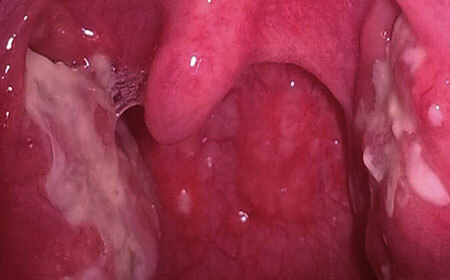
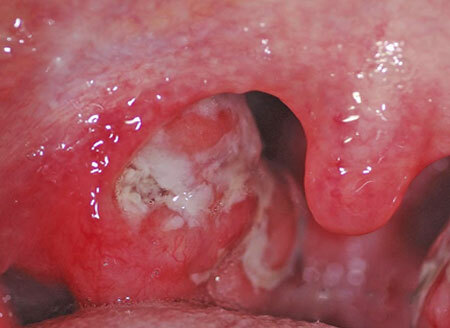
What is it? Laryngitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract in the larynx region. The disease can occur in acute and chronic form.
A sharp form is often accompanied by aphonia - loss of voice, as well as symptoms of intoxication, which leads to poor health and reduced efficiency.
Chronic adult laryngitis, as a rule, does not show significant malaise. But, if it is connected with the profession, its aggravation can also cause disability of people using their voice as an "instrument" of labor, for example, in singers.
Content
- 1 causes of laryngitis
- 1.1 Acute laryngitis
- 1.2 Chronic laryngitis
- 2 Symptoms of acute laryngitis in adults
- 3 Symptoms of chronic laryngitis in adults
- 4 Diagnostics
- 5 Treatment of laryngitis in adults, medications
- 5.1 drugs from laryngitis, antibiotics
- 6 Treatment of laryngitis in adultsat home
- 7 Laryngitis prophylaxis
Causes of laryngitis

The causes of acute and chronic laryngitis are different. In the first case, speech is most often about microorganisms that cause inflammation of the respiratory tract.
In the second case, the role of the causative microbe becomes less significant, becauseThe imbalance of the immune system becomes predominant. He leads to her perverted reaction, which is accompanied by defeat of the larynx.
Acute laryngitis
1) As an independent disease manifested in the pathological multiplication of microflora, which inhabits the laryngeal mucosa in normal and is saprophytic and conditionally pathogenic, i.e.not causing harm in normal conditions.
However, a violation of these conditions leads to the transition of saprophytes into pathological forms capable of causing inflammation. The following factors can disrupt the microbiological balance:
- Throat cooling, for example, when using cold liquid with general overheating, which is often observed when drinking cold drinks in the summer, in the heat, and also by the sudden inhalation of cold air in the winter. In this regard, it is recommended to wear scarves covering the mouth and nose in the cold season;
- Sharp cooling of the whole body after considerable heating, which can occur when it comes from a hot street in a small room with cold air, for example, in a car with the air conditioner turned on;
- Long-term general hypothermia of the body;
- Load on the vocal cords: sharp( screaming) and significant, prolonged in the professional work of singers, teachers, announcers, etc.;
exposure to a large amount of dust, gas, chemical reaction vapors, i.e.occupational hazards; - Smoke inhalation during smoking( both active and passive);
- Regular use of alcohol, especially strong drinks, scorching mucous.
Also, acute inflammation of the larynx can be post-traumatic and occurs as a result of mechanical trauma when a foreign body enters, a thermal or chemical burn of the laryngeal mucosa.
2) The frequent cause of acute laryngitis - the transition of inflammation from other areas of the mucous:
- Nose and throat in infectious diseases of the respiratory tract, such as influenza and other SARS, whooping cough;
In chronic forms of tonsillitis inflammation, tonsillitis, ear - otitis, throat - pharyngitis, sinus sinuses - sinusitis;
3) May accompany common diseases such as:
- gout;
- rheumatism;
- diabetes mellitus;
- of blood disease.
Acute laryngitis most often occurs in the form of catarrhal, that is, superficial inflammation. Less severe form - purulent( phlegmonous), which is dangerous with the development of complications: abscess and edema of the larynx.
These conditions must be diagnosed in time, becausethreaten human life. They need an emergency autopsy surgically.
