Thanks to the modern vaccination against many diseases, we almost forgot about measles, rubella, parotitis. Now young parents learn about some ailments from booklets or the Internet. About measles are remembered only when somewhere accidentally there is an epidemic outbreak of the disease. Experts believe that vaccination is the main method of preventing this serious pathology.
Contents
- 1 Measles: Danger to life
- 2 Immune prophylaxis: vital necessity
- 3 Types of immune preparations: monovaccine, a comprehensive vaccine against measles, rubella, mumps
- 3.1 Comparative characteristics of domestic and imported drugs, including Indian
- 4 Childhood vaccination
- 4.1 Stages of formation of specific immunity, including revaccination
- 4.2 Adverse reactions, including rash, temperature increase
- 4.3 Complications, at thatnumber of vaccine-associated
- 4.3.1 Dr Komarowski on measles vaccination: video
- 5 Active immunization of adults
- 5.1 Formation of strenuous immunity
- 5.2 Preparatory actions before grafting
- 5.3 Complications in the absence of strenuous immunity
- 6 Measles vaccination and pregnancy
- 6.1 Pregnancy andInoculations: video
- 7 Contraindications to vaccination: allergy, oncology, exhaustion
- 8 Precautions
- 8.1 How to protect yourself and yourMeasles from measles: video
Measles: life threatening
It is established that measles is an acute infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract, which possesses not only the catarrhal symptoms of .In parallel, specific skin and mucous membrane eruptions appear.
Scientists believe that if every country was vaccinated against measles in a timely manner, then this disease was forgotten forever after 10 years. However, due to some illiteracy and religious prejudices of people, for reasons of low funding in underdeveloped countries, this can only be dreamed of.
Measles is a terrible disease, not a banal infection, which initially occurs without any special signs, until the incubation period passes to the next stage.
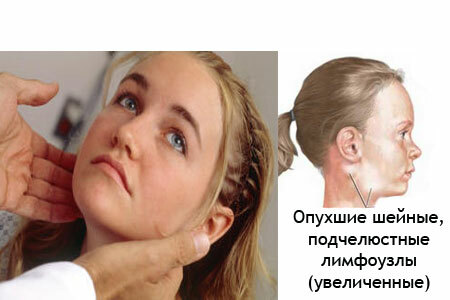
Measles is a dangerous disease that can cause serious complications.
Infection can cause:
- diseases of the nervous system;
- is an inflammation of the brain;
- chronic otitis with development of deafness;
- lung abscess;
- severe pneumonia;
- pleurisy;
- stenosis of the larynx;
- pyelonephritis;
- loss of sight and hearing;
- cardiovascular disease;
- nomu( oncology of the face).
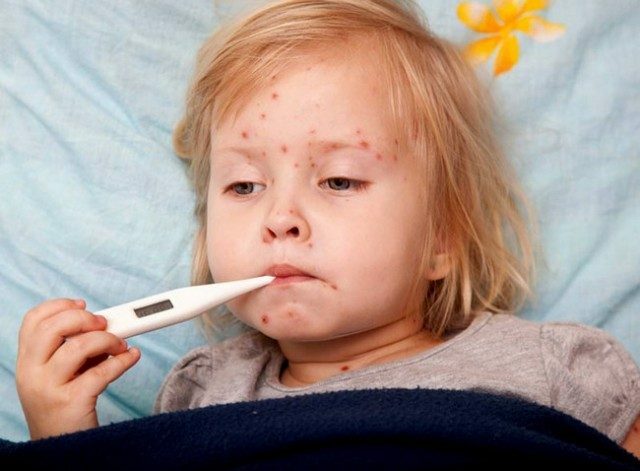
Distinctive feature of the disease are spots - an important diagnostic feature of
The optimal time of year for measles epidemic occurrence is the last weeks of spring and the first days of summer.
According to WHO, every hour from this infection on the planet, 15 people die( this is about 900 thousand per year).The highest mortality rate is observed in the countries of Asia and Africa.
Outbreaks occur during periods, usually every 8-10 years. An exception to this is "imported" infection. The most frequent measles epidemics occur in closed children's educational and preschool institutions, where there are people susceptible to the disease.
Until 1966, when measures of mass prophylaxis and vaccination were developed, in Russia every fourth child died from infection. During this period measles began to be called a childhood plague.
