According to historical data, Quincke's edema was first described in 1576 by Marcello Donati. However, the term angioedema was introduced in 1882 by Henryk Kvinke, whose name this condition still bears.
However, it was only in 1964 that chemicals were discovered that triggered the development of a pathological reaction. Since then, there has been an opportunity for targeted pathogenetic treatment.
Contents
- 1 Quincke Edema - what is it?
- 2 Symptoms of Quincke edema, photo
- 3 Quincke edema in children - features
- 4 First aid for edema Quincke
- 5 Treatment for edema of Quincke, preparations
- 6 Complications of
- 7 Reasons for edema Quincke - frequent allergens
- 8 Prevention
Quincke Edema - what is it?
Quincke Edema is one of the most difficult problems of allergology - this is due to the high prevalence of this pathology. So, its frequency in combination with urticaria is 49% among allergic reactions, and isolated angioedema is observed in 11% of cases.
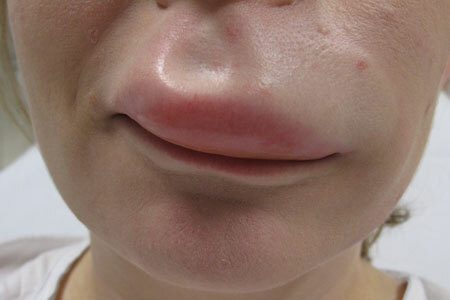
Acute Quincke photo 1
And the greatest prevalence is observed in persons of working age. It is worth noting that in 2% of cases, angioedema may be hereditary, associated with a specific pathological response of complement( a specific link of the immune system that protects a person normally from pathogenic microorganisms).
Quincke Edema is a condition in which swelling of the skin and subcutaneous fat is observed. At the same time it can be combined with mucosal edema. Therefore, the respiratory, urinary, digestive and nervous systems can be affected, which leads to the appearance of the corresponding symptomatology( see photo).
For Quincke's edema, some features of the symptoms are characteristic:
- Sudden appearance( sometimes it's not so easy to identify the causative agent);
- Development of puffiness in the lower layers of the skin layer and fat;
- Prevalence of soreness with minimal itching;
- Frequent involvement in the pathological process of mucous membranes;
- Slow puffiness resolution - within 72 hours, in comparison with blisters with hives, which quickly pass.
Clinical signs of Quincke's edema appear after contact with allergens, various substances may act in their roles( see the list at the bottom of the article ).
However, regardless of the causative factor, allergic edema and urticaria develop due to increased histamine formation in the body. This is confirmed by the following facts:
- The appearance of characteristic skin reactions with the administration of histamine;
- Proven release of granules from mast cells( macrophages);
- Increased release of histamine in some forms of urticaria;
- The clinically proven effectiveness of antihistamines.
Symptoms of Quincke edema, photo
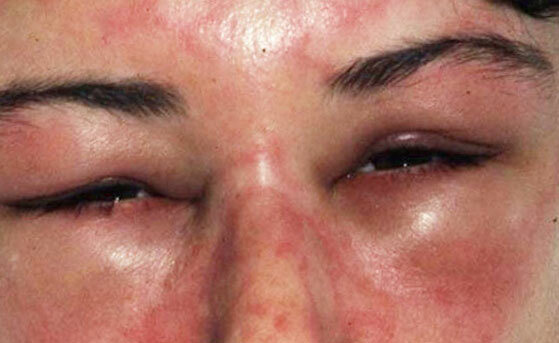
puffiness and skin manifestations
Quinck allergic edema can be of 2 main types:
- Acute - suddenly appears when the causative factors get into the body;
- Acutely relapsing when for at least 3 to 6 months there is at least 3 clinical relapses.
Symptoms of edema Quine have the following features:
- The asymmetry of the lesion is most often noted;
- Color-pale pink or not different from skin color;
- Rare identification of itching, more often there is pain and burning sensation;
- To suppress clinical manifestations, it takes more than 24 hours;
- Favorite tissues are tissues rich in water - the periorbital zone, the scalp, tongue, pharynx, brushes, genitals, feet( back surface).However, swelling can occur anywhere;
- Skin manifestations can be combined with swelling of the mucous membranes of any organ and joints.
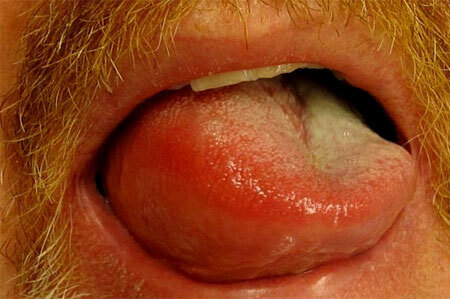
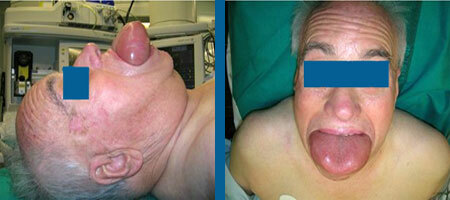
Acute Quincke, photo, language - very dangerous condition
Symptoms in adults, with Quinck's swelling in the larynx, as a variant of angioedema, threaten life. Death comes because of suffocation.
