Infections caused by pathogenic staphylococci, belongs to a special group. The fact that staph is opportunistic, almost always living on the human body, widely distributed in nature microbe. Either way, the person in contact with them every day.
Staphylococcus aureus can produce inflammation in almost every system and every body - skin and subcutaneous tissue, internal organs, nerve tissue, the brain and heart. Toxins of certain types of Staphylococcus give clinic of food poisoning.
types aureus
For a person of particular importance in the pathogenesis of diseases are three types of play:
- Staphylococcus aureusCausing infection in almost any organ of the body in adults and children, on the skin, mucous membranes, and even in nervous tissue.
- Staphylococcus epidermidis, the most dangerous in premature, debilitated children and patients with immunodeficiencies, cancer.
- Staphylococcus saprophyticus is of great importance in the urinary tract infection.
Each species has a plurality aureus strains (varieties), differing degrees of aggressiveness and pathogenicity.
Depending on the strain of certain types of Staphylococcus selectively affect certain organs.
The etiology of staph infection
The cause of staph infections is a human infection by pathogenic strains of Staphylococcus (eg, nosocomial infection) or getting staph in those organs where it normally not be must. Aureus is highly resistant to the environment, are stored up to six months in the dried, frozen, lives well in water and food products, is sun.
Staphylococcus aureus is able to secrete exotoxins that affect the skin or white blood cells (leukocytes), enterotoxins, affecting the digestive system and cause symptoms of poisoning.
Also aureus allocates special substances that suppress the immune mechanisms of the body, which helps the microbes actively reproduce in the body.
The source of infection - a healthy carrier of Staphylococcus (eg, the parents of a child), or the patient staphylococcal infection of any form (streptoderma, Pneumonia, purulent staphylococcal mastitis). Up to 40% of the people in one way or another, are infected with staphylococcus.
Dangerous is the nosocomial infection with staphylococcus, as these strains are usually aggressive, resistant to antibiotics and is very contagious. Infection occurs:
- by contact from person to person by bodily contact and use common things and toilet articles (such as, e.g., at postnatal mastitis)
- droplet infection, particularly against nosocomial pneumonia,
- by food (with staphylococcal gastroenteritis outbreaks)
- through the hands of the staff, which is a carrier of pathogenic Staphylococcus.
Especially important factors in the development of infection are:
- lowered immunity,
- the use of strong medications, immunosuppressants,
- chronic disease,
- thyroid problems,
- stress, environmental influences.
Especially hard staphylococcal infections occur in young children and the elderly.
Immunity to staphylococci unstable, you can recover a lot of times. Specific immunization is not designed for it.
manifestations aureus
Symptomatology will depend on where aureus will penetrate and reproduce furthermore displays depend on the strain of staphylococcus and aggressiveness.
Aureus can infect virtually all systems, tissues and organs, giving clinic staphylococcal local or general disease. It can affect the skin, subcutaneous tissue, nervous system, kidneys, liver, lungs, urinary system, bone and occur common infecting organism (sepsis).
skin lesions
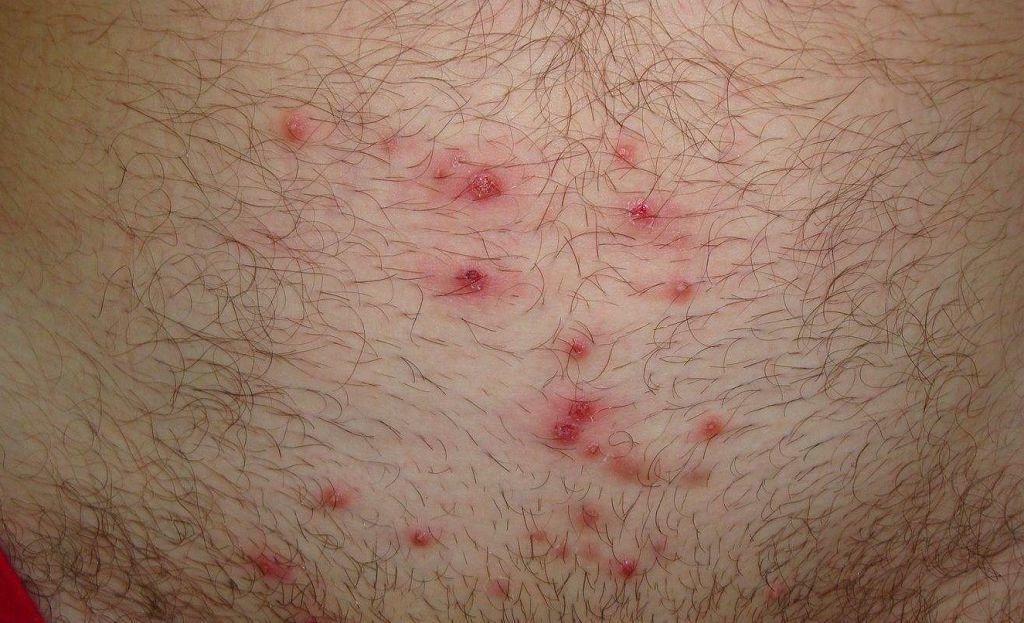
skin lesions - pyoderma, Pustular lesions arise as a result of the defeat of the mouth of the hair follicle. Small lesions called folliculitis, Deeper lesions with fiber - boils, purulent fusion hair follicles. If it affects the subcutaneous tissue there carbuncles. Most often they appear on the neck, buttocks and thighs, on his face.