Susceptibility to the virus is very high:
- during the first 24 hours after direct contact with the patient, about 40% of people get infected;
- in a three-day communication with a person infected with measles, sick more than 80%.
All this provided that the surrounding people do not have measles vaccinations! If earlier the infection affected the body of children aged 1 to 5 years, now the disease is very "aged".There are outbreaks of the disease among the adult population. The likelihood of serious complications is very high. All these facts are important arguments in favor of vaccination against measles.

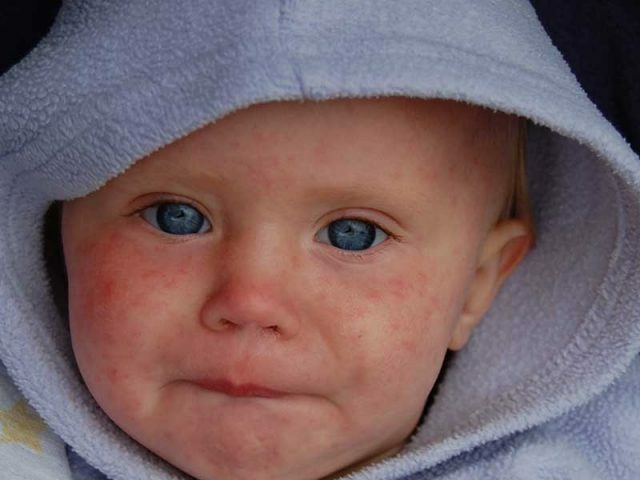
Measles can provoke stenosis of the larynx
Immune prophylaxis: vital necessity
To date, effective methods for treating this ailment have not been developed. Only carrying out of mass measures on immunization can prevent the emergence of foci of infection.
Vaccination against measles is considered to be a planned procedure in our country, accompanied by filling out a special vaccination card for each child.
A complete guarantee to avoid infection does not exist. However, people vaccinated in childhood against measles, tolerate the disease in mild form without subsequent possible complications. This is due to the development of immunity to the virus after vaccination.
If the risk of measles disease in unvaccinated people is 100%, then after vaccination the possibility of infection is reduced to 0.5%. At the same time the disease is atypical, without risk to life.
Vaccination is carried out in several stages.
- After the first vaccination, the risk of infection is reduced to 15%.
- After revaccination, the probability of infection within the next 15-20 years is reduced to zero. That is, the body's defense is almost 100%.
- The third stage of vaccination against measles takes place at adulthood.

Repeated immunization against measles is performed at 5-6 years.
If a person has had measles, then he automatically has immunity to infection. Repeated infection can occur only in 1% of cases for a number of objective reasons, for example, the patient has immunodeficiency. Accordingly, if a person has had measles, vaccination is not done. This should be documented confirmation.
Vaccination against measles begins in early childhood. It is carried out in 2 stages, since not all people have immunity formed immediately after the first vaccination.
In the vaccination calendar of the Russian Federation, which lists all the schedules for the planned implementation of active immunization, vaccination against measles goes in parallel with vaccinations against other infections: rubella, hepatitis and mumps. In this, there is nothing terrible, because the immune system of the child is able to withstand multiple attacks of various viruses. It has been established that the degree of side effects in combining several vaccines does not increase.
Simultaneous vaccination of several infections allows you to combine costs and time for preventive measures. A combined multiphase drug is a minimum of stress in a small patient.
Active immunization is a key element of preventive work, which is aimed at combating infectious diseases. The principle of vaccination is the introduction of live, but weak, viral strains into the body. The vaccine infection is reduced to a minimum and does not pose any threat to the patient and his environment.
After vaccination, the human body produces a weak immune response, although even it is enough to fully protect against infection.
Types of immune preparations: monovaccine, a comprehensive vaccine against measles, rubella, mumps
In our country, several types of vaccines are used from different manufacturers:
- monocomponent( or monovalent):
- single-component measles live lyophilized vaccine of the Russian manufacturer;
- the Ruvax monovaccine, made in France by Aventis Pasteu;
- is a measles one-component vaccine, created at the Serum Institute in India;
- combined( or multivalent):
- diverticum parotitic-measles live, produced by the Russian Federation;
- is an Indian triple-action vaccine against mumps, measles and rubella;
- combined vaccine against rubella, mumps and measles Priori, manufactured by GlaxoSmithKline, Belgium;
- Trimovax triple vaccine produced in France;
- trivaccine MMR from Merk Sharp &Dohme Idea from Holland.
