Antibiotics Fluoroquinolones presented rather large group of drugs possessing antibacterial activity against various pathogenic microorganisms groups. List of drugs belonging to these antibiotics, broad, includes a plurality of means having high efficiency.
The content of the article:
- 1 What is a fluoroquinolone
- 2 Mechanism of action
-
3 Classification: four generations
- 3.1 Non-fluorinated quinolones
- 3.2 gram
- 3.3 respiratory
- 3.4 respiratory anti-anaerobic
-
4 Indications for use of medical areas
- 4.1 gastroenterology
- 4.2 Venereology and gynecology
- 4.3 Dermatology
- 4.4 Otolaryngology
- 4.5 Ophthalmology
- 4.6 pulmonology
- 4.7 Urology and Nephrology
- 5 Antibiotics Fluoroquinolones
- 6 Possible side effects
- 7 Special instructions for receiving
- 8 Video of fluoroquinolones
What is a fluoroquinolone
In the external environment faced by people on a daily basis with a large number of pathogens. Much of dwells directly inside ones are useful in certain other circumstances cause a particular disease.
Fluoroquinolones presented an extensive group of drugs that possess a wide spectrum of action, kill various germs when ingested. The notion of funds formed in the 60-ies. last century. Since then, scientists have conducted a lot of research and have developed a safer drug than those used 50 years ago.
Mechanism of action
Fluoroquinolones (list of drugs includes means with varying degrees of efficiency) have a detrimental effect on gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria types. They quickly kill Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus and Streptococcus. There is a high efficiency in the fight against Shigella, gonococcus and pneumococcus.
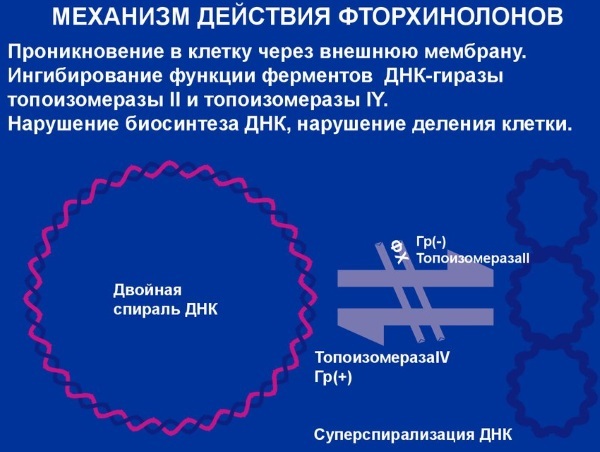
In addition, fluoroquinolones are allowed to use in the fight against different types of bacilli, chlamydia and tuberculosis bacteria. The latter type of microbial agents do not completely destroyed, but used as an auxiliary element of complex therapy.
The mechanism of action of drugs due to the sequence of several processes:
- After penetration into the body components tablets or other dosage forms are rapidly distributed of all organs and systems, to freely penetrate into different cells, providing a high efficiency.
- Further substances concentrated in the areas of inflammation, after which inhibit the synthesis of DNA molecules in cells that trigger the disease.
- Additionally fluoroquinolones violate them metabolic processes that lead to disruption of the reproduction and distribution process on healthy areas.
- Through these mechanisms, there is a fairly rapid destruction of microbes of different types, started the process of regeneration.
It should be noted that the active substances in the composition of an agent have a pronounced effect is due to the rapid penetration into all tissues of the body. They easily pass the placental barrier, so they can be dangerous for women during pregnancy.
The advantage of this group of drugs is also considered high bioavailability, after the maximum concentration of active ingredients is achieved after 3 hours after administration and persists for a long time. Due to the slow removal after the end of antibiotic activity of drugs is reduced gradually.
Classification: four generations
To date, experts allocate 4 generation fluoroquinolones. Each of them is effective in combating different groups of microorganisms.
Non-fluorinated quinolones
Fluoroquinolones (extensive list of drugs, allows you to choose in each case the appropriate means) of the first generation referred to as non-fluorinated. This is the first group of assets that includes the different drugs used to treat patients today. Active ingredients obtained by any means of processing nalidixic, oxolinic, pipemidic acid.

They are completely synthetic drugs, but they have a relatively narrow spectrum of action. Actively used in the treatment of diseases of the urinary system, as displayed in unchanged form, exerting a pronounced therapeutic effect. Another advantage is the high concentration of the drug in the patient's blood and several organs, e.g., bladder, intestines.
However, non-fluorinated quinolones barely able to penetrate the cells of the liver, lungs and other organs, so the extent of their use is narrow, unlike the funds of future generations. In addition, they cause a lot of side effects, even when used properly.
The first generation fluoroquinolones include the following drugs: nevigramon, Palin, blacks and others.
gram
The second generation of antibiotics of this group became known as Gram-negative because they are active mainly against Gram microorganisms. Study and research of drugs lasted for about 20 years, after which the first antibiotic norfloxacin this generation was launched.
We received it by addition of fluorine atoms in a particular molecule. Unlike non-fluorinated antibiotics, Gram-negative, fluoroquinolones have the ability to rapidly penetrate into the cells of almost all internal organs and concentrate them. This ensures high efficiency and performance.
A great advantage of Gram-negative antibiotics - high activity against Staphylococcus aureus. This organism provokes quite dangerous diseases and in the absence of treatment the patient's condition deteriorates greatly, there is a danger to life.

The most popular representative of this generation is now Tsiprfloksatsin. It is very effective in the fight against diseases of the respiratory, digestive, reproductive and urinary system. Among the shortcomings can be identified pronounced side effects on the central nervous system, the digestive system.
respiratory
3 generations of fluoroquinolones called respiratory. The list of drugs includes Levofloxacin, temafloxacin and others. Its name, this group was due to the high efficiency in the treatment of diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract.
Many microorganisms that trigger sinusitis, sinusitis, bronchitis and pneumonia, are very resistant to antibiotics of the penicillin group. Only a few decades ago they used in large quantities for the treatment of children and adults.
But with the advent of respiratory fluoroquinolones number of deaths from pneumonia and bronchitis running significantly reduced because they destroy even those microorganisms which are characterized by high resistance to other antibiotics. Medicines used not only for the treatment of respiratory diseases, but also to eliminate the symptoms of infectious conditions.

Bioavailability means any 3rd generation is close to 100%, which is also considered an advantage. Among the shortcomings is to provide a high concentration not only affected, but also in healthy tissues. Active substances quickly penetrate into the bodies cells, which does not allow to use them for the treatment of pregnant and lactating women.
respiratory anti-anaerobic
The mechanism of action of anti-anaerobic respiratory fluoroquinolones is not very different from the products introduced in the previous generation. They are also effective against pneumococci, staphylococci and streptococci, which are resistant to penicillin and even macrolides.
The latter are among the most effective antibiotics, but even they were not always able to cope with bacteria.
With a wide range of action and rapid achievement of the therapeutic effect of drugs widely used to treat bronchitis, otitis media, sinusitis. They are effective and sinusitis, pneumonia, varying degrees of severity, and even not running form of tuberculosis.

High bioavailability approaching the absolute, helps to achieve therapeutic results in a short time and when using the minimum dose of medication.
However, the concentration of large doses of active substances in healthy tissues could provoke toxicity. Some tools of this generation has recently been taken off the market and is not used in the treatment precisely because of the high toxicity.
Indications for use of medical areas
Drugs of the fluoroquinolone group are widely used in various fields of medicine. In some cases they are used as the primary method of treatment, in others - as a subsidiary.
gastroenterology
Even first-generation quinolones actively used as the primary method of treating inflammatory bowel disease. The patient is in a few days he could get rid of the acute symptoms of colitis, enteritis, or enterocolitis. The course of treatment then lasted at least 2 weeks, but improvement was noted already at 4-5 days after the beginning of reception.
As the progression of the pharmaceutical industry were more improved medicines, expanding their field of application. When cholecystitis, bacterial gastritis, peptic ulcer, fluoroquinolones have been used, which helped to suppress the activity of pathogenic microorganisms.

As the main method of treatment medications are not assigned, as a set of tools is needed. But thanks to such antibiotics is minimized the risk of complications.
Venereology and gynecology
Chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, gonorrhea, and other diseases are successfully treated using fluoroquinolones. In this case, antibiotics are almost always the only treatment that eliminates the possibility of developing complications from the use of several different groups of medicines.
In gynecology funds are also used extensively with endometritis, salpingitis, adnexitis. bacterial vaginitis as well to treatment using fluoroquinolones 2 and 3 generations.
Dermatology
In the treatment of infected wounds, trophic ulcers and other skin diseases are widely used formulations 2, 3 and 4 generations. In most cases, they are assigned locally in the form of ointments and creams because they help to destroy the bacteria directly into the lesion.

However, with major trauma and infection of the lesions experts decide on the appointment system means in the form of pills or injections. For a long time, scientists could not get a second form, but her appearance has expanded the scope of the drug.
Otolaryngology
Fluoroquinolones (list of drugs in the last few years has increased) 3 generation are widely used in the treatment of all diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract inflammatory disorders. This is due to the high efficiency of respiratory antibiotics against pneumococci, streptococci, staphylococci.
It should be noted that the treatment of bronchitis, sinusitis, sinusitis often in the early stages are obtained from the group of penicillins. After 7-10 days of treatment failure specialist decides on the appointment of fluoroquinolones. In the past few years, many doctors once used this group of drugs, reducing the period of treatment and preventing complications.
Ophthalmology
For the prevention and treatment of postoperative complications in the visual apparatus are widely used drops and ointments that contain antibacterial ingredients in the composition of the group of fluoroquinolones.
Means 2, 3 and 4 have a high generation efficiency in combating keratitis, bacterial conjunctivitis. In this case, drugs are not addictive, rarely provoke complications and almost always help to completely cure the disease.
pulmonology
In any lung disease lung specialists often prescribe fluoroquinolones, especially 2 and 3 generations. It is these funds quickly kill pneumococci, streptococci, staphylococci, sometimes help suppress the activity of the tubercle bacillus.

