1 Biochemical analysis of
When referring to a doctor about a disease, the patient is usually referred for a blood test, both general and biochemical. It is the second and determines the level of bilirubin, which is a bile pigmentary compound.
Do you have gastritis?
GALINA SAVINA: "How easy is it to cure gastritis at home for 1 month. A proven method - write down a recipe. ..!"Read more & gt; & gt;
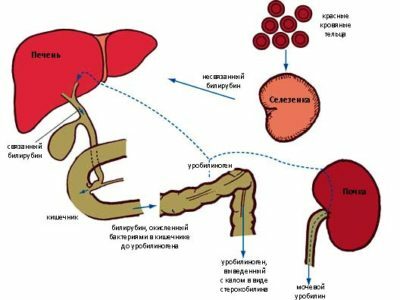
Its formation is the result of the decomposition of erythrocytes, that is, red blood cells, which leads to the release of hemoglobin. And hemoglobin as a result breaks up into two of its components: heme and globin. The combination of heme and enzymes leads to the formation of free bilirubin, also called indirect bilirubin. This kind of enzyme pigment has a high density and does not have the ability to dissolve in water.
We recommend that you read
- What you can not eat before the ultrasound of the abdominal cavity
- The norm of diastasis in the urine
- Effective preparations for intestinal dysbiosis
- Effective remedy for gastritis and stomach ulcer
As soon as free bilirubin penetrates the liver, it immediately begins its processing. There, it loses its toxic properties and without much difficulty leaves the body along with bile. This kind of pigment is called direct.
If the liver does not perform some of its functions and is not able to properly process bilirubin, then it does not have the ability to go from an indirect state to a direct one. Accordingly, does not leave the body, but accumulates in it. As a result, various disorders and pathologies develop. That's why the blood test for bilirubin is so important.
In addition to the direct and free pigment in the blood biochemistry, the patient can see another value that can cause misunderstanding - bilirubin is common. This parameter indicates the sum of the concentration of bilirubin free and indirect.

2 To whom is assigned and how is the
performed? Such an analysis is necessary for the patient to undergo if the following diseases are suspected:
- hepatitis, neoplasms in the liver, cirrhosis;
- pancreatitis;
- cholelithiasis;
- cholecystitis;
- intoxication of the body;
- hemolytic disease;
- for the purpose of monitoring ongoing treatment;
- for the determination of hypothyroidism in a newly born baby;
- complex diagnostic measures of the whole organism.
Blood sampling for bilirubin analysis is done from the patient's vein. For the results to be as reliable as possible, the procedure is carried out in the morning before eating. The last time a person can eat 8 hours before visiting a hospital laboratory. This applies only to adults. This restriction does not apply to children.
-
 IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
The results of the analysis may affect the intake of a number of drugs that affect blood clotting, as well as choleretic medicinal herbs.
In very young children, blood is taken from a vein on the head or from the heel. The procedure is quite unpleasant and painful. But so far there is nothing else that could replace it. In modern clinics, doctors determine the total bilirubin in the blood of babies, measuring the degree of pigmentation of the skin.
3 Pathology
The norm of bilirubin in the blood of men and women is almost identical. But in representatives of the strong half of mankind, a hereditary pathological condition - the Zhibera syndrome - is much more likely than in the opposite sex. It is characterized by an elevated level of bilirubin in the absence of any ailments. The reason for this is that the body lacks the liver enzyme responsible for the pigment transition to the direct state. A person with this pathology can easily be distinguished by the yellowness of the skin of the skin and eyeballs.
