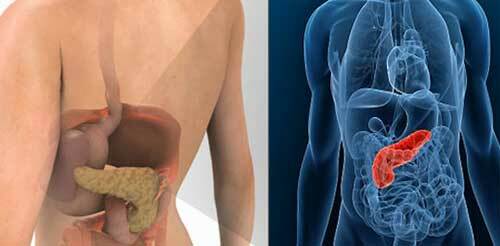
Ascites( hydrocephalus) can occur as a consequence of many diseases, but in most cases it is one of the complications of liver cirrhosis. This condition always indicates serious violations in the work of internal organs or whole systems and poses a danger to human health and life.
What is it?
Ascites of the abdominal cavity - this is a symptomatic phenomenon in which an accumulation of fluid( transudate) is observed in the abdominal cavity. It is a mistake to consider him a separate disease - this is just a manifestation of certain health problems.
The abdominal cavity contains the spleen, gall bladder, part of the intestine, stomach, liver. It is closed and delimited by the peritoneum - a shell consisting of two layers - the inner one, adjacent to the named organs, and the outer one, attached to the walls of the abdomen.
The task of the peritoneum is to fix the organs in it and to participate in the regulation of metabolism. It is abundantly supplied with blood vessels that ensure the metabolism through blood and lymph.
A healthy person between two layers of the peritoneum has a certain volume of fluid that does not accumulate, but is constantly absorbed into the small lymph vessels, freeing up space for the admission of a new one.
The transudate in the peritoneum begins to accumulate if the rate of its formation is increased or its absorption into lymph is slowed. Progression of the main pathology gradually increases its volume and it begins to press on internal organs, ascites develops, and the course of the underlying disease is aggravated.
Possible causes of abdominal ascites:
- cirrhosis;
- tuberculosis;
- peritonitis;
- portal portal compression;
- disease of Budd Chiari;
- some childhood illnesses;
- bleeding;
- pancreatitis;
- malignant liver tumor;
- anasarca;
- pregnancy and pathology of intrauterine development;
- heart failure;
- endometriosis.
The risk group includes people with alcohol and drug dependence, with a diagnosis of chronic hepatitis, residents of regions with a high incidence of this pathology. Impact on obesity, increased cholesterol, diabetes mellitus type II can affect the accumulation of transudate.
Contents
- 1 Ascites of the abdominal cavity for oncology, prognosis
- 2 Symptoms of ascites, photos - clinical manifestations
- 3 Diagnosis
- 4 Treatment of ascites of the abdominal cavity, drugs
- 4.1 What is the prognosis?
Ascites of the abdominal cavity with oncology, prognosis
In cancer, malignant cells proliferate uncontrollably. If they get liver during metastasis, it provokes squeezing of its sinusoids( spaces between groups of cells filled with blood) and increasing pressure in the portal vein and the vessels closest to it.
As a result, the outflow of blood and lymph from the peritoneum slows down and ascites the abdominal cavity in oncology. How many live in this state? Only half of patients with dropsy who received timely treatment of her, remains to live for two years. High mortality is due to the rapid development of complications of dropsy, among them:
- hydrothorax;
- respiratory failure;
- intestinal obstruction;
- formation and pinched umbilical hernia;
- peritonitis;
- hepatorenal syndrome;
- prolapse of the rectum.
More often than other cancers, the cause of ascites is:
- pancreatic tumor;
- mesothelioma;
- ovarian cancer;
- abdominal carcinomatosis;
- Meigs syndrome.
The prognosis for development of oncological ascites worsens in old age, with a significant number of metastases and renal failure.
Symptoms of ascites, photos - clinical manifestations of
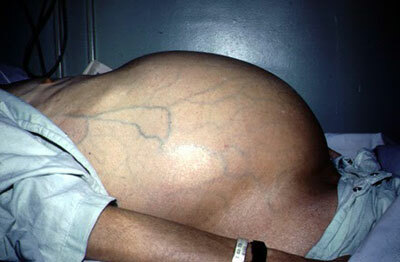
photos of ascites of abdominal cavity
The dropsy can develop gradually, for 1-3 months and even six months or more, or spontaneously, for example, with thrombosis of the portal vein. The first signs of ascites of the abdominal cavity appear after the accumulation of 1000 ml of fluid and more, among them:
- Pain and feeling of raspiraniya in the abdomen;
- Flatulence and burp;
- Increased body weight and abdominal volume;
- Heartburn;
- Puffiness of the legs, in men sometimes - scrotum;
- Shortness of breath and tachycardia when walking;
- Difficulty trying to make a torso bend.
If a person is standing, then the stomach takes a spherical shape, and in the horizontal position it spreads out. The skin will eventually become covered with light striae( stretch marks), and the navel will bulge outward as it accumulates in the abdominal cavity.
With increased pressure in the portal vein, the subcutaneous veins widen on the sides and in front of the abdomen, becoming noticeable, this symptom being called the "jellyfish head".
Such symptoms of abdominal ascites as jaundice, nausea and vomiting occur with portal hypertension due to blockade of the subhepatic vessels.
