Renal colic should be considered not as a pathology, but a concomitant symptom. The attack of sharp, unbearable pain in the lower back or on the sides of the abdomen develops suddenly - the condition is caused by the broken passage of urine.
Pain in renal colic is cramping, spreading in the groin. Observe either complete anuria( no urination), or frequent urge with painful output of small portions.
Contents
- 1 Causes of renal colic
- 2 Symptoms of renal colic in women, attack
- 3 Treatment of renal colic in women, drugs
- 4 Emergency care for renal colic
- 5 Diagnosis of the disease
- 6 Complications of
- 7 Features of renal colic in pregnant women
- 7.1 Symptoms in pregnancy
- 8 Prevention of renal colic inwomen
Causes of renal colic
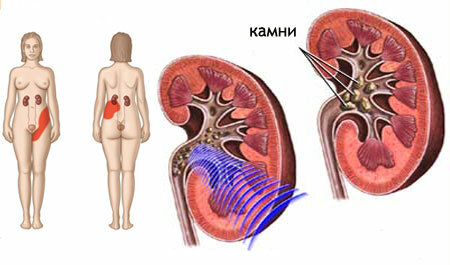
Pain caused by an attack of renal colic occurs due to stretching or squeezing of the ureter when it opense go calculi: urinary stone, blood clot, mucus and pus lumps. The musculature of the ureter contracts, preventing the free flow of urine.
The pressure of the fluid in the pelvis of the kidney rises sharply, the venous outflow is disturbed, the tissues of the parenchyma of the organ swell. Fibrous capsule of the kidney is overstretched. The attack of renal colic requires a strong medical anesthesia( narcotic drugs group) or urgent surgical intervention.
The main cause is urolithiasis. In 60% of attacks, the "stopper" is formed of urinary stones. With pyelonephritis, a bladder and mucous clots;at a tuberculosis of a kidney - slices of the died out epithelium.
There is a twisting( bend) of the ureter, which provokes nephroptosis or kidney dystopia. Tumor of the organ, traumatic hematomas - the cause of external compression of the ureter. Consider vascular pathologies( venous thrombosis of the kidney, infarction of the organ, etc.) and congenital anomalies.
Group of inflammatory and congestive diseases responsible for the onset of renal colic in women:
- hydronephrosis, nephritis and cystitis;
- pathology of the uterus;
- polycystic kidney;
- inflammation of the appendages( adnexide) and damage to the uterine tube;
- twisting of the "leg" of the ovarian cyst;
- ovarian apoplexy( organ tissue rupture);
- pregnancy ectopic( ectopic);
- spontaneous abortion;
- pregnancy.
Symptoms of renal colic in women, attack

The main symptom of renal colic is the suddenness of pain. There is no pattern of occurrence. After physical activity, a long walk or shaking while riding, the probability of feeling a "knife in the back" increases. The waist and abdomen - bilateral renal colic aches, only from one side pain - one-sided.
A woman experiences acute pain, chaotic movement in bed in the hope of finding a comfortable position and to ease the condition. The pain spreads into the thigh, the perineum. Skin pale, cold, wet with sweat. Severe weakness, attacks of nausea alternate with vomiting, blood pressure rises. Later the temperature will rise.
The attack of renal colic lasts from 3 hours or more, sometimes up to a day, if there is no medical care. Over this period of time the nature of the pain, and its irradiation is changing. The patient has thirst, flatulence, chills. From severe pain develops shock. As soon as the renal colic ends, the urine leaves freely. When it settles, there is a precipitate.
During the seizure, it is important that the doctor can correctly "read" the clinical symptoms and differentiate the condition of the woman. The examination is carried out by a gynecologist in conjunction with a urologist.
Conditions with similar symptoms and pains:
- acute appendicitis;
- acute pancreatitis;
- cholecystitis;
- perforated stomach;
- aortic aneurysm;
- hernia of the spine.
Treatment of renal colic in women, drugs
In most cases, renal colic treatment in women is inpatient, although some attacks safely end with the release of the stone. The first three days a woman is under medical supervision to help in time relapse.
Indications for compulsory hospitalization:
- does not manage to stop pain in the patient;
- is the only kidney or donor;
- high fever and suspected infection in the body.
Medication:
- drugs that relieve pain;
- anti-spasm;
- reducing urine production;
- antiemetics.
In parallel, prescribe vitamins, nutritional supplements, which treat the cause of the formation of urolithiasis.
Surgical method of removing the stone is used when it is impossible to do this by conservative treatment. Modern methods are minor traumatic. It is not always necessary to even puncture the skin. Apply ultrasound, laser, endoscopic instruments, stents.
Open operations are performed only if it is not possible to carry out other treatments and severe damage to the kidney.
Emergency care for renal colic
Emergency care for a woman should be provided close to the arrival of doctors. At home, use local warming compresses, apply a heating pad to the place of intense pain on the abdomen or back. If possible, take a sedentary bath. The water temperature is about 40º C.
With certainty that the cause of pain is renal colic, first aid should be given promptly.
It is necessary to take a medicine that will remove spasm from smooth muscles( No-shpa).The drug against pain( Ibuprofen, Ketanov, etc.) at home can be safely assumed if it is localized on the left. Otherwise, the symptoms of other acute inflammations may be blurred.