Chronic laryngitis
Chronic laryngitis develops with a constant, "chronic" effect of factors that irritate the laryngeal mucosa. Depending on the severity and nature of the developing pathological reaction, it is divided into the following forms:
- Catarrhal, associated with superficial inflammation of the laryngeal mucosa;
- Hyperplastic, characterized by the appearance of growths on the mucosa of the vocal cords, of different shapes and sizes;
- Atrophic, manifested by inflammation and irritation of thinned and dry mucosa.
The causes of catarrhal and hyperplastic forms of chronic laryngitis are:
- Frequent acute laryngitis and other inflammations of the upper respiratory tract;
- Voice overvoltage associated with the profession( singers, trumpeters);
- Exposure to tobacco smoke;
- Regular intake of alcohol;
- Exposure to chemical and mechanical hazards such as dust, gas, chemical vapors, dry hot air;
- Exchange diseases, such as diabetes mellitus;
- Allergic reaction of the mucosa of the respiratory tract.
Atrophic form of chronic laryngitis is associated with thinning of the nasal mucosa and pharynx after infectious diseases, as whooping cough, diphtheria. Also, this form is promoted by dry, dusty air, gassed city atmosphere, as well as smoking and drinking alcohol.
Thus, some factors of some form of chronic laryngitis are similar. But what form will develop in this patient depends on his general condition.
If the body is inclined to respond to inflammation with proliferation of connective tissue, then the hyperplastic form develops. If the reaction of the immune system is so strong that it damages the mucous membrane, then it leads to atrophy.
The catarrhal form of laryngitis is the primary reaction, which, if inflammation lasts for a long time, passes into one of the two listed above.
Symptoms of acute laryngitis in adults
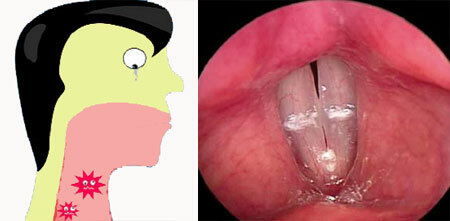
Acute laryngitis has a characteristic sudden appearance of symptoms on a background of complete health. First, there is a feeling of perspiration and saddening in the throat with growing signs of coarsening and hoarseness of voice. With the development of the disease can develop a complete loss of voice - aphonia.
This manifestation is associated with the appearance of sputum and swelling of the laryngeal mucosa and vocal cords. Against this background, they lose their inherent functions.
After 2-3 days from the onset of laryngitis, a dry cough may appear with a small amount of viscous sputum.
Body temperature increases if laryngitis accompanies a viral infection. If the inflammation of the larynx has arisen as a result of hypothermia, trauma or stress on the vocal cords, then there will be no fever and general malaise.
If after a few days the patient has a sharp rise in temperature and worsens overall well-being, this suggests either that the inflammation descends into the bronchi and lungs, or the development of a purulent form of laryngitis. In this case, a strong pain in the throat appears and grows, swallowing is difficult.
If worsened, symptoms of breathing disorders may appear, indicating the development of stenosis( constriction) of the larynx and requires the use of emergency care without delay.
In some patients with immunodeficiency, the development of complications against the background of laryngitis may go unnoticed. Because of the depressed immunity, the temperature does not increase in accordance with the severity of the inflammatory process, but the pathological changes in the body progress.
- And if in time to not render due therapeutic measures, then the patient's condition is sharply aggravated.
Symptoms of chronic laryngitis in adults

For chronic forms are characterized as periods of exacerbations, proceeding according to the type of acute laryngitis, and remission periods. The latter may be asymptomatic, and may have minimal clinical signs.
The degree of expression of permanent symptoms is due to the intensity of the influence of irritant factors at a particular time:
- When catarrhal form there is rapid fatigue of a voice of varying intensity, hoarseness, foreign body sensation, dry throat, cough, cough.
- In hypoplastic form - it is hoarseness, rarely there is dysphonia or aphonia, associated with deformation and decreased mobility of ligaments.
- When atrophic form - dryness in the throat, pershenie, increasing voice changes. During a conversation, reflex shortness of breath often occurs,air irritates the respiratory tract.
Diagnosis
Initially, the diagnosis can be made by a general practitioner or by a therapist. Further diagnosis of laryngitis, identification of symptoms and treatment in adults and children is performed by ENT - a doctor and is based on a survey and laryngoscopy - examination of the patient's larynx using a special device( laryngoscope).
