection of thrombus.
There is also a possibility of infection with blood transfusion. Therefore, the harvested donor material is tested for 6 months. This is the window stage for most infections, when serological tests can not detect antibodies to them.
There is a risk when performing operations. It is especially significant for gynecological interventions, conducted on emergency indications. The intra-hospital pathway can be realized through dressing, personnel hands and tools.
Often the source of bacterial invasion can not be detected. This condition is called cryptogenic sepsis.
Various microorganisms can become the cause of blood infection:
- of staphylococci;
- meningococci;
- pneumococci;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- protey;
- E. coli;
- herpes virus;
- mushrooms( Candida, Aspergillus and others).
As a rule, sepsis is the result of contamination of blood by one kind of microorganism, which starts to uncontrollably divide, "breaking through" all the protective barriers. The combination of several pathogens or their replacement during illness is an exception, not a rule.
First signs and symptoms of blood infection

When the blood is infected, the symptoms and manifestations of the disease depend on the type of causative microbe and the state of the immune system. Clinical symptoms consist of general and specific manifestations. Common features are:
- Significant temperature rise up to 39-40 ° C;
- Chills;
- Increased sweating, especially at night, coming to change chills;
- Weakness;
- Hepato- and splenomegaly( an increase in the liver and spleen, respectively);
- Rash that appears on the skin and has various characteristics( pinpoint eruptions, spots with uneven contours, etc.);
- Lack of appetite, leading to significant weight loss up to cachexia;
- Pain in muscles and joints( in the absence of morphological changes in them);
- Pressure drop to critical values, which may be accompanied by the development of septic shock with loss of consciousness.
The appearance of the first symptoms of blood poisoning is not always acute. Sometimes there may be a gradual increase in temperature and intoxication. However, in a short period of time, the condition of a person is noticeably heavier - it becomes difficult for him to move around, perform any work, he completely refuses to eat, etc.
Specific manifestations are determined by the type of causative microorganism. Depending on this fact, the infection of the blood has the following features.
Staphylococcal sepsis manifests itself with severe muscle pain and high fever. Single skin rashes appear on the skin. The condition of the patient with initially very difficult, but the mind at the same time is maintained at the proper level. At the same time, a dry cough may be present, which is then accompanied by a large amount of sputum yellow.
Meningococcal sepsis begins very violently. The patient's condition is very difficult. Within a few hours, a shock may develop. The distinctive features of this infection are a rapid increase in congestion with loss of consciousness, the skin appears multiple hemorrhages of a diverse form.
The development of septic shock is promoted by hemorrhage in the adrenal glands, often complicating meningococcal infection.
Pneumococcal Infection of the blood is characterized by such signs: temperature rise to very high values, the appearance of severe chills and weakness, adynamia( both physical and mental), intoxication of the body.
For generalized pneumococcal infection, loss of consciousness and shock are not characteristic. Despite the extremely serious condition of the patient, this type of blood infection does not involve muscle pain, rash, and severe disturbances in the functioning of organs.
In comparison with meningococcal infection, pneumococcal is not characterized by rapid flow. In this case, the clinical improvement against the background of the therapy is much later.
This fact is explained by the peculiarities of meningococci, which show immunity to many antibacterial drugs. In most cases, their final choice becomes possible only after obtaining the results of bacteriological research.

signs of blood poisoning, photo
Gram-negative sepsis most often accompanies immunodeficiency and is caused by an infection that has developed as a consequence of postoperative complications( suppuration in the abdominal cavity or pelvis in gynecological operations).Infection of blood after childbirth is also very often associated with gram-negative microorganisms.
Clinical differences of these microbes is an increased tendency to necrotic hemorrhages in the skin. They are single painful dark red rashes, surrounded by a dense shaft, which gradually increase in size.
Gram-negative infection is characterized by a low body temperature( up to 38 ° C).Therefore, patients often seek medical help late.
The exception of the typical clinical course is the pseudoaginous form of , which develops against the backdrop of inhibition of the immune system. It proceeds lightning fast, with the probability of rapid development of shock( 2-3 hours after the appearance of fever).
The development of herpetic blood infection is always due to the pronounced immunodeficiency observed in leukemias and lymphogranulomatosis( due to the decrease in antiviral activity of the organism), HIV infection in the stage of AIDS and after transplantation.
The infectious generalized process begins with the appearance of a rash of herpetic vesicles on the skin along the ribs. Then there is a massive spread of rashes on other parts of the skin, on the mucosa of the trachea and bronchi, the oral cavity and the esophagus.
After the opening of the vesicles, a staphylococcal infection may re-join, leading to suppuration.
Treatment of blood contamination