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome or "scalded" skin - staphylococcal lesion in the newborn with a bright skin redness and peeling its layers.
at pemphigus on the skin produces a voltage large bubbles with serous content. It occurs under the action of staphylococcal toxins.
Phlegmon and abscess arise deeply located tissues being limited or widespread purulent lesion tissues. When abscess pus limited capsule in phlegmon spreads between the tissues, which can lead to dangerous lesions.
lung disease
Pneumonia staphylococcal etiology is very difficult to proceed, giving a massive lung infection, resistant to therapy and often lead to death.
There is a severe intoxication, chest pain, shortness of breath. The lungs are formed multiple foci of pus to form abscesses.
brain lesions
With the penetration of Staphylococcus primary foci in the brain formed abscesses and purulent meningitis.
These complications are severe and life-threatening, poorly to therapy and leave residual (remaining for life) consequences often lead to disability.
Manifested by fever, headaches, vomiting, toxicity, neurological symptoms. Staphylococcal thrombophlebitis of veins of the brain may be a cause of strokes.
Lesions of Bone
Staphylococcus aureus can infect the bone tissue with the formation of osteomyelitisWhile destroys all layers of bones, there are pathological fractures, fistulae and pain in the affected bone may be joint damage with purulent arthritis.
severe staphylococcal mastitis endocarditis are also possible, pyelonephritis, and the heaviest defeat of a staphylococcal septicemia.
Diagnostics
diagnostic base - clinical picture and serological methods, foremost among which are the coagulase sample and latex agglutination.
Standard in vitro coagulase test lasts 4 hours, but when a negative result is extended to day.
Latex agglutination using commercial kits latex particles bound with antibodies to Staphylococcus aureus (protein A, clumping factor and a number of surface antigens), which makes it also useful for the identification of strains and species exciter.
It is important to crop pathogen with definition of sensitivity to antibiotics (MRSA), as well as staphylococci are resistant to most conventional therapies.
Additional for diagnostics will be a common blood and urine tests, biochemical tests and other methods studies depending on which organs are affected - X-ray for pneumonia and osteomyelitis, with ultrasound and liver injury kidneys, etc.
Treatment of Staphylococcus
The mainstay of treatment - the fight against the agent and deal with the consequences of his life.
For purulent wounds and abscesses mainstay of treatment - surgical opening of abscesses, with further washing with antibiotics and drainage.
Staphylococci are treated using advanced new generation of antibiotics due to multidrug-resistant (insensitivity) to their usual antibiotics.
apply
- semisynthetic penicillins and protected (amoxiclav, nafitsillin)
- aminoglycosides (neomycin, kanamycin),
- some other species (vancomycin, clindamycin, ofloxacin).
For Staphylococcus one of the treatments is phage therapy. This special "eaters" Staphylococcus, specific viruses, namely selectively killing staphylococci, e.g., bacteriophage protivostafilokokovy liquid. For external treatment, ointments with antimicrobial components, antiseptics.
When staph infection is very important the use of immunomodulators and means to strengthen the immune system. Applied protivostafilokokkovye immunoglobulins hyperimmune plasma, etc. autohaemotherapy Used multivitamins, drink plenty of liquids and detoxification.
Forecast
The prognosis for a staph infection is largely dependent on the type of staphylococcal and strain, the severity of the injury and the hearth, the patient's age and resistant microbes to antibiotics.
In nosocomial infection prognosis may be disadvantageous in death due to high resistance of microbes to antibiotics and the high aggressiveness of the pathogen.
Today staphylococcal infection is a leading cause of septic complications in debilitated, operated patients and young children, especially infants and prematurity.