To understand the causes of prostatic diseases, it is necessary to refer to its structure, functioning and purpose.
The prostate gland is a male organ having the shape of an inverted trapezium. It is located in the pelvic region to the bottom of the bladder, between the anterior part of the urinary diaphragm and the anterior wall of the end part of the digestive tract. The prostatic gland partially covers the vas deferens and urethra. This is an unpaired organ with an elastic consistency, consisting of glandular and muscle cells.
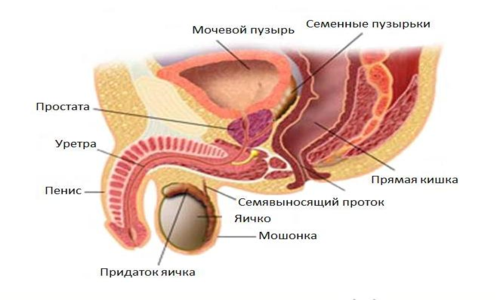
In the prostate gland secrete several parts. The part directed to the urogenital diaphragm is called the apex, as it is narrower in comparison with the base of the prostate. The base of the prostate, that is, the upper part of the gland differs a little concave, smoothed and wider surface, it touches the bladder. Also, there are anterior and posterior parts of the gland, having a smooth-convex surface. The anterior part faces the pubic adhesion, the posterior part towards the gut. Areas of the gland are rounded, which are located on the sides, called nizhnekbokovymi surfaces.
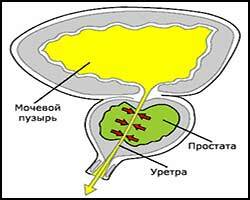
The prostate gland consists of two lateral lobes resembling the shape of a chestnut. These lobes are interconnected by an isthmus, which plays a very important role in the mechanisms of the onset of prostate diseases. With age, the isthmus grows and thickens, exerting a squeezing effect on the urethra, which passes through the thickness of the gland. The outflow of urine is disturbed.
The basic functions of the prostate
The functions performed by the prostate gland are different. The organ keeps urine and ensures normal urination, and also reproduces cells and hormones that are very important for the male body. Prostate functions are divided into:
- Secretory function
- Motor function
- Barrier function
Secretory function
Prostate is the most important accessory sex gland that performs secretory exocrine function. Cover cells of the prostate gland are responsible for stimulating complex secrets that take part in the fertilization of the egg. The secretory function of the prostate is regulated by testosterone and is controlled by the endocrine system. If the amount of testosterone decreases, the prostate gland begins to produce it intensively.
Motor function
The motor function is that the muscle tissues inside the prostate form a sphincter, which is responsible for holding the urine. The motor function is carried out using two paths:
- With the smooth muscle fibers that are in the prostatic part of the urethra, and also in the caudal and cranial parts of the
- By ejection of the secretion of the prostate during ejaculation
Barrier function
Barrier function is the main obstacle to penetration of infection from the urethrain the upper urinary tract. This function is achieved due to the zinc-peptide complex, lysozyme, cellular immunity factors, spermine and other polyamines contained in secret.
Prostate pathology
There are two major groups of prostate pathologies:
- Acute infectious and chronic inflammatory diseases
- Tumor diseases - prostate cancer and adenoma
Acute and chronic prostate diseases
The bacterial and chronic congestive prostatitis belongs to the group of inflammatory diseases. Acute bacterial prostatitis is more common in men in adulthood after forty years. Origin of acute bacterial prostatitis
A typical pathogen of this pathology is bacteria( Trichomonas, ureplazmy, gonococcus, Mycoplasma, Chlamydia, Gardnerella, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus), but another flora is possible - Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella, Escherichia coli. Microorganisms enter the prostate from the rectum, kidney and bladder, the urethra, into which many prostatic ducts are open. Violations in the prostate, congestion in the pelvic organs, hormonal imbalance - all this contributes to an easier spread of infection and a rapid development of the inflammatory process.
There are 3 forms of acute prostatitis:
- Catarrhal
- Follicular
- Parenchymal
With catarrhal form, only prostatic ducts are inflamed. If the inflammation spreads to the follicles and affects the individual parts of the prostate, the catarrhal form grows into the follicular. If the symptoms of this infection have not been treated for a long time, the inflammation covers both lobes of the prostate, involving the connective tissue. In this case, note the parenchymal form. To a parenchymatous prostatitis carry also such a serious form of the disease as an abscess of the prostate.
Symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis can be divided into: - General - are caused by intoxication of the body
- Local - caused by inflammation in the prostate tissues
Local symptoms include intense pain in the perineum, in the abdomen, in the anal passage and in the genitals. Pain can increase with urge to urinate, during defecation or in a sitting position. Pain syndrome is particularly pronounced in prostate abscess. There is also frequent painful urination or the allocation of small portions of urine. Obstructive violation of urination is caused by compression of the neck of the bladder due to an increase in the size of the inflamed prostate. Such disturbances can be characterized by a sluggish intermittent stream of urine or by the release of drops. In this case, after urination, there is a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
A rise in body temperature of 37.5 ° C also refers to general symptoms. At the catarrhal form - up to 40 ° C.With abscess of the prostate, the temperature can be even above 40 ° C.Simultaneously with the fever, the man is noted for weakness, general lethargy, lack of appetite and dizziness.
Diagnosis and treatment of
In most cases, it is already possible to establish a diagnosis by the typical complaints of the patient. With digital rectal examination, an enlarged, edematous, dense and painful prostate gland is found. In case of acute bacterial prostatitis, it should be very carefully examined, avoiding pressure on the gland. Massage in this case is strictly contraindicated, since the slightest mechanical pressure can provoke the rapid spread of the inflammatory process to tissue that is not yet damaged or an abscess breakthrough.
To establish the causative agent of the disease and begin treatment, it is necessary to pass a urine culture to the microflora and a general blood test. Acute bacterial prostatitis is treated permanently. A strict diet is recommended, completely eliminating sharp, salty, fatty and fried foods. Alcohol and smoking are also contraindicated. The main direction in the treatment are antibiotics. Duration of treatment is determined by the dynamics of the disease and the severity of the patient's condition.
Origins of chronic congestive prostatitis
The diagnosis of congestive or chronic congestive prostatitis is made in the case of symptoms in the absence of a foci of inflammation. The first symptoms of congestive prostatitis are pain in the groin, inconvenient urination in the morning and a constant feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. Symptoms can be felt not constantly, with time the sexual inclination ceases, the risk of impotence is possible. Stagnant prostatitis provokes the appearance of aggression, decline of strength, depression.
Causes of
The cause of stagnant prostatitis can be two factors:
- Stagnation of blood in the venous system of the prostate
- Stagnation of the secretion of the prostate
Stagnation of blood in the venous system of the prostate can arise due to varicose veins, sedentary lifestyle, frequent smoking and alcohol abuse, hypothermia, stress and long abstinence from urination.
To the reasons for stagnation of the prostate secret include: incomplete sexual acts, prolonged sexual abstinence, seminal fluid stagnation during prolonged excitation, active sex life after a long break, incomplete release of the prostate.
The main direction of treatment is to remove symptoms and achieve remission. A prerequisite for treatment is prostate massage and physiotherapy. Inflammation and pain syndrome are removed with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Advantages of prostate massage
Prostate massage is characterized by a high level of efficiency. It allows you to determine the presence of infections and cancer cells, eliminates the accumulation of seminal fluid in the prostate gland, reduces muscle tension, which allows you to overcome stagnation of blood, improves blood circulation. Regular prostate massage helps reduce the chances of developing cancer. Stimulation of the flow of seminal fluid improves their circulation and significantly reduces the risk of impotence.
Contraindications to massage: 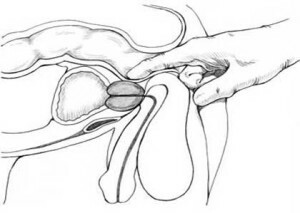
- Cysts or stones in prostate
- Prostate cancer
- Rectal disease
- Acute prostatitis
- Prostate adenoma
- Urethritis
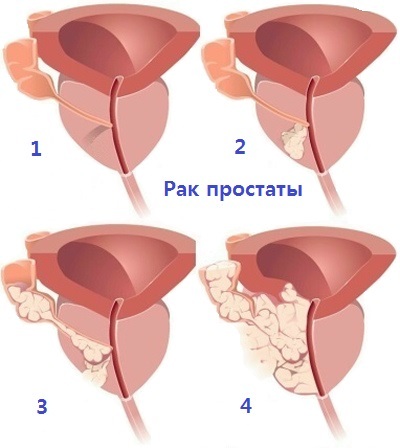
Tumor prostate diseases
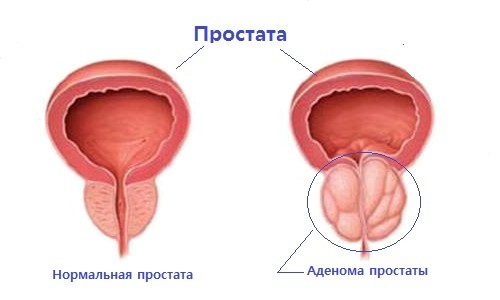
Among tumorous prostate diseases, cancer and prostate adenoma should be noted. In this case, adenoma, in contrast to cancer, is a benign neoplasm.
Prostate adenoma is widespread in men of older age. A generally accepted theory that explains the development of prostate adenoma does not exist at the moment. The most common theory is the hormonal change in the body of a man, associated with the age factor. Also, the risk of prostate adenoma increases due to excess weight and atherosclerosis, stress and previous inflammation of the prostate gland.
Symptoms of prostate adenoma
The severity of symptoms of prostate adenoma depends directly on the size of the tumor and the degree of compression of the urethra. There are 3 stages of prostate adenoma:
- Compensated
- Subcompensated
- Decompensated
With a compensated stage, there is an increase in the difficulty of outflow of urine, which is accompanied by frequent urination with constant urges. Nevertheless, it is possible to empty the bladder to the end.
In the sub-recommended stage, there is a thinning and increase in the volume of the muscular layer of the bladder, leading to a loss of the ability to actively contract it. As a result, it is not possible to empty the bladder to the end. Urination occurs intermittently, with a thin sluggish stream. In the compensated and sub-recommended stages of the disease, there is a threat of acute urinary retention. In such a state, patients are completely unable to cope with poverty.
In the decompensated stage, the compensatory capacity of the bladder is completely lost. This may be a consequence of primary renal failure. Bladder contractions become so ineffective that even with additional effort it can not be emptied. At the same time, patients constantly experience severe pain in the lower abdomen and constant urge to urinate. Urine is released only by small, frequent drops.
The prostate gland is the second heart of a man, therefore, to prevent the development of advanced stages of prostate adenoma, men after the age of forty, it is recommended to undergo annual preventive examinations with the participation of a urologist.