With edema of the larynx, characteristic first signs are cough and hoarse voice, as it develops, noisy breathing and symptoms of suffocation are manifested.
With edema of the stomach and intestinal mucosa, characteristic symptoms appear - nausea, vomiting, abdominal pains of a spastic nature.
In some cases, rare forms of Quincke edema may be noted, their symptoms:
1) Recurrent, associated with hypereosinophilia. In this state, the number of eosinophils is several times higher than the norm for a given age period, and leukocytes and the level of antibodies directed against the endothelium( the inner shell of the vessels) are also increased.
Clinically determined elevated temperature to 40 ° C and skin allergic rash.
2) Hereditary form of the Quincke edema, which is transmitted by an autosomal dominant type. Occasionally, there is edema of different locations. This disease is characterized by genetic deficiency of the protein, which inhibits the activation of complement.
For the first time the disease manifests itself before the age of 20 years. Before this period, clinical symptoms are absent. The main danger of the hereditary form is the increased risk of death, which is observed in 35% of patients. Therefore, all relatives are subject to inspection.
3) Acquired form of angioedema occurs more often in elderly patients and is associated with lymphoproliferative diseases, systemic lupus erythematosus and viral hepatitis.
Hereditary forms of allergies can be of three main types:
- The first type is observed in 85% of cases. The causative mutation arises spontaneously, so the genotype usually remains normal with relatives;
- The second type is less common - in 15% of cases. It is associated with a high concentration of complement activators due to the fact that it is not consumed;
- The third type is observed only in women, tk.the disease is linked to the X chromosome. This form has been described recently.
For hereditary form of angioedema, the following features are characteristic:
- A frequent association with a chronic infection;
- Recurrent occurrence of edema;
- Frequent abdominal pain, combined with nausea and vomiting( they can cause unreasonable surgical interventions);
- Reduced content of C4-fraction of complement( an important diagnostic feature, since at its normal values the probability of hereditary form is minimal);
- Absence of itching;
- Frequent development of laryngeal edema with involvement in edematic syndrome and language;
- Hives are rare;
- Exacerbations are repeated at different intervals. In some patients - once a week, in others - once a year.
Quincke edema in children - features of
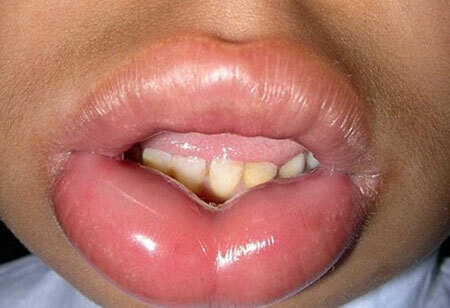
signs of edema in children, photo
Symptoms of Quincke in children are somewhat different from adults - this requires utmost care from parents. The appearance of any suspicious symptoms should be an occasion for consultation with a doctor.
Features of edema in childhood are:
- Possibility of manifestation in any part of the body, not just hydrophilic( containing a large amount of water);
- Frequent appearance of rashes on the skin according to the type of urticaria;
- Excited state;
- Increased temperature, loss of consciousness;
- Abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting.
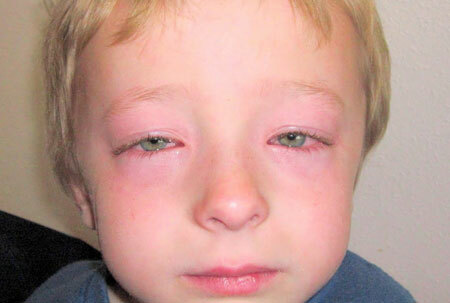
Quincke's swelling in the child is often accompanied by a lesion of the larynx. This is fraught with deadly choking if not helped in time.
First aid for swelling of Quincke
First aid for swelling of Quincke includes the following activities:
- Mandatory emergency call with a description of the situation;
- Stop the supply of an allergen to the body;
- When an insect bites, an ice pack is placed on this place, and a pressure bandage is placed above the site of the bite, preventing further ingress of the allergen into the bloodstream;
- Gastric lavage and administration of activated charcoal if edema is associated with food;
- Provide oxygen to the room( open the window);
- Give to take any antihistamine. However, in the presence of edema of the mucosa of the digestive tract, its absorption is disturbed, so intravenous or intramuscular injection is required( this is done by ambulance doctors).
If Quincke's swelling in a person repeats, then he already has specially prepared syringes with adrenaline and a hormonal drug. They are manufactured by the pharmaceutical industry.
Quincke edema treatment,
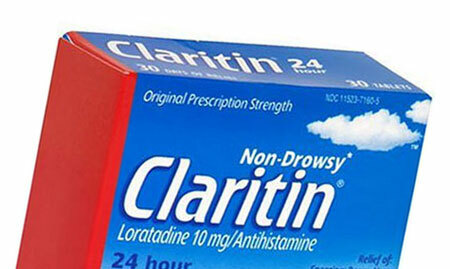
preparations The second-generation antihistamines take the top line in the treatment of Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock. Their effectiveness is due to the suppression of histamine synthesis and its action with receptors. An additional effect is anti-inflammatory.
Representatives of the first generation of antihistamines are:
- Dimedrol;
- Tavegil;
- Pipolphen;
- Suprastin;
- Fenistil;
- Diazoline;
- Fenkarol.
However, the second-generation preparations for the treatment of angioedema are preferred, it includes:
- Claritin;
- Zirtek;
- Telfast;
- Erius.
Simultaneously it is recommended to create a hypoallergenic way of life:
- If possible, remove as much as possible from the premises extra things that accumulate dust( carpets, soft toys and others);
- Use of special anti-allergic covers for pillows, mattresses and blankets. Synthetic covers in insufficient volume protect against ticks parasitizing in down;
- Bed linen should be washed at a temperature above 60 ° C, so that all mites that can remain in it are killed;
- If there are carpets in the house, they should be treated with special acaricides( benzyl benzoate, methylpyrimiphos);
- Heavy curtains should be replaced with cotton or linen, washed in hot water;
- Wipe the furniture with a damp cloth;
- Furniture with upholstery should be vacuumed 2 times a week;
- Do not over-humidify the air;this creates good conditions for the life of ticks;
- Detergent vacuum cleaner protects against the smallest particles that can cause allergies;
- Do not allow a child to take fur toys on the bed;
- Fur toys should be washed or frozen in the freezer;
- Abandon pets and birds;
- Remember that fungi that lead to mold can multiply in flower pots;
- Ventilate the room every day;
- Books, underwear and clothing should be stored in closed cabinets;
- Check for damp spots on ceilings and corners.
Symptoms and treatment of Acute Quincke directly depend on nutrition - therefore a hypoallergenic diet is recommended. Its main principles are:
- Complete exclusion of highly allergenic products( coffee, chocolate, eggs, cocoa, fruits, vegetables and berries, having orange and red coloration);
- Complete elimination of allergens that cause angioedema;
- Adequate replacement of excluded products to meet human needs for energy and nutrients;
- Phased expansion of the diet with the introduction of prohibited products in small doses and an assessment of individual tolerability;
- Acute and extractive substances - broths, canned food, smoked products, pickles, etc.;
- Prohibited foods containing food additives( marmalade, pastille, marshmallows, cakes, etc.);
- Salt, flour products and butter are limited;
- Fruits and berries of light color are allowed;
- Rice, buckwheat, pearl barley is allowed;
- Dairy products are used;
- You can eat turkey meat and rabbits;
- Vegetable oils are allowed;
- Food should be steamed or boiled;
- Cereals and potatoes should be soaked for 18 hours before cooking;
- The first water when cooking meat should be drained.
Complications of
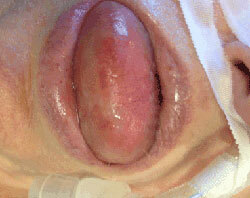
The most dangerous complication of Quincke's edema is the laryngeal edema that leads to asphyxia. As a result, acute respiratory failure can result in death if treatment is not performed on time. Other complications of angioedema are:
- Acute abdominal syndrome, simulating the surgical pathology of the abdominal cavity;
- Acute allergic cystitis leading to acute urinary retention;
- Mineral syndrome with swelling of the inner ear mucosa( this is a manifestation of dizziness and noise in the ears);
- Combination of edema with hives.
Causes of Quincke Edema - frequent allergens
Among the foods most dangerous are: fish, egg, milk, chicken, beef, apples, nuts, pork, honey, carrots, stone stone
citrus fruits, melon, smoked foods, various food additives and soy products.
Drugs can also be powerful allergens. In this regard, the greatest danger is represented by:
- penicillins from the group of beta-lactams;
- cephalosporins;
- non-steroids, especially aspirin;
- B-vitamins;
- angiotensin enzyme blockers;
- retungencontrast preparations;
- insulin.
The venom of bees, wasps and hornets also has strong allergenic properties. With him, the strength is comparable and some infections:
- Hepatitis C and B, HIV infection;
- Diseases associated with the Epstein-Barr virus and Coxsackie;
- Herpetic infection;
- Helicobacter pylori diseases;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- Dysbacteriosis of the intestine;
- Chronic bacterial and fungal conditions.
Some autoimmune diseases and parasitic infestations can also become Quincke edema provocateurs:
- Sjogren's syndrome, lupus erythematosus, thyroiditis;
- Rheumatoid arthritis;
- Giardiasis;
- Trichomoniasis, amebiasis;
- Malaria and others.
Among the physical factors there are also provokers of allergic reactions:
- Increased solar exposure;
- Heat or cold;
- Vibration effects.
Prevention
The only preventative measure is to exclude contact with a possible allergen. Therefore, a thorough examination with an allergist is required to determine the causative factor.
These patients should be careful in their diet and lifestyle in general.