Doctors assess the condition of the patient upon arrival. Renal colic in a woman requires an immediate response. Emergency care is provided by doctors, the algorithm is as follows:
- Complete patient rest;
- Thermal procedures for the removal of spasm and urinary outflow;
- Enter an anesthetic for renal colic, sometimes a drug group;
- Apply drugs that remove spasm and antiemetic;
- No effect on the above measures the signal for the introduction of narcotic drugs( morphine, promedola, etc.);
- Localization of the calculus in the ureter of the pelvic department allows to carry out the blockade according to Lorin-Epstein( introduction of novocain 0.5% into the round ligament of the uterus);
- When the stone is located in the upper part of the ureter, the intracellular blockade according to Shkolnikov is used.
- Physiotherapy( vibration therapy, ultrasound therapy, diadynamic therapy), aimed at excretion of small stones
The lack of positive dynamics - a signal for urgent hospitalization of the patient. In a hospital take measures: catheterization of the ureter, puncture nephrostomy or surgical intervention.
Warning! Algorithm for renal colic only. If there is a suspicion of concomitant pathology of the abdominal organs, thermal procedures are prohibited.
Diagnosis of the disease
For the doctor it is necessary to ask the patient in detail about the lifestyle, daily diet, hereditary diseases. When performing palpation, part of the back will be painful.
- Urinalysis will reveal the inclusions of red blood cells, protein, elevated leukocytes and epithelial cells.
- For the elimination of abdominal pathology, x-rays are prescribed.
- Intravenous urography. The result of changes in the contours of calyxes and pelvis of the kidneys, the position of the ureter and its bend inform the doctor of the cause of the pain.
- ultrasound of the pelvic organs and abdominal cavity.
- Chromocystoscopy. Determines the delay in the isolation of indigo carmine from the overlapped ureter.
- MRI of the kidneys.
- Blood test is clinical and on the level of creatine.
Complications of
 Because of a delay in urine, there is a risk of developing pionephrosis or hydronephrosis. The accumulation of urine causes the kidneys to increase in size, overstrains tissues, leads to loss of body functions.
Because of a delay in urine, there is a risk of developing pionephrosis or hydronephrosis. The accumulation of urine causes the kidneys to increase in size, overstrains tissues, leads to loss of body functions.
The lack of adequate treatment of urolithiasis leads to obstructive pyelonephritis, and then increases the risk of urosepsis and bacterial shock.
Features of renal colic in pregnant women

When carrying a child, the burden on the kidneys increases, the probability of exacerbation of chronic pathologies and the risk of colic attack increases. In pregnant women, the renal colic has symptoms and treatment is the same as that of other women.
Pain occurs on the background of pyelonephritis or urolithiasis. Localization of pain more often on the right.
You can try to change the position of the body and find more convenient, in which the pain is less. Hot tubs and warmers for pregnant women are prohibited by .
Symptoms in pregnancy
You can determine the renal colic by the tone of the uterus. The remaining symptoms are not much different from the usual attack in not pregnant women. The same sharp beginning, pain, chills, thirst and weakness.
Danger in increased uterine tone, which increases the likelihood of childbirth. You can not wait, the pregnant call an ambulance.
In the absence of a doctor or the duty of waiting for a team, they independently take antispasmodics in the form of tablets or intramuscularly( no-shpa, baralgin).They will relieve spasm and facilitate the excretion of urine.
Prophylaxis of renal colic in women
With timely response to an attack, relief of pain and restoration of the passage of urine, it is possible to avoid complications and relapse. If adequate treatment has not followed, then the changes that have occurred in the kidneys are irreversible.
You can prevent a second attack if you exclude risk factors that contribute to the development of urolithiasis:
- See what kind of water you drink. The formation of stones affects the content of salts and minerals.
- In the diet it is necessary to reduce the share of chocolate, smoked foods and marinades. Limit sorrel, parsley.
- Low intake of vitamin A slices the epithelium in the renal pelvis. Such "garbage" serves as a building material for future stones.
- Vitamin D is essential for the absorption of calcium. It, in turn, neutralizes the oxalic acid inside the intestine. Its danger is expressed by the formation of oxalate stones in the kidneys.
- The excessive content of vitamin D is also bad for the body, it provokes dehydration of the body, and it thickens the urine and increases the accumulation of calcium salts.
- Congenital malformations of the urinary tract and kidneys can not be ruled out, but knowing about its particularity it is necessary to monitor the health status.
- Avoid infections of the genitourinary system. Pathogens alter the composition of urine, its properties and promote the crystallization of stones. Certain bacteria damage kidney tissue and create a material for the formation of stones.
- Keep away from drafts, hypothermia.
- Maintain an active, mobile way of life.
Urolithiasis before renal colic does not manifest itself. It is important to adhere to a diet that prevents or reduces the likelihood of the formation of stones. Limit:
- Green salad, sorrel, potatoes, cheese, chocolate and tea. These products contribute to oxalate stones.
- Eggs, beans, chicken, corn, peanuts to avoid the formation of cysteine stones.
- Dairy products, vegetables( phosphate stones).
- Meat, beans, chocolate, coffee. Increase the formation of uric acid stones.
It is not always possible to avoid kidney colic. But preventive measures significantly reduce the likelihood of recurrence of an attack. Pay attention to herbal infusions, decoctions. Enrich the diet with vitamins, calcium. Drink plenty of clean water and do not neglect exercise.