 In English, the word malformation means the wrong development of something. Physicians under this term mean different pathological deviations, which entail failures in functionality or changes in the structure of any organs.
In English, the word malformation means the wrong development of something. Physicians under this term mean different pathological deviations, which entail failures in functionality or changes in the structure of any organs.
By and large, malformations appear at birth or during the development of a person. But it is possible that they can arise as a result of injuries or as a consequence of serious illnesses.
Contents
- Vascular malformations of the brain
- About the causes in the theory of
- General symptomatology
- Arteriovenous malformation
- Dandy Walker's disease
- Arnold Chiari malformation
- General approach to treatment
- What is dangerous for malformations?
- Prophylaxis of complications
Vascular malformations of the brain
There are several types of malformations, and one of them relates to the pathology of cerebral vessels. This type of disease is characterized by changes in arteries, veins and their communication. Also, as in other cases, pathological changes manifest themselves as a chronic disorder and appear as a result of certain diseases.
The main feature of malformations of cerebral vessels is that they are directly related to the central nervous system, and appear either in the brain or in the spinal cord.
Outwardly, the disease looks like knots or weaves of a spherical shape and different sizes that make it difficult for blood to flow through the vessels.
According to medical statistics, such an anomaly in the chronic form is manifested in 15-19 newborns per 1000 people.
About the causes in the theory of
The exact causes of the appearance of pathology in infants have not yet been revealed, but there is one theory-assumption.
The final formation of the entire structure of the vessels of the fetal brain occurs by the 20th week of its development in the womb. Hence, the vascular network at this time is in an unstable form and prone to deformation, especially under the influence of negative factors.
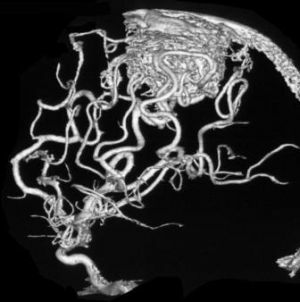
Vascular malformation on MRI
For example, the cause of this can be a serious illness of the mother:
- infectious disease;
- birth trauma of a pregnant mother;
- sickle-cell anemia.
And also in the list of provoking factors it is possible to include medicines or narcotic drugs, which the mother took during the bearing of the child.
There are no exact causes that directly affect the development of the disease to date.
General symptomatology
Often patients live with vascular malformation for many years and are unaware of the presence of this disease. The disease has a property not to manifest for a long time. It is during this period that the hiding disease progresses, increasing its size. And in the case of "ripening", there is pressure on the GM( the brain), which leads to the manifestation of symptoms.
General symptoms of vascular malformation:
- apathic condition and depressiveness;
- lethargy and rapid exhaustion;
- failure of human coordination;
- motor impairment;
- increased pressure of the intracranial box with a pulsation in the head;
- visual impairment;
- seizures;
- noises in the head;
- auditory or olfactory hallucinations;
- headaches and dizziness.
If the disease appeared at birth, then it begins to manifest itself at the age of 12-14 years, when the child grows physically. In any other cases, it can make itself felt even in middle age( 47-65 years).There are several types of malformations, on which the symptomatology directly depends.
Arteriovenous malformation
This is a pathology that affects the connection of veins and arteries. The essence of the violation is that when the veins and arteries are connected, capillaries are absent. It is directly related to the central nervous system, but its manifestation is possible even in remote areas.
For example, there are often cases where a disorder can manifest itself in a heart disease, between the bulb of the aorta and the pulmonary trunk.
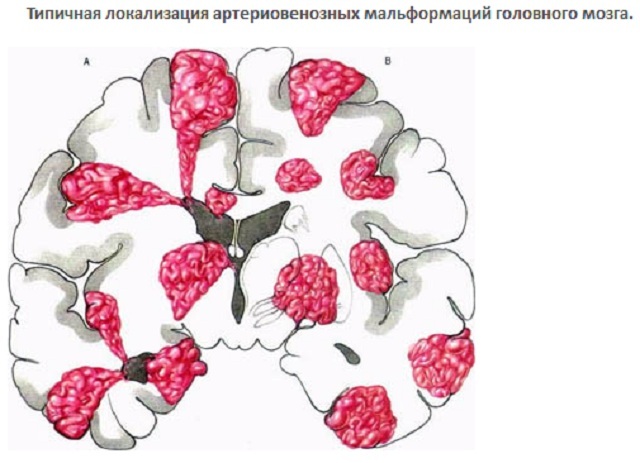
The causes of AVM can serve as:
- damage to the vessels of the head as a result of craniocereberal trauma;
- chronic structural disorders of the vascular system;
- deposition of fatty elements on the walls of blood vessels.
AVM is considered the most serious type of malformation of the vascular system and has symptoms by which it can be determined:
- nausea and frequent vomiting;
- loss of consciousness;
- hemorrhage inside the GM;
- sharp headaches;
- partial and generalized convulsions;
- partial loss of vision and hearing;
- olfactory hallucinations;
- speech function malfunction.
Completely eliminate the disease of this kind can only be at the initial stages of its development. After diagnosis, knowing all the subtleties of the existing pathology, the attending physician should prescribe a method of treatment. In most cases, three types of operations are performed:
- surgery;
- Radiosurgery;
- embolization.
Dandy Walker Disease
Dandy Walker's anomaly is characterized by cerebellar hypertrophy or a cerebral cortex. The anomaly is caused mainly by genetics, but there are cases when it is manifested due to viral infections, exposure to alcohol or diabetes of a pregnant woman.