As a rule, in public medical institutions, budget vaccinations are used: one-component vaccines of Russian manufacturers. On a fee basis, a combined vaccination is suggested.
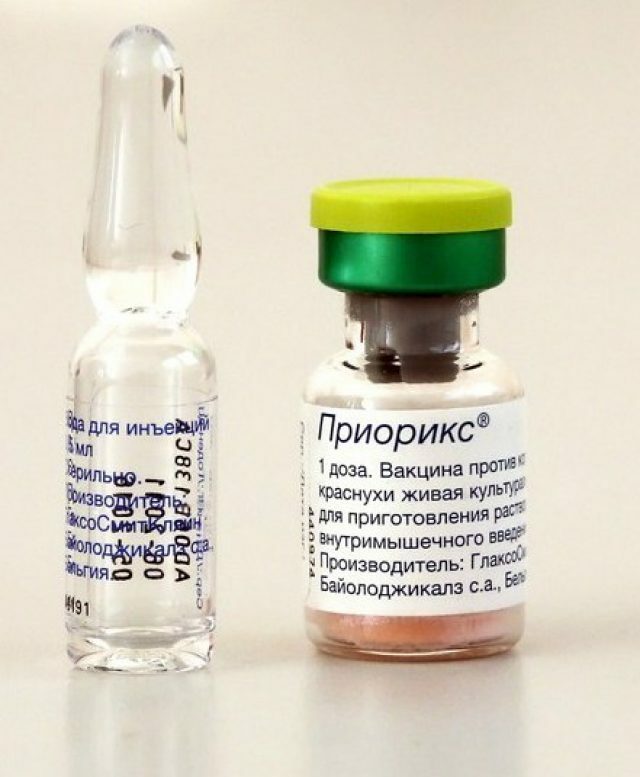
Priority - one of the popular combined vaccines
Comparative characteristics of domestic and imported drugs, including Indian
Before choosing a drug for immunization, it is worth consulting with a medical specialist, because each of the vaccines has its advantages and disadvantages:
- After vaccination with a monovalent complicationare extremely rare.
- Combined vaccine does not require multiple inoculations: one injection is sufficient.
- The efficacy of monovalent and multivalent vaccines is equivalent in controlling the disease. All of them are able to replace each other without negative consequences for patients.
- The shelf life of dry preparations is higher than that of ready-made vaccines.
- The possibility of subsequent complications( reactogenicity) of combined vaccines is not higher than that of single-component vaccines.
- The differences between the numerous types of vaccines are insignificant.
- The site of introduction of measles monovaccine is defined( subcutaneously in the scapula or shoulder area).Imported multicomponent vaccinations can be done under the skin or intramuscularly in any convenient area.
- Simultaneous administration of several monovalent vaccines requires the use of separate syringes. Each injection is done in different parts of the body. Combined vaccines are a single injection.
Immunization of the population against measles occurs according to a certain scheme in accordance with the calendar of vaccinations of the Ministry of Health. Parents can refuse these activities, but such actions are fraught with further consequences for the health of the child.
Vaccination in childhood
Before starting the vaccination, the baby should be examined by a pediatrician to check for the presence or absence of any ailments. For this purpose, a number of studies and analyzes are carried out. Based on the results, the patient's health is assessed.
Children with allergies are usually prescribed a small course of antihistamines on the eve of and after the vaccination.

This is fortunate when your child is healthy
If the child is often sick, one week prior to the vaccination, they are treated with interferon to boost immunity. Finish it 14 days after vaccination.
On the eve of the first vaccination, parents should minimize their child's contact with someone. It is necessary to protect the baby from accidental hypothermia, stress and changes in climatic conditions.
Ill people do not get vaccinated!
Stages of formation of specific immunity, including revaccination
Planned measles vaccination includes 2 stages:
- Inoculation of children aged 8 to 15 months, which depends on individual factors and epidemic conditions in the region of the country.
- Revaccination takes place in five years, on the eve of the child's admission to school. This provides almost 100% protection against measles and helps to carry out a positive immune response to the disease, if at the initial stage this did not happen.
Weak doses of drugs are not always able to help the body from the first time to develop specific antibodies that form the immune system.
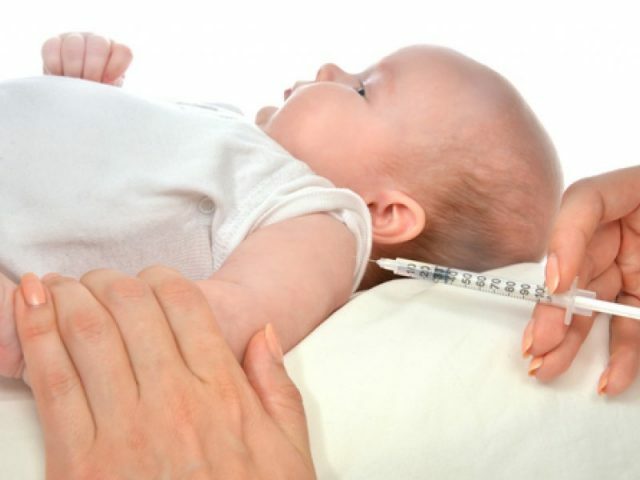
The first measles vaccine is given to babies at the age of one year.
. If the baby has had measles before the vaccination, vaccination is not done. In the event that the mother of the child does not have antibodies to infection, the baby is additionally immunized at the age of 6-8 months.
Sometimes measles vaccine is delayed for a certain period. This may be due to the fact that other planned vaccinations are not completed for various reasons.
As an unscheduled passive immunization, when unvaccinated neonates come in contact with a person who has measles, use:
- immunoglobulin if the child is absent for six months;
- live measles vaccine, provided that the baby is older than 6 months.
All this should be done in the shortest possible time to avoid infection.
Adverse reactions, including rash, increased temperature
After immunization in a small patient, there may be some malaise:
- specific rash at the site of the introduction of the vaccine;
- short sharp increase in body temperature to 40 degrees;
- conjunctivitis;
- febrile seizures;
- runny nose.
The possibility of side effects is no more than 15%.The reaction may occur in the first three days after vaccination.

After the vaccination, the occurrence of a common cold
is possible. Complications, including vaccine-associated
. In cases where after the vaccination there are manifestations of some complications, the following measures are carried out:
- To cope with the temperature jump, use antipyretic and antihistamines that are prescribed by the doctor.
- In case of severe allergic reaction to vaccination, inpatient treatment with corticosteroids is used.
- Antibiotics will cope with bacterial complications.
A child is not considered infectious to others, regardless of the presence and severity of adverse reactions to vaccination.
Very rarely( 1 case per 40 thousand) the consequences of vaccination are:
- thrombocytopenia;
- toxic shock.
Dr. Komarovsky on measles vaccination: video
Active immunization of adults
It should not be considered measles only as a child's disease. For adults, this pathology is much more dangerous than for children. If a person did not get vaccinated against this disease in childhood and did not get sick at an early age, then vaccination is simply necessary.
Formation of strenuous immunity
Depending on the individual characteristics of the human body, immunity to diseases is formed. The protection period for the production of antibodies after vaccination is 10 to 20 years. After this time, additional stimulation of immunity is required. Adolescents from 15 to 17 years in educational institutions carry out massive revaccination.
In adulthood, after reaching the age of 35, another measles vaccine is recommended. This is due to the unfavorable epidemiological situation in Russia due to the large number of migrants from eastern and African countries, where the government at the state level does not control the planned conduct of active immunization of the population.
Preparatory actions before vaccination
A vaccine against measles can be vaccinated free of charge in a community clinic. For this purpose it is enough to make an appointment for an appointment with a doctor, take a blood test for antibodies and get a referral. In addition to the municipal medical institution, special vaccination centers and accredited clinics are involved in this.
Preliminary it is required to pass the test for immunity against measles. The patient's venous blood should be examined. This exercise will help to identify the presence of antibodies and confirm or deny the feasibility of revaccination in adulthood.
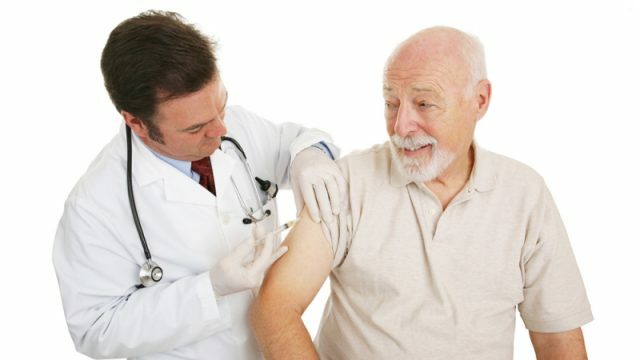
There are no age restrictions for vaccination
If desired, after 10-20 years you can repeat the vaccination against measles, but in this case, the vaccine will not be free. Such a procedure is not prohibited and does not require any additional authorizations. Vaccination at this age is almost safe, if there are no strict contraindications.
Complications in the absence of strenuous immunity
Unconditionally refusing immunization, it is necessary to remember the possibility of dangerous consequences. Against the background of this disease, transferred to adulthood, can develop:
- myocarditis;
- cornea eye damage;
- glomerulonephritis;
- deafness.
Untimely vaccination or lack of vaccination is a guarantee of measles. In old age, measles often leads to death.
When planning long-distance overseas trips to southern countries, additional vaccination must be completed 30 days before departure.
Vaccination against measles and pregnancy
Revaccination is gentle. It is practically safe, since it contains a minimum number of strains. But during pregnancy it is better not to risk the health of a future child.
If it is decided to give birth to a baby, it is better to vaccinate 6 months before the planned pregnancy.
In cases where the pregnancy occurred "unexpectedly" and the vaccination was performed in the early stages, two solutions are considered:
- If the vaccine was given as a combined preparation, it is recommended to terminate the pregnancy. It is established that even a mild rubella virus in 50% of cases leads to fetal damage.
- Monocomponent vaccine is less dangerous, and the probability of developing a pathology in the fetus is no more than 20%.There is an opportunity to leave the child.
If a woman wishes to save pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo an examination for antibodies and ultrasound screening. Probably, there will be a need to pass biochemical blood tests. If abnormalities in embryo development are detected, abortion is suggested.
Sometimes( if urgently needed), doctors recommend immunoglobulin preparations instead of measles.
You can vaccinate immediately after the birth of the baby, even if the mother is breastfeeding. The vaccine virus does not penetrate into the mother's milk and is not transmitted to the newborn.
Pregnancy and Vaccinations: video
Contraindications to vaccination: allergy, oncology, exhaustion
There are a number of contraindications for measles vaccination activities. The following conditions are considered to be the most important among them:
- allergic reactions to vaccine components:
- aminogluclosides;
- antibiotics;
- protein of chicken and quail eggs.
- oncological diseases, including those accompanied by exhaustion;
- severe reaction to primary vaccination;
- primary immunodeficiency.
In addition, there are temporary restrictions in which measles vaccination is transferred to a later date:
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- development of ARVI and ARI;
- receiving prescribed medications;
- recent blood transfusion;
- period of worsening of allergy;
- introduction of immunoglobulin.
Precautions
Some restrictions and precautions must be followed in carrying out vaccination activities in the following period.
Care should be taken to monitor the health after vaccination. If any abnormalities are present for more than 10 days, you should consult your doctor.

After vaccination, it is necessary to monitor the health of your baby
To reduce the negative consequences of vaccination to zero, some safety measures must be observed:
- restrict the use of new dishes so as not to provoke an allergic reaction and / or food poisoning;
- refuse to visit crowded places in the first three days after vaccination;
- use a medical mask when visiting crowded places and using public transport;
- Immediately after vaccination, you can not take a bath and rub the injection site;
- adults are for 1-2 weeks completely refuse to take alcohol, as this can cause an allergic reaction.
It is not necessary to take any medications on your own in the first days after the vaccination, even if it is immunomodulators, for example, Isoprinosine. Although if a person suffers from frequent colds and has low levels of immunity, the doctor can prescribe appropriate therapy. It has been proved that the correct selection of the treatment regimen allows to obtain a quick, high-grade response to vaccination in patients suffering from various pathologies.
How to protect yourself and children from measles: video
Vaccination against measles is vital, as a person becomes protected from a serious ailment. Ubiquitous immunization helps to reduce not only the number of cases of measles, but also to reduce the death rate from this pathology. Vaccination is a real preventive measure aimed at helping people to fight a serious virus.