The peculiarity of the infectious disease is the massiveness of microbial blood seeding in combination with severe disorders of coagulation activity( DIC syndrome).Therefore, the treatment of blood poisoning is aimed at eliminating these two pathogenetic factors.
Patients with an established diagnosis( or only if suspected) are always hospitalized in the intensive care unit or intensive care unit.
The main direction of treatment is the antibacterial .For this, a drug is selected that corresponds to the sensitivity of the pathogen.
If it is impossible by clinical signs to establish the most probable causative microorganism, therapy is appointed empirically. The drugs of choice in this case are gentamicin + cephaloridine or cefazolin.
Treatment is considered adequate if there is a clinical improvement:
- Decreased weakness.
- Disappearance of chills.
- No appearance of new skin rashes.
- Downward trend in temperature( but it may remain elevated for several days)
- A decrease in the percentage of stab neutrophils( young immature forms, indicating an increased load on immunity, with which they can not cope) occurs in the blood test.
In cases when there are no improvements within 24 hours after the start of treatment, a group of antibiotics should be replaced. Preference is given to stronger means for a class higher in activity.
The presence of immunodeficiency complicates the treatment of blood poisoning, since not all antibiotics are effective. Such patients are prescribed gamma-globulin therapy( endobulin).These substances directly destroy pathogenic microorganisms.
For the treatment of DIC syndrome appoint: heparin, plasmapheresis, transfusion of freshly frozen plasma. However, the choice of a particular drug depends on the stage of the syndrome. Thus, in the phase of hypercoagulable heparin and its analogs are shown, and in the phase of hypocoagulation - categorically contraindicated. Plasmapheresis as a method of purifying blood from bacterial toxins is indicated at any stage of coagulation disorders.
Consequences of
The absence of timely treatment of blood infection always leads to the development of multiple injuries throughout the body that are incompatible with life.
With high sensitivity of causative microorganisms to treatment and satisfactory clinical improvement, antibacterial therapy continues for 2-3 weeks. If the process is delayed and complications develop, then the treatment is carried out for several months.
Late-onset therapy threatens the development of gangrene of the extremities( necrosis of their tissues), irreversible changes in the internal organs and hemorrhage in the adrenal glands. These complications are deadly.
After 2-4 weeks from the onset of the disease,
- joint pain may appear;
- laboratory signs of glomerulonephritis;
- noises in the heart;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- changes on the ECG.
Answers to Frequent Questions About Blood Contamination
How does HIV manifest after infection?
In severe forms of immunodeficiency, which include the stage of AIDS in HIV infection, infection of blood can cause opportunistic microorganisms. Normally, they constantly live on the skin and mucous membranes, but do not harm a healthy body.
In immunodeficiencies, they become the cause of severe infectious processes. Another feature of HIV infection is polymicrobial infection, the emergence of which is associated with several types of infectious agents - this condition is characterized by extremely severe course.
How long does it take to infect blood?
Reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms( corresponding to an incubation period in which there are no clinical manifestations) can last from a few hours to several days.
After the appearance of the first symptoms, blood infection can occur at different rates. Distinguish the following options:
- fulminant - the development of shock within 1-2 days with a lethal outcome;
- acute - lasts 3-4 weeks;
- subacute - 3-4 months;
- recurrent( characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission) - 4-6 months;
- chroniosepsis - 12 months or more.
Details of the manifestation of different forms and flow velocity are described above.