In some cases, a bacteriological study is required. It allows to identify the causative microbe, leading to the development of inflammation. Without this study, patients who are not able to achieve clinical improvement and cure are not eligible for the use of standard antibacterial agents.
Based on the results of bacteriological analysis, it is possible to select the most effective antibiotic to which the microbe will be sensitive.
Treatment of laryngitis in adults, drugs
Beginning to treat laryngitis in adults is necessary with the appointment of restrictive voice mode. Some authors recommend to adhere to complete silence, but, according to other sources, such a recommendation, especially among representatives of "speech" professions, can cause psychological discomfort.
Therefore, in most cases, the voice load should be sharply limited for a while, until the inflammation subsides, but completely not ruled out.
Also it is not recommended to talk in a whisper - at the same time the load on the bundles is not less than in ordinary conversation. It is recommended to reduce the number of spoken words.
If there is a temperature, bed rest and sick leave are shown. However, people whose professions are connected with voice are also disabled: singers, teachers, speakers, regardless of whether there are signs of intoxication or not.
It is necessary to wrap your throat with some soft material to create dry heat, drink a lot of warm, non-irritating drinks, and also create an optimal level of humidity with a humidifier, often ventilate the room where the patient is.
These general recommendations will help accelerate the healing process and increase the effectiveness of drug therapy.
Drugs for laryngitis, antibiotics
In adults, for the treatment of acute laryngitis, use local antibacterial drugs in the form of tablets for resorption, aerosols, sprays such as Strepsils, Geksoral, Tantum Verde, etc.
- For severe pain in the throat, NSAIDs are prescribed - nonsteroidalanti-inflammatory drugs: Nimesil, Naise, Nurofen. They effectively eliminate all the symptoms associated with inflammation - pain, voice disturbance, etc.
- Antiviral agents and immunomodulators( inducers of interferon) are used to treat ARVI that caused laryngitis.
Antibiotics for laryngitis are prescribed if, on the 4th-5th day, there is no effect from symptomatic treatment, or intoxication persists.
Numerous studies confirm the effective use of laryngitis antibiotics from the macrolide group: Erythromycin, Clarithromycin, Azithromycin. But the appointment of these drugs is only a doctor, self-medication is not acceptable!
Treatment of laryngitis in adults at home
Hospitalization with laryngitis is carried out only with the presence of purulent inflammation, the threat of edema and stenosis of the larynx. Usually the whole volume of therapeutic measures is carried out at home. With laryngitis treatment at home should be supplemented with nebulizer therapy.
This is a modern, safe and effective way of treatment. He is in the conduct of inhalations through the nebulizer - a special chamber in which the drug is turned into an aerosol.
Due to this, the drug easily enters the body in an effective dose, without losses and side effects and acts directly on the pathological focus in the airways.
Inhalation with laryngitis is carried out with the following types of drugs:
- Antibacterial: Dioxydin, Miramistin;
- Hormones that have a local anti-inflammatory effect;
- Mucolytics, agents that dilute sputum, such as chymotrypsin, ACTS( acetylcysteine);
- Mineral alkaline water: Essentuki No. 4, No. 17, Smirnovskaya and others. Inhalations with the help of these waters have a softening effect, improve the sputum discharge;
- For chronic atrophic form, use oily solutions for inhalation, softening dry mucous membranes, for example, an oil solution of citral.
Active heating of the area with alcohol compresses, as well as steam inhalations are ineffective. In addition, they can provoke purulent complications and swelling of the larynx.
Treatment of exacerbations of chronic laryngitis is carried out in the same way as acute. In the case of the presence of growths on the vocal cords with hypertrophic form, they are removed by laser.
In chronic laryngitis, antibiotics are used only when the body temperature rises. In other cases, only non-steroids are required as a means of combating the inflammatory response.
Prophylaxis of laryngitis
- Elimination of the maximum possible number of irritant factors, especially for people in the "voice" professions;
- Regular unloading of ligaments, rest, climatic effects;
- Activation of metabolic processes of immunity - exercise, active way of life in order to prevent catarrhal diseases;
- Microclimate at home - maintaining the optimum temperature of 20-22 C and humidity 50-70%, especially in the heating season;
- Refusal from smoking and alcohol.