GENERAL INFORMATION
In nature, there are more than 27 species of staphylococci. Most of them are completely harmless to humans. Separate "sad" niche in this variety of staph bacteria Staphylococcus aureus takes as one of the common causes of septic lesions of the human body at any age.
Facts about Staphylococcus aureus:
- Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus; S. aureus) - This gram-positive bacterium, which has the shape of a sphere or an oval. It refers to facultative anaerobes.
- This is the kind of pathogenic staphylococci to humans.
- Very resistant to adverse environmental effects, while not form spores as a result of a protective response to such influence.
- It tolerates drying, heating to 150 degrees, the effect of ethyl alcohol and hydrogen peroxide.

- Survival in hypertonic sodium chloride solutions. Consequently, the only microorganism which is able to exist in human sweat glands.
- Very vulnerable to the action of aniline dyes, e.g., the well known "green fodder."
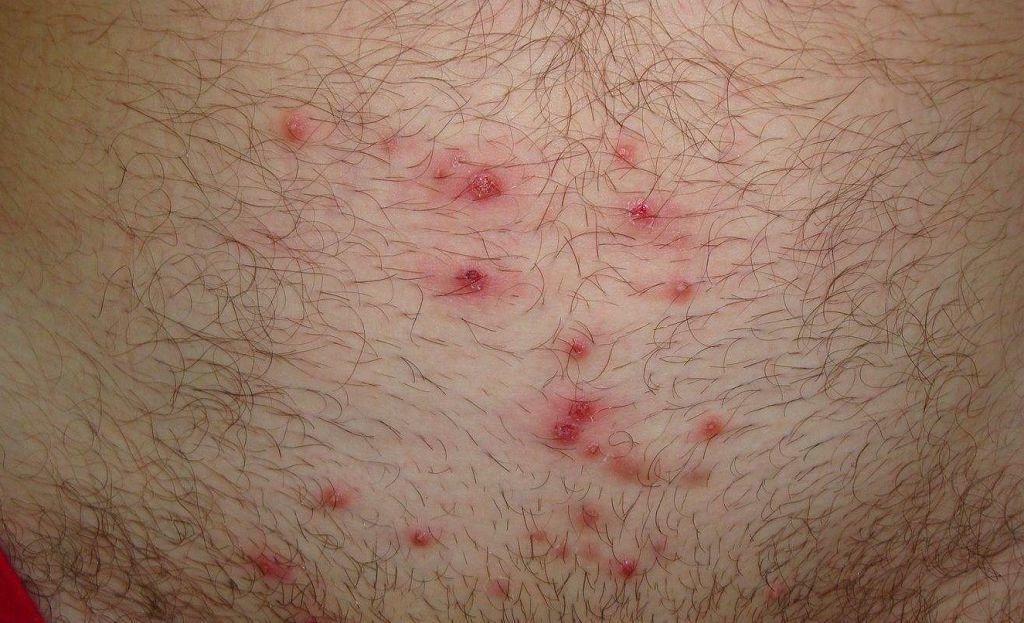
- Yields lipase enzyme, which dissolves the sebaceous plug into the mouths of hair follicles. This causes practically 100% detection at microbiological investigation and symptoms such aureus to the skin (furuncles, acne, barleys and t. D.).
- Coagulase enzyme, which is produced only by Staphylococcus aureus, causes the formation mikrotrombov in the bloodstream and protect the microbe from the human immune system factors. In this way the bacteria can penetrate almost all organs and systems of the human body.
- Staphylococcus aureus is able to produce the strongest action of toxins. They cause severe food poisoning, toxic shock syndrome (TSS) or some skin lesions in newborns.
- However obvious the pathogenic properties of Staphylococcus aureus are shown not always. He can be quite long-term "peace" exist in the skin and mucous membranes in the intestines and in the vagina in women.
- According to statistics, about 40% of the population are asymptomatic carriers of the microbe.
- Almost 120 known diseases that are due namely Staphylococcus aureus.
- Most often, these diseases occur in infants and immunocompromised individuals.
- Staphylococcus aureus tops the list of pathogens of nosocomial infection.
WAYS OF INFECTION
The source of infection staphylococcus infection can be a sick person or bacillicarriers.
Risk factors for staph infection:
- Any damage to the skin and mucous membranes - cracks, abrasions, punctures, etc...
- Failure to comply with the basic rules of personal hygiene.
- Primary or secondary immunodeficiency, such as AIDS.
- Prematurity.
- Prolonged use of antibiotics, immunosuppressive drugs or hormones.
- Adverse environmental factors.
- Chronic somatic disorders, e.g., diabetes, thyroid disease, and so on. D.
- Acute and chronic infectious diseases of any localization, as well as other pathological conditions.
SYMPTOMS
The manifestations of infection with Staphylococcus aureus depend on the implementation of the place and the aggressiveness of the pathogen and the immune system of the patient.
Staphylococcus aureus is able to destroy virtually all tissues of the body - from the skin to the peritoneum and internal organs. It can also be the cause of the common blood infection.
The most common diseases caused by S. aureus:

- Various pustular skin lesions - pyoderma. According to the depth of the inflammatory lesions distinguish folliculitis, boils, carbuncles, abscesses and cellulitis.
- Purulent mastitis in lactating women.
- Lesions of the upper respiratory tract - rhinitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, etc... The main symptom of Staphylococcus aureus in these cases is the presence of purulent discharge from the nose and throat.
- Bronchitis, pneumonia and pleurisy. Staphylococcal pneumonia occurs especially hard. Pronounced intoxication symptoms, chest pain, as often in the pathological process involved and pleura. Characterized by the formation of purulent foci (abscess) in lung tissue, which can break into the pleural cavity - empyema.
- This pathogen - the leading cause of purulent lesions of the musculoskeletal system (arthritis and osteomyelitis). Such conditions often develop in adolescents. In adults, staphylococcal arthritis are often formed on the background of existing rheumatism or after prosthetic joints.
- The defeat of the inner lining of the heart - endocarditis. It occurs in about one in ten patients with bacteremia. In the short term there is a destruction of the heart valves with the occurrence of severe complications and a high rate of deaths.
- Toxins that produces Staphylococcus aureus, sometimes cause severe intoxication of the human body - food poisoning, TSS and others.
- The first symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus food poisoning usually appear within a few hours after eating contaminated food. Nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, watery stools. Usually these symptoms disappear on their own within a day.
DIAGNOSTICS
Credibly claim that it is Staphylococcus aureus, only on the basis of clinical manifestations in most cases impossible, since the symptoms of this infection are non-specific.
Accurate diagnosis allows to establish bacteriological crop discharge from lesions followed by microscopic examination. When this is carried out and determination of the sensitivity of the microbe to the effects of antibiotics.
On nutrient media Staphylococcus aureus forms a smooth convex unclear colonies about 4-5 mm in diameter. Such colonies are painted in different shades of yellow, which causes the pathogen name.
TREATMENT
Staphylococcus aureus treated comprehensively.
Principles of treatment of Staphylococcus aureus:
- Suppression of microbial growth. Various antibacterial agents and staphylococcal bacteriophages.
- Antibacterial agents are the basis of treatment. It is highly desirable, if possible, use the antibiotics to which the identified type of sensitive Staphylococcus aureus.
- The most commonly used drugs of penicillins (semi-synthetic, combined with clavulanic acid and t. P.). It is also widely used aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones, macrolides, tetracyclines, and so on. d.
- Required local treatment is carried out and antibacterial agents in the form of ointments, creams, lotions and the like. N. Typically, such surgical procedures are assigned after readjustment infection foci and evacuation of pus.
- Correction of the immune status of the appointment is made immunomodulators, antioxidants, vitamin complexes, and so on. D.
- For specific immunotherapy using anti-staphylococcal immunoglobulin and plasma.
- Be sure to carry out full treatment of comorbidity, which reduces the reactivity of the organism.

Cure Staphylococcus aureus - a very difficult task. This microbe very quickly forms a resistance (resistance) to many antibacterial agents. This is associated with uncontrolled use of antibiotics in cases where they are not needed.
It is important to remember that the antibacterial treatment of staphylococcal infection should be carried out only in the presence of its manifestations. "Positive" test for Staphylococcus aureus in an apparently healthy person - is not a reason for prescription of antibiotics.
COMPLICATIONS
The main complication is the formation of Staphylococcus aureus purulent foci of various localization. Hit the pathogen into the systemic circulation is fraught with the development of severe conditions seriously threaten the health and even life (sepsis, endocarditis, meningitis, and so on. N.).
For example, the localization pustular formations on the facial skin, Staphylococcus aureus from the bloodstream can be entered in the meninges and the brain to form a brain abscess or meningitis.
PREVENTION
The basis for the prevention of staphylococcal infection is to increase non-specific immunity. It is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, good personal hygiene, eat right and give up bad habits.
It is important to timely diagnose and treat all somatic and infectious pathology.
FORECAST FOR RECOVERY
Prognosis depends on the localization of the foci of staphylococcal infection, disease severity and treatment efficacy.
When lung lesions of the skin and mucous membranes prognosis is almost always favorable. With the development of bacteremia visceral outlook is deteriorating as more than half of the cases are fatal condition completed.
Found a bug? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter