During the gynecological examination, the specialist always pays attention to the condition of the uterine mucosa and its cervix.
Normally, it is pale pinkish and the presence of foci of a different color and structure is considered as a pathological process. Consider what is the cervical leukoplakia, how to treat it and why it develops.
Contents
- 1 Cervical leukoplakia, what is it?
- 2 Symptoms of cervical leukoplakia, photo
- 3 Cervical leukoplakia and pregnancy
- 3.1 Diagnostic criteria
- 4 Treatment of cervical leukoplakia
- 4.1 Complications
- 4.2 Prevention
- 5 Questions to the doctor
What is leukoplakia of the cervix, what is it?

In medical terminology, the term "leukoplakia" refers to a change in the epithelial layer, which externally manifests areas of whitish color and visually differs from normal mucosa.
Cervical leukoplakia itself is not considered a disease, but is used to visualize the appearance of the mucosa. It can be a manifestation of various gynecological diseases that require additional examinations and studies.
It is often possible to detect this problem during a routine examination with a doctor, since in most cases it does not manifest itself in any way.
- The danger of this process is the possibility of degeneration into a malignant neoplasm, which occurs in approximately 20-25% of patients with this pathology.
There are 3 forms of leukoplakia:
- Simple( flat).Outwardly resembles a whitish plaque, which does not rise above the level of the epithelium. If the disease is in its early stages, then even a specialist can at first not notice these foci;
- Leukokeratosis( warty).Modified, keratinized areas rise above the level of the epithelium, the surface of the cervix becomes rough. This form does not cause problems with recognition and often requires a biopsy to exclude malignant degeneration of the mucosa;
- Erosive. With this form, alongside typical whitish spots, erosions or cracks appear which can bleed.
Causes of leukoplakia
There is no single proven cause for the development of cervical leukoplakia. Assume two groups of factors that contribute to the development of this pathology:
1. External:
- Inflammatory processes( endometritis, etc.);
- Infection( papillomavirus, chlamydia, mycoplasma, etc.);
- Traumatic mucosal damage( diagnostic curettage, hard sexual intercourse, etc.).
2. Internal:
- Associated somatic diseases( diabetes mellitus, etc.);
- Allergy or contact dermatitis, for example, when installing an intrauterine device;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Decreased immunity, etc.
Thus, only a combination of certain factors can lead to the development of this pathology, and in some women leukoplakia occurs for no apparent reason and is found absolutely randomly.
Symptoms of cervical leukoplakia, photo
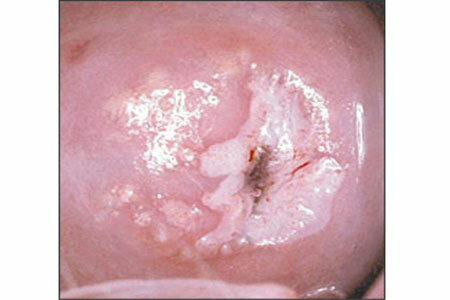
photo of cervical leukoplakia when viewed from a gynecologist
In most situations, cervical leukoplakia does not show any symptoms. This process may be accompanied by other signs of the underlying disease, which was the factor of the origin of pathological foci.
So, with infectious and inflammatory processes a woman will be disturbed:
- Pain in the abdomen;
- Unpleasant discharge from the vagina;
- Problems with urination;
- Soreness during intercourse.
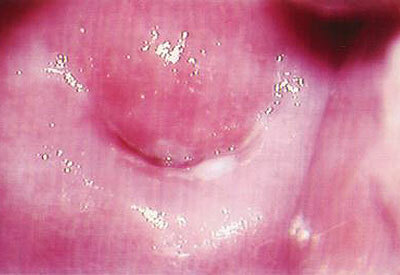
leukoplakia, photo 2
If the cause of this pathology is traumatic injury, then the above symptoms can be associated with bloody discharge from the vagina, not associated with the menstrual cycle.
Important! Symptoms of leukoplakia may differ depending on the form of the pathological process and the underlying disease. In addition, this process can not show itself for many years.
Cervical leukoplakia and pregnancy
Pregnancy with cervical leukoplakia is possible, but ideally a woman is recommended to undergo examination and be treated at the conception planning stage.
This pathology does not affect the fetus and condition of a woman during pregnancy, but it can start to progress, so pregnant women with this problem are under the close attention of a gynecologist.
Diagnostic criteria
The appearance of leukoplakia is quite typical, but if the doctor has doubts, he can recommend a biopsy. This allows you to study the site of the altered mucosa under a microscope and make sure of the diagnosis.
Additionally, other studies, such as ultrasound of the reproductive organs, analyzes for hidden infections, general clinical trials are also prescribed.
Treatment of leukoplakia of the cervix

If the patient is diagnosed with leukoplakia, the specialist can offer several treatment options, depending on the situation of the woman and the nature of the altered foci. What treatment is used for cervical leukoplakia:
- Chemical removal of lesions of leukoplakia. The modified tissues are affected by a chemically aggressive solution that acts only on the area of exposure and does not damage healthy tissues.
- Surgical intervention is indicated in cases of common foci that can not be removed by other methods.
- Electrocoagulation. One of the oldest methods of treatment. There are a number of drawbacks:
- can damage healthy close-fitting tissues;
- leaves behind a scar that creates problems in subsequent pregnancy;
- heals for a long time;
- if the focus is not completely removed, relapses occur.
- Cryogenic exposure( moxibustion by liquid nitrogen of cervical leukoplakia).The effect of low temperatures is practically painless and less traumatic. There is a possibility of relapse with deep and widespread foci of leukoplakia.
- Laser treatment. A high-precision method that acts efficiently and does not leave gross scars behind. Relatively expensive, but allows you to remove the altered foci quickly and painlessly.
- Radio wave technique. Effects on the foci of leukoplakia by radio waves of a certain length, which do not affect healthy tissues.
In addition to removing areas of altered epithelium, doctors prescribe drugs( antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.) aimed at treating the underlying disease that could cause the problem.
Complications of
The main danger of this pathology is its ability to degenerate into cervical cancer. In medical terminology, this condition is called "facultative precancer";a condition that can most likely go to cancer.
In this regard, this problem is under strict medical supervision, and experts recommend removing the altered foci of the mucosa.
Prevention of
The clear cause of this pathology is unknown, therefore, prevention is the timely treatment and protection from genital infections, inflammatory diseases and other factors that can cause mucosal degeneration.
Questions to Dr.
Question: How to treat leukoplakia in a nulliparous girl?
Answer: For treatment choose gentle methods( laser therapy), which do not lead to the development of scars. In addition, the main pathology is treated, for example, infection of the genital tract.
Question: Do I need to prepare before removing leukoplakia?
Answer: This intervention is usually carried out on the 5th-6th day of the menstrual cycle. Before removal, it is recommended to abstain from sexual intercourse for 3-4 days, to stop taking medications that affect coagulation, to exclude visits to baths, saunas and swimming pools a week before the proposed intervention.
Cervical leukoplakia is an optional precancer. This condition requires medical control and removal of altered foci of the mucosa.