In men in the blood, bilirubin should be at a level of 3.4 to 17.1 micromolar per liter. This is the norm of the overall indicator. Direct - from 0.7 to 7.9, free - up to 16.2.Percentage of the norm of direct substance is 20-22%, and free - 78-80%
-
 Gastroenterologist. VAZHENOV: "I beg you, if you started to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not do gas. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
Gastroenterologist. VAZHENOV: "I beg you, if you started to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not do gas. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
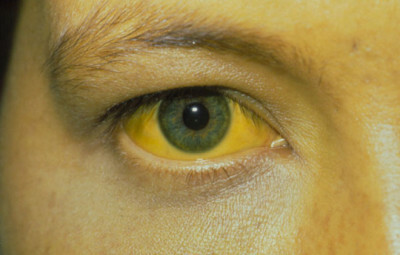
An increase in the level indicates a number of diseases. Among them:
- jaundice;
- liver diseases that are infectious;
- malignant neoplasms of the liver and spleen;
- cholelithiasis;
- cirrhosis;
- pathology of the biliary tract;
- syphilis of the 2 nd or 3 rd stage.
If the level of the indirect fraction increases, then it is possible to develop disorders of the circulatory system: hemolytic anemia, internal bleeding. It happens that the increase is due to the use of certain medicines.
The norm in women is slightly lower. Total bilirubin - from 3.2 to 17.2 micromol per liter, indirect - from 6.4 to 16.8, direct - from 0.9 to 4.3.
A blood test for bilirubin is mandatory for all pregnant women. This is done to find out how effective is the outflow of bile.
The increase in the level of this substance in the blood in women occurs for the same reasons as in men. A decrease in the level for a long time was not considered something pathological. But recent medical observations indicate that such a condition can be with the development of cardiac ischemia.
Other studies are being carried out to diagnose pathologies. Biochemical analysis is only one of them.
ADVICE FROM THE MAIN GASTROENTEROLOGIST
Korotov SV: "I can recommend only one remedy for the rapid treatment of Ulcer and Gastritis, which is now recommended by the Ministry of Health. .." Read the reviews & gt; & gt;
4 Diagnosis in children
In childhood, bilirubin changes its level depending on how old the child is. The highest rate is in newborn babies. This is explained by the imperfection of the work of removing the bile from the body. It takes only a few weeks, and the indicator is approaching the norm. This is because the process of gallbladder is getting better.
Often a newborn has a physiological jaundice, characterized by the skin's yellow skin. It is considered quite normal condition and should not cause alarm to the mother. Such babies need more fresh air and sunlight.
But this condition should not cause fear until the child's four-week age. And if the child is already more than a week, you can suspect violations in the metabolism. He needs medical help.
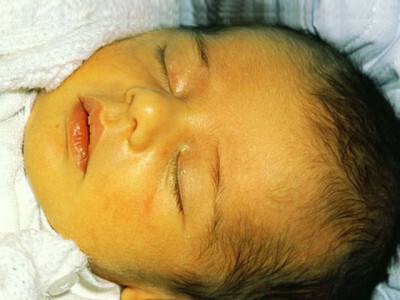
Blood bilirubin norm in children newly born:
- total: 23.9;
- indirect fraction: 8.72;
- direct fraction: 14.4.
In children up to 4 days of life:
- total: from 54.3 to 90.1;
- indirect fraction: from 7.87 to 7.82;
- direct fraction: from 45.5 to 82.3.
Those children who are from 5 days to 10 years old:
- general: from 52.02 to 69.1;
- indirect fraction: from 7.72 to 8.71;
- direct fraction: from 44.3 to 63.3.
To whom the month turned:
- general: from 9.2 to 14.5;
- indirect fraction: from 1.2 to 4.5;
- direct fraction: from 6.7 to 10.4.
The older children have the same norm as adults.
There are several reasons for the increase in the level of bilirubin. This is hemolysis, Zhibera syndrome, hepatitis, a deficiency of folic acid and a number of others.
If only the direct fraction rises, the doctor suspects hemolytic jaundice, liver abscess or her dystrophy. Poisoning by various fungi can also be manifested by an increase in the level of this substance. Also influenced by antibiotics, taken by the child for a considerable time.
But a professional specialist will never diagnose only one parameter. Violation of the level of bilirubin serves only as an assumption that pathology is possible. The diagnosis is diagnosed after several diagnostic procedures.