The development of the syndrome may be manifested by the following symptoms: 
- nausea;
- aggression;
- appearance of seizures;
- vision disorder;
- traffic coordination malfunctions;
- violation of muscle movement consistency;
- movements of the eye( nystagmus).
The disease can be cured only by surgery. It consists of an artificial ventriculoperitoneal bypass to reduce the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid in the brain.
But at the same time there is a risk that some defects that have appeared can remain for life.
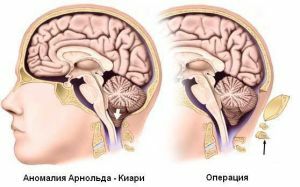
Arnold Chiari malformation
The essence of the anomaly lies in the fact that the tonsils of the cerebellum of the GM fall into the opening of the occipital region and at the same time compresses the medulla oblongata.
Until 2005, it was believed that this malformation was inherent. But after appropriate studies it was found that Chiari syndrome occurs as a result of the tension of the end thread, which leads to tension of the spinal cord.
And also there is a version that the cerebellum is shifted to the upper part of the spinal canal, thereby disrupting the stable circulation of the CSF and blocking the signals coming to other organs.
This disease is characterized by symptoms of cerebellum and oblong lesions of the GM:
- headache with the manifestation of cold symptoms;
- occipital pain descending to the shoulder girdle;
- loss of balance;
- decreased motor hand activity;
- numbness of the upper limbs.
 As with any such disease, treatment will be performed only after examination of the patient. It depends on the degree of its manifestation.
As with any such disease, treatment will be performed only after examination of the patient. It depends on the degree of its manifestation.
Physicians can prescribe conservative drug treatment, which will be aimed at eliminating primary symptoms. But, with the progression of the disease, the problem is solved by surgical intervention.
Arnold Chiari malformation II degree is characterized by large dimensions of the posterior part of the skull, compared to the anterior. Due to the enlarged dimensions, a large occipital opening is also enlarged, into which the lower part of the cerebellum flows. This leads to their counterpressure with the spinal cord.
This malformation can be determined using MRI, CT( neck area, neck vertebrae) and symptoms:
- extraneous tinnitus;
- dizziness and exhaustion;
- increased pressure inside the head;
- periodic nystagmus.
Surgical operation is aimed at removing the interfering part of the bone in the posterior region of the skull. There is more room for the brain, which reduces pressure. Such an operation is considered serious, but not too difficult. It lasts about 2 hours.
General approach to treatment of
As already mentioned above, the main treatment base for this disease is three types of operations: microsurgical, radiosurgical and endovascular.
The expediency of applying this or that type of intervention is determined by several factors:
- the location of the malformation;
- dimensions of the pathology and external shape;
- presence of hemorrhage of the GM in the history of disease;
- type of pathology;
- laboratory tests of the patient.
More about each method:
- The microsurgical operation is a complete excision of pathology, but is one of the most dangerous ways because of possible internal bleeding. If the disease touches the arteries and veins, then trepanation of the skull is performed. In parallel with the vascular node, intracranial hematoma is also removed. Such operations are performed under high-level anesthesia.
- Radiosurgery - this operation is only possible if the AVM in diameter does not exceed 30 mm. It is customary to perform the detected and residual changes for removal with newly
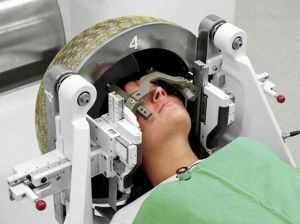 .Therapeutic rays are fed gradually, with retention. As a result of getting the optimal number of rays, the vessels "become infected" and the movement of blood along them stops. The treatment process can be carried out in parts, stretching for 1-3 years.
.Therapeutic rays are fed gradually, with retention. As a result of getting the optimal number of rays, the vessels "become infected" and the movement of blood along them stops. The treatment process can be carried out in parts, stretching for 1-3 years. - Embolisation of - is performed before a surgical operation, for the prevention of hemorrhage. Through the hip puncture, a thin catheter is introduced, directed to the vessels that supply the GM with blood and are supplied to the pathology itself. The tube is fed with an embolizing material and blocks the affected areas of the blood vessels and stops the flow of blood.
In some situations, a conservative method with pharmacy products is included in the course of treatment.
What is the danger of malformation?
It should be noted that vascular malformation is fraught with complications. Among them, there are three that are dangerous for the life of the patient:
- Oxygen starvation of GM .Because of it, brain cells die( full or partial).First, this leads to a cerebral infarction, which is manifested by loss of memory, vision, coordination of movement. In the absence of treatment, a person falls into a coma or a sopor.
- Thinning of vessels .As a result, the vessel may break with a hemorrhage as a result. Blood enters the cavity of the skull, which is characterized by a violation of the blood circulation of the brain. There is a hemorrhagic stroke.
- Paralysis of the .When squeezing the spinal cord, there is a risk of developing paralysis.
Prevention of complications
Preventive measures here are aimed at preventing the development of complications. This can be done as follows:
- not be subjected to psycho-emotional influences, which provoke stress;

- to abandon the physical activities associated with lifting weights;
- to control blood pressure and not to give it to go up, to reduce blood pressure it is allowed to use pharmaceutical preparations for hypertensive patients;
- eat foods high in sodium;
- to give up harmful habits and drinking alcoholic beverages.
For more detailed recommendations, contact your doctor.