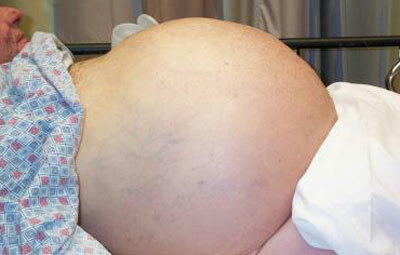
With tuberculosis, a person quickly loses weight, feels headaches, severe weakness, the pulse becomes frequent. The abdomen is enlarged very quickly with a disturbed outflow of lymph, and slowly, if the cause of ascites was protein deficiency. In the latter case, swellings are expressed, which also occur with cardiac, hepatic and renal insufficiency.
Increased body temperature is not a direct sign of ascites and occurs only in certain diseases that cause dropsy:
- liver cirrhosis;
- tumors;
- peritonitis;
- pancreatitis.
If ascites develops due to myxedema, then the temperature, on the contrary, falls below the norm - up to 35 ° C.This is due to the inadequate production of thyroid hormones, which affect the intensity of metabolism and the release of heat from the body.
Diagnostics
At the initial examination, the doctor conducts percussion - tapping on the stomach and analyzing the resulting sounds. In ascites, the sound over the liquid is dulled, and light strokes along the abdominal wall form waves on one side, which can be felt by placing the palm on the other side of the peritoneum( fluctuation).
In the diagnosis of ascites of the abdominal cavity ultrasound and computer tomography are used - these methods determine the volume of accumulated fluid and the main cause of development of dropsy.
List of tests for ascites:
- Blood - general and biochemical - can show an increase in bilirubin and nitrogenous decomposition products, hypoproteinemia, high ESR;
- Urine - common - reveals the presence of protein, erythrocytes, increasing urine density depending on the cause of dropsy;
- Fluid obtained by abdominal puncture - it is clear, whitish or with a slight admixture of blood, its reaction is never acidic - it is neutral or slightly alkaline;
- Rivolt test - helps to distinguish between the transudate and the inflammatory discharge - exudate with the help of a qualitative chemical reaction to the protein.
The liquid taken from the abdominal cavity is also examined for the presence of pathogenic microorganisms and cancer cells.
Treatment of ascites of the abdominal cavity, preparations
With ascites of the abdominal cavity, the treatment consists in eliminating the pathology that caused the dropsy. The general measures of therapy are:
- A diet with a limited salt content( not more than 2 g per day) or complete absence of it, with cirrhosis - a decrease in the fluid intake;
- Taking medication depending on the disease and in all cases - diuretics - Veroshpirona, Furosemida, - in combination with potassium preparations( Asparcum, potassium orotate);
- Supervision of weight loss - with successful treatment, the loss is 500 grams per day.
Tactics of treatment for various diseases:
- For heart failure, diuretics, vasodilators, and ACE inhibitors are indicated. In this case, diet No. 10 or 10a is prescribed with decreasing water and salt. Apply cardiac glycosides( Digoxin, Strophantine) and other drugs to stimulate the contractile activity of the myocardium.
- Strict bed rest and diet number 7( up to the exclusion of salt) are indicated in kidney pathologies accompanied by nephrotic syndrome - with amyloidosis, glomerulonephritis).In this case, the amount of liquid drunk per day should not exceed the amount of urine isolated by more than 300 ml.
- Pediatric infants due to latent blood loss are treated by blood and plasma transfusion. Exudative enteropathy also involves the use of glucocorticosteroid agents and diuretics.
- In case of disorders in protein metabolism, diuretics are indicated, a menu with the optimal protein content, and the inhibition of ACE inhibitors, albumin transfusions, helps to reduce the loss of protein in the urine.
If the volume of the transudate is significant, the peritoneal cavity is drained and slowed, in order to avoid the development of collapse, the accumulation of fluid from it. The procedure is called laparocentesis and is performed under local anesthesia.
Surgical intervention of is indicated in ascites due to portal hypertension. Two types of operations are common:
- Intrahepatic transjugular bypass, in which the portal and hepatic veins are artificially communicated;
- The operation of the Kalba is the excision of the peritoneum and muscles in the lumbar region, as a result of which the transudate begins to absorb the subcutaneous fatty tissue. This procedure is effective in 1/3 of the cases, and the result is kept no more than six months.
When liver cirrhosis and other severe liver diseases are started, liver transplant surgery is performed.
What is the prognosis?
The prognosis for ascites directly depends on the cause of fluid accumulation and the timeliness and effectiveness of treatment. In half the cases, in the absence of the effect of diuretics, there is a fatal outcome. Adverse factors also include:
- elderly age - 60 years or more;
- hypotension;
- diabetes;
- liver cancer;
- bacterial peritonitis;
- albumin level in the blood is less than 30 g / l;
- decreased glomerular filtration of the kidneys.
The danger of ascites is also that as a symptom, a consequence of the underlying disease, it, in turn, aggravates its course.