5 Reasons for the appearance of pigment
The level of this pigment provokes only 3 reasons:
- erythrocytes are destroyed at high speed;
- violations of those liver functions that are designed to process this pigment from one state to another;
- the output of bile is broken.
The first cause( destruction of erythrocytes) causes an increase in the level of hemoglobin. This leads to a large number of indirect bilirubin fractions. And erythrocytes destroy at an increased rate because of hemolytic anemia. It is congenital and acquired. The development of congenital forms begins because of the existing blood problems, in particular, because of the defects of the erythrocytes themselves.

Acquired anemia begins in connection with autoimmune pathologies that develop in the body. This is a state where the immunity system suddenly starts to fight against cells of its own organism, for example, against its red blood cells.
A number of diseases, for example, malaria, the use of certain medications can also cause the acquired form of such anemia. With her, the bilirubin of the indirect fraction is elevated in the blood.
Anemia of the hemolytic type is manifested by the following symptoms:
- yellowness of the skin, eyeballs;
- regularly observed high figures on a thermometer when measuring body temperature;
- unpleasant sensations in the left part under the ribs;
- urine of such dark shade that is often close to black color;
- regular headaches, high fatigue, a frequently occurring heart rate failure.
The second provoking factor of increasing the yellow pigment are various liver pathologies. This organ is given great importance by nature in the metabolic processes associated with bilirubin. If the liver is sick, then the transition of the indirect fraction into a straight line becomes impossible. This condition can occur with some forms of hepatitis, including with medicamentous and alcoholic. Cirrhosis and oncology work in exactly the same way. In addition to jaundice, there are also some signs:
- area of the right hypochondrium makes itself felt by the severity and discomfort;
- nausea;
- after eating a belch and a feeling of bitterness;
- is colorless, almost white, feces and too dark urine;
- state of permanent weakness, reduced performance;
- in some cases, high temperature.

The third cause leading to a high level of this pigment is an inadequate outflow of bile from both the liver and the gallbladder. This condition occurs with diseases of the gallbladder and pancreas - cholelithiasis, oncology.
With this state, the straight fraction is increased. Besides the yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes, the following conditions may occur:
- colic;
- painful manifestations in the right side of the abdominal cavity under the ribs;
- skin itching;
- nausea and vomiting;
- decreased appetite;
- dark urine and light, almost white, feces;
- flatulence( bloating);
- diarrhea or constipation.
6 Methods of lowering
Before taking measures to reduce the level of yellow pigment, a thorough diagnosis is carried out. The doctor necessarily determines the cause that caused this increase, and chooses a treatment regimen. This is the only way to bring the pigment performance back to normal. Self-medication is unacceptable.

If bilirubin in the blood is elevated due to the presence of any ailment, then it is necessary to start treatment of the underlying disease. If the culprit is stagnation of bile, then the body should be rid of the obstacle that prevents the bile excretory system from functioning properly.
As a supplementary measure that the patient himself can take, a special diet is recommended. It can relieve the load from the liver. The diet provides for the refusal of fried and spicy food. You can not drink alcohol and drink carbonated sweet water. You can not overeat. In food you should eat only cooked and baked.
If you follow these recommendations, you can so relieve the liver that it can cope with excess bilirubin.
Help her in this and herbal medicinal herbs, chamomile tea, motherwort infusion. Taking these fluids, you can normalize the level of bilirubin - it will decrease.
The doctor usually prescribes medicines from Karsil and Phenobarbital. But some patients are contraindicated. Therefore, you should take them, like any other medication, only as directed by your doctor.
- 1 Biochemical analysis of
- 2 To whom is assigned and how is performed
- 3 Pathology
- 4 Diagnosis in children
- 5 Causes of appearance of pigment
- 6 Methods of reduction
The process of decomposition of hemoglobin is completed by the formation of a special pigment, called bilirubin, its norm is necessarily present in the serum of a healthy person. In bile, he is also present.
The high level of this substance enables the doctor to suspect the patient of liver disease, in some cases - the spleen, and the wrong metabolism.