Due to its effectiveness, fluoroquinolones may be used as part of a tuberculosis treatment of acute and chronic forms. As the basic method are used to eliminate the symptoms of bronchitis, sinusitis, sinusitis varying severity.
Urology and Nephrology
In urology specialists also use antibiotics in this group. The first generation of non-fluorinated quinolones suitable for the treatment of cystitis, urethritis in men and women. These medicines are concentrated in the organs of the urinary system, which helps to rapidly achieve the therapeutic effect.
Pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, inflammation of the duct or other kidney diseases nephrologists can use fluoroquinolones as tablets or injections.
Antibiotics Fluoroquinolones
Fluoroquinolones have a list of drugs is quite large. However, there are one or more resources you use most often in each generation.

| name of product | Description and operation |
| nevigramon | Available in capsule form. The present composition nalidixic acid. Agent refers to the non-fluorinated quinolone, has a bacteriostatic and bactericidal action. When ingested, it stops the growth of harmful microorganisms, which leads to their gradual demise. Drug used primarily to treat diseases of the urinary system. |
| levofloxacin | It refers to the fluoroquinolone group of 3 generations. The composition comprises the active component of the same name. Has a marked effect on the microorganisms quickly destroys streptococci, staphylococci, pneumococci and other bacteria. It is effective in diseases of the respiratory, urinary, reproductive system. |
| ciprofloxacin | The antibiotic of gram-negative group of fluoroquinolones. It has a pronounced effect, active against gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, bacilli and even gonococci. It inhibits the growth of microorganisms and leads to rapid death. The only drawback is considered to be at high risk for adverse reactions in violation of instructions. |
| abaktal | Antibacterial drug generation 2, comprising pefloxacin composition as an active component. When ingested rapidly concentrated in the affected area, it kills bacteria and prevents their spread to healthy parts. It is produced in tablet form and as a lyophilisate for the preparation of the solution. |
| Floksal | The preparation of the Group 2 fluoroquinolones generation. It contains ofloxacin as an active ingredient. Effectively cope with Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens. Available in the form of eye drops and ointments. The most commonly used in the treatment of ophthalmic diseases. |
| Lomatsin | The antimicrobial agent from the group of Gram fluoroquinolones, produced in tablet form. As part of the present lomefloxacin. The substance has a strong effect, quickly suppress the vital activity of bacteria and destroys them. |
| Vigamoks | The drug 4-generation fluoroquinolones, developed specifically for the treatment of eye diseases of bacterial origin. Available in the form of drops. As the active compound in the composition is present moxifloxacin. After contact with the mucous membrane of the component is rapidly absorbed and starts acting. |

These tools are used quite often. However, in the group there are other drugs with high efficiency. In each case, the expert selects the desired formulation.
Possible side effects
When using any generation fluoroquinolones may develop adverse reactions. Most often complications occur in violation of instructions, but can also occur under other circumstances.
The most common side effects are the following:
- Sleep disturbance (insomnia or drowsiness).
- Inability to focus on any subject.
- performance decline, weakness, fatigue.
- Loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, which does not bring relief.
- Pain in the stomach, intestinal colic.
- Loose stools, flatulence.
- Itching and skin irritation, vials filled with transparent or turbid liquid.
- Increased salivation, lacrimation.
- Apathy, depression.
- Headache, dizziness.

The most severe complication of long-term uncontrolled antibiotics of this group is considered angioedema. In this case, the patient not only symptoms of allergies, but there is swelling of the mucous membranes of the throat, which can lead to suffocation. It recommended that the appearance of complications immediately stop taking and consult a specialist to prevent such complications.
Special instructions for receiving
Taking medication is recommended only after survey and identify the true cause of the disease.
Experts insist on the observance of certain rules to facilitate the healing process and to minimize the risk of complications:
- To use drugs should be strictly according to the scheme and appointed doctor dosage. Excess or reduced doses may degrade overall condition.
- Should strictly follow the doctor's recommendations and not to prolong the course of its own.
- It is also forbidden to stop taking ahead of schedule, as the antibiotic can not kill all the germs, but his re-appointment will be ineffective.
- Tablets should be consumed after a meal, to minimize the negative reactions on the part of the stomach and intestines.
- course of antibiotics is recommended to combine with taking drugs to normalize the intestinal microflora. For this fit Linex or Bifiform.
- During treatment, it is strongly advised not to take alcohol. After completing the course should still adhere to this for 2 weeks, which will reduce the burden on the liver cells.
- When using the external forms of medication should first check their sensitivity to the drug. Duration of the course, as with other forms of application should not exceed recommended.
- In the absence of the effect of treatment for 10 days or deterioration should consult a doctor. Perhaps, the drug is not suitable to the patient and required to appoint another.

If a patient is already taking any medication and considers it an effective, doctors do not allow re-treatment without prior examination. The decision on the appointment of drugs to children is accepted only after pediatrician examination of the child.
Effective broad-spectrum antibiotics, fluoroquinolones, allow you to quickly treat many diseases. The list of drugs is replenished every year, so each patient can choose the right tool.
Registration of the article: Lozinski Oleg
Video of fluoroquinolones
Fluoroquinolones - mechanisms of action and resistance: