Pain syndrome during ovulation is considered to be the physiological norm for women who do not have health problems. Its intensity is rarely high and usually does not limit the mobility of a woman and does not affect her performance. If a woman has no problems with the menstrual cycle, ovulation usually occurs 12 to 14 days before the onset of menstruation. With hormonal diseases, the cycle is most often irregular - in this case, you can determine the exact date of ovulation only during ultrasound diagnosis.

Ovulation pains the abdomen: causes and treatment
Painful sensations during the rupture of the follicular membrane and the release of the ready-to-fertilize egg into the fallopian tube are experienced by more than 60% of women aged 18 to 40 years. Pain usually has a pulling character and can resemble cramping sensations caused by contraction of the muscular layer of the uterus. These manifestations are not pathologies and completely go through 1-2 days after ovulation. If this does not occur, or the intensity of the pain syndrome is too high, you should consult a district gynecologist. Medical care for a woman is also required if the pain is acute, pricking or cutting, or accompanied by high fever, vomiting and other symptoms of intoxication.
Content of the material
- 1 Is it worth worrying?
- 1.1 Damage to the blood vessels of the follicular walls
- 1.2 Irritation of the peritoneum
- 1.3 Follicular cyst
- 2 Pathological causes
- 3 Diseases of the uterus
- 3.1 Treatment
- 3.2 Video - Where does the pain in the lower abdomen in women?
- 4 Diseases of the appendages
- 5 Other causes
Is it worth worrying?
Ovulation is a monthly process that occurs two weeks after the onset of the menstrual cycle( approximately at day 13-16).During ovulation, a graafa vesicle ruptures - a ripe follicle, which is a large bubble, the cavity of which is filled with liquid. This follicle is also called dominant, because it is much larger than other follicular sacs. The size of the mature follicle can reach up to 20-25 mm. At the time of ovulation, the walls of the follicle do not withstand the pressure exerted by the liquid, and it bursts, releasing the egg ready for fertilization into the fallopian tube.
Causes of abdominal pain
At the time of rupture, many women with low pain threshold experience moderate acute or traumatic pain from the localization of the process, which lasts no more than 10-15 minutes. No signs and symptoms in this case usually does not appear, therefore women do not pay attention to such painful sensations.
Unpleasant sensations on the day of ovulation and within 1-2 days after it can also be caused by other physiological processes occurring in the body during this period.
Damage of the blood vessels of the follicular walls
The mucous membranes and connective tissue, of which the follicle walls consist, contain a large number of blood vessels and capillaries. At the time of rupture, some of them may be damaged, which is usually accompanied by a weak pulling pain( less often - acute pain syndrome) and other signs. Among them:
- clotting or scant drip spotting;
- loss of appetite against a background of mild nausea;
- a slight increase in temperature( within the lower limits of low-grade values);
- headaches.
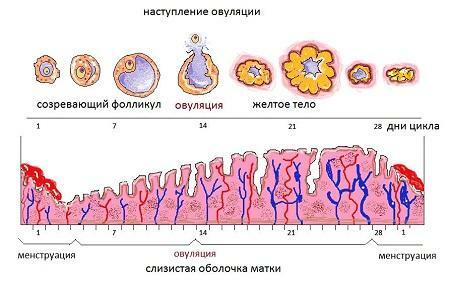
Ovulation onset
Important! All these signs should go through 2-3 days after ovulation. If the spotting continues and the pain does not go away or worsens, you need to turn to the gynecologist to rule out ectopic pregnancy, erosion of the cervix and other gynecological diseases.
Irritation of the peritoneum
Graafov vial is filled with a liquid in which the egg is during its maturation. This liquid contains protein components, salts, amino acids and other elements necessary for the normal growth of the egg and prevention of defects in its structure. When the dominant follicle bursts, some of the fluid can enter the peritoneum - the organs of the abdominal space and the serous membrane, to which the walls of the abdominal walls are covered.

Graafov vial
The substances contained in the liquid, reaching the surface of the peritoneum, can cause irritation, which is manifested by slight burning or stitching pains in the lower abdomen with possible irradiation into the central zone( around the navel).
Follicular cyst
When connective tissue covering the follicular walls is damaged, a glandular tissue is produced in its place, producing hormones necessary to preserve possible pregnancy and successful implantation of the fetal egg in the mucosal uterine layer( one of them is progesterone).This gland is called the yellow body. If during the ovulation period a woman did not have sexual intercourse or used contraception( that is, the pregnancy did not occur), the yellow body resolves itself after 30-90 days.
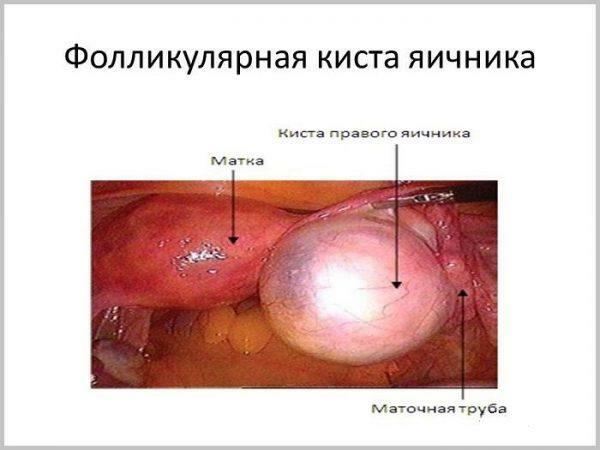
Follicular cyst
Pathological causes of
In the vast majority of cases, the abdomen with ovulation hurts when the hormonal balance is disturbed. Inadequate( or excessive) production of female sex hormones can lead to serious abnormalities in the work of reproductive organs and cause dangerous complications: uterine bleeding, infertility, excessive proliferation of the mucous layer and the epithelium of the uterus and ovaries, often recurrent miscarriages. Most often, these disorders occur when the balance of the three major hormones: prolactin, progesterone and estrogen.
| Name of the hormone | Characteristic of |
|---|---|
| Prolactin | Peptide hormone with a protein structure and consisting of acidophilic cells of the adipose pituitary |
| Progesterone | Refers to a group of steroid hormones, participates in brain activity processes and affects the synthesis of corticosteroid and sex hormones in a woman's body. Is the main compound that controls the functions of the reproductive organs and the development of the embryo in the event of pregnancy |
| Estrogen | Steroid hormone responsible for the proper functioning of the ovaries, uterus and other organs of the reproductive system and the appearance of the woman |
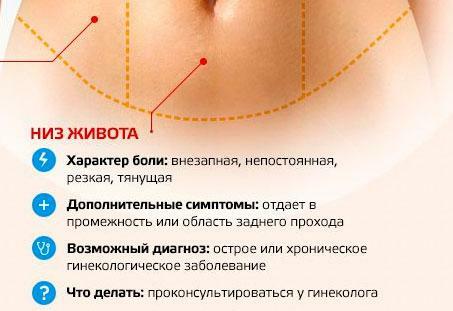
When it is necessary to consult a doctor
Important! To control hormone levels, a woman can take a blood test or undergo a diagnostic scraping procedure. The instrumental method of diagnosis is recommended for women who have pain during ovulation accompanied by bloody discharge or bleeding.
Diseases of the uterus
The uterus is a muscular organ consisting of smooth fibers and located in the anterior part of the small pelvis. At the front, the uterus is covered by the bladder, and behind it is supported by the intestine - which is why pregnant women often experience difficulties with bowel movements and frequent urge to urinate. The uterus is a hollow organ intended for bearing the fetus and covered from the inside with endometrium( mucous membrane).If a woman has hormonal problems, the pathological growth of epithelial cells begins, and the endometrium begins to expand beyond the mucosal layer.
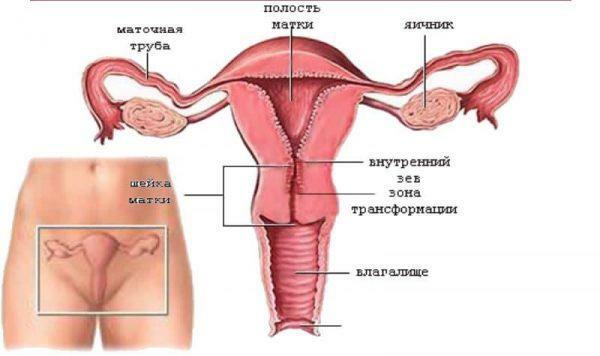
Structure of female genital organs
This pathology is called endometriosis and is the result of endometrial hyperplasia. These diseases are often accompanied by painful sensations in the lower abdomen, which are amplified during ovulation due to the fact that the uterus begins to actively contract. The signs of endometrial pathology can be:
- temperature fluctuations( from normal values to 37.6 °);
- increase in baseline;
- uterine bleeding between menstruation;
- menorrhagia - profuse menstruation, which lasts more than 7 days;
- headaches;
- nausea.
Please note! Because of the constant loss of blood, a woman can develop various forms of anemia, so a general blood test will show a decrease in hemoglobin( for women the norm is 120-140 g / l).
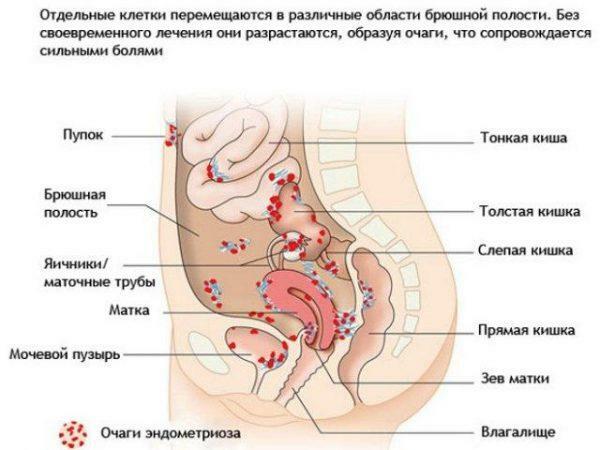
Locations of endometriosis localization
Other uterine diseases that can cause abdominal pain during ovulation include:
- erosive defects of the mucous layer covering the cervix;
- myoma is a benign tumor of the muscular uterine layer( myometrium), which in most cases occurs with hormonal disorders;
- endometritis is an inflammatory process in which the surface shells of the uterus body are involved;
- polyposis - multiple benign uterine formations( polyps).

Symptoms and consequences of uterine fibroids
Important! Strengthening abdominal pain in the ovulatory period can be observed at the initial stages of the malignant process, so consultation of a doctor in such a clinical picture is mandatory.
Treatment of
Treatment of uterine pathologies most often requires the use of surgical methods. Cervical erosion is most often treated with electrocoagulation( electric cautery) or cryodestruction( freezing with liquid nitrogen).In relation to miom, expectant tactics are usually chosen if they are of small size or single flow. The same applies to polyps - if they do not manifest themselves in any way, surgical treatment is usually not prescribed.
Endometrial pathology requires the intake of hormonal drugs from the group of oral contraceptives. If a woman starts bleeding against a background of hyperplasia or endometriosis, her uterine curettage is usually used to stop it( it can be replaced by a more gentle method - vacuum aspiration) followed by antibiotic therapy.
Video - Where does the pain in the lower abdomen of women?
Diseases of the appendages
Abdominal pains during ovulation, with unilateral localization, may indicate inflammatory processes in the appendages - salpingoophoritis. Less common are its isolated forms:
- salpingitis - affection of one or both fallopian tubes;
- oophoritis is an inflammatory process in the ovaries.
These diseases are always accompanied by intense acute pain in the lower and lateral parts of the abdomen. Simultaneously, a woman has fever, fever, chills. A single vomiting can occur. With such symptoms, the patient is recommended hospitalization in a hospital.

Symptoms of salpingitis
Treatment of inflammatory processes in the appendages involves the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics from the penicillin or macrolide group( Azithromycin, Ampicillin, Sumamed, Flemoxin), anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of injections or oral dosage forms( Ibuprofen, "Diclofenac") and funds for symptomatic therapy.
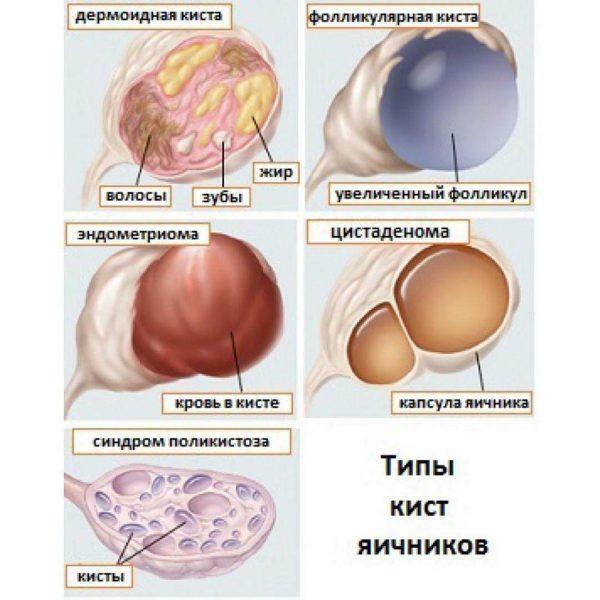
Another possible pathology that can go unnoticed for a long time is cystic ovarian formation. Cysts are pouches, the cavity of which is filled with exudate. If the cyst does not grow, wait-and-see tactics are chosen, since there is a possibility of independent resorption of the formation. If the cyst is inflamed or large, the woman is prescribed laparoscopy or laparotomy - surgical methods of removing cysts through the abdominal wall.
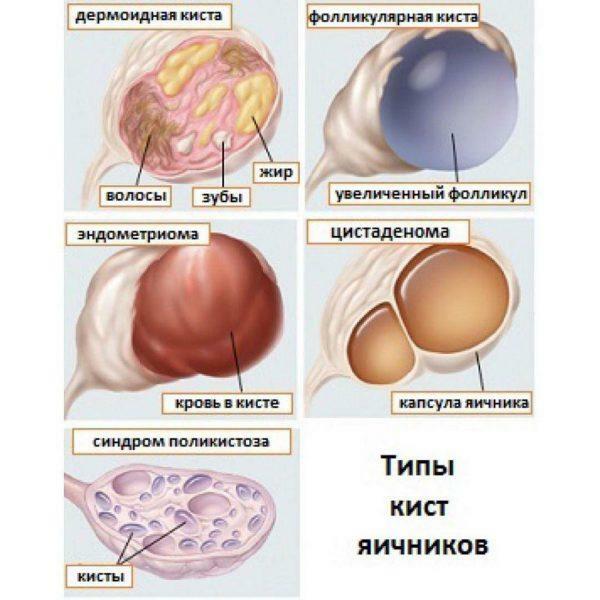
Types of Ovarian Cysts
Other Causes of
In rare cases, the abdomen during ovulation may be sore for reasons unrelated to the functioning of the organs of the reproductive system. These can be intestinal diseases( duodenitis, colitis), pathology of the digestive system or genitourinary diseases. Almost half of women suffer from chronic cystitis, so pain can indicate an exacerbation of the disease, especially if they are accompanied by pain during urination, burning at the beginning and end of bladder emptying, fever and intoxication.
Abdominal pain is sometimes a sign of adhesive process in the pelvic space. The nature of the pain in this case can be very different, but more often than not women complain of strong drawing pains and single stitching sensations.
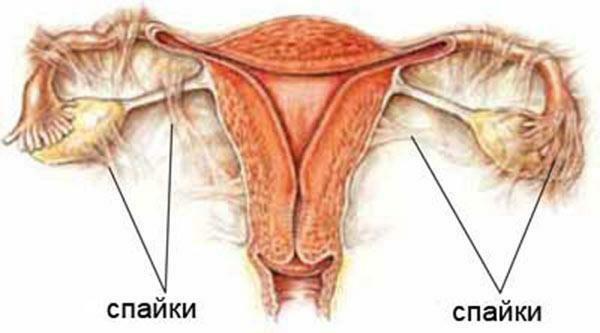
Spikes in the uterus area
Important! In very rare cases, this symptomatology may occur with mastopathy. If the pain in the abdomen is combined with swelling and local painful sensations in the mammary glands, it is recommended to consult a mammologist.
Abdominal pain is the most frequent complaint of women during ovulation. In most cases this symptom is a variant of the physiological norm and does not require special treatment. To reduce the severity of pain, you need to drink more pure water, broths of berries and herbal teas. If there are no signs of inflammation, you can put a hot water bottle on the stomach with warm water or take a bath. At strong pulling sensations reception of spazmolitikov on the basis of a papaverine or drotaverin is supposed. If these measures did not help, and the pain did not go through 1-2 days after ovulation, you should see a doctor.