Overview
Chickenpox - illness, which is characterized by typical for papulovezikuleznyh appearance of rashes and fever. Rash affects only the surface layers of the epidermis and, if it does not disturb trace extends as human recovery. But if you tear off papules nails, then their place is formed atrophic scar that will remain on the skin for a lifetime.
Calling it Varicella Zoster virus of the family gerpevirusov It affects mainly patients of preschool and school ageBut sometimes it can be a target, and a grown man, not ill with chickenpox as a child and has no immunity. The virus is resistant to the effects of the environment and dies quickly outside the body, so you can catch them only in direct contact with the carrier.

Susceptibility to varicella extremely high - it is 100%, which means that when the virus enters the body disease necessarily manifest itself at the end of the incubation period. Disease are particularly susceptible children from 6 months to 10 years. A person who has had chicken pox once, develops stable immunity for a lifetime, so
it is impossible to re-infestation. The exception is immunodeficiency: a patient suffering they may have had chickenpox more than once, with chickenpox, most likely, will take place in different forms.After recovery, the virus does not die completely - place their lifelong localization he chooses neurons of spinal ganglia, trigeminal ganglia and facial nerves and cranial nuclei nerves.
Like all members of the group Herpesviridae, it has a negative impact on the state of the immune system, which is why some body loses its ability to resist viral infections. I had been ill with chickenpox and age of patients who received immunity Herpesviridae can manifest itself in the form of shingles.
Causes
The causative agent of chicken pox virus is one of the family Herpesviridae (gerpevirusy) having a high level of volatility (up to 20 m) and transmitted by airborne droplets. The incubation period is quite long - a person who has visited in contact with the patient, the first symptoms of chickenpox can appear only on the 10-21 th day after that. ATViruses are spread very quicklySince the carrier is unaware of what is epidemic danger. Danger of infection disappears only after a patient goes completely rash.
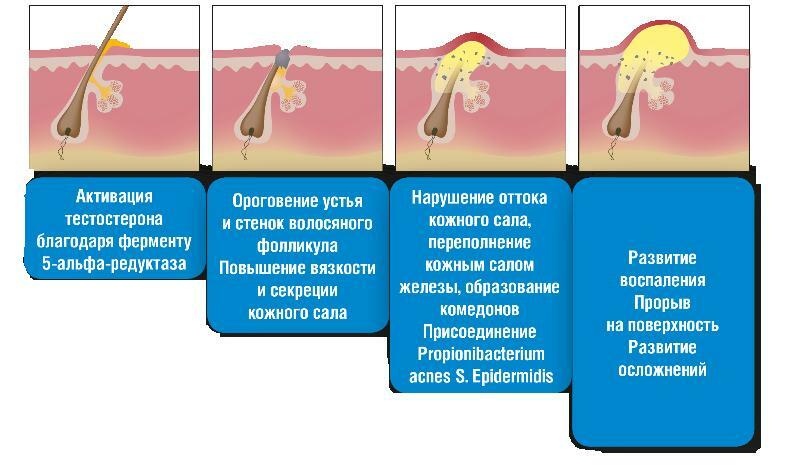
After the virus enters the body focuses on the mucous membranes of the nose, throat and begins to proliferate there. Lymph and blood stream carries it throughout the body, and after reaching a critical number begins to show symptoms. Infection affects mainly the skin - spinous layer of the skin and mucosal epithelium.
Classification
Doctors are two types of windmills: typical and atypical. They are different symptoms, and the severity of the diagnosis, and are divided into the following types:
- Typical chickenpox mild: fever to subfebrile level (37,1-38ºS), a small number of lesions.
- Typical chickenpox in secondary form: Body temperature may rise to febrile (over 39ºS), abundant rash, headache, general weakness, the possible presence of minor signs of intoxication (dehydration, vomiting, diarrhea, increased blood acetone levels).
- Typical windmill in severe fever, a large number of itchy rashes, pronounced signs of intoxication, seizures, high risk of developing complications.
- A rudimentary form of atypical chickenpox: very mild symptoms (body temperature up to 37 ° C, two or three lesions), or complete lack thereof. Often, the patient is not even aware that they are infected.
- Gangrenosum form atypical chickenpox: against high temperature and considerable deterioration - damage soft tissues, their immobilization appearance suppurations.
- Hemorrhagic form of atypical chickenpox: serious illness, often ending in death. It characterized by lesions of the vascular system of the whole organism.
- Generalized form of atypical chickenpox: multiorgan failure, at which all the organs cease to function fully. Most often it occurs as a complication of severe typical chickenpox in adults against the backdrop of a strong decrease in immunity (eg HIV-infected patients).

There is a differentiation of reinfection. Its atypical forms (except for rudimentary) patients often suffer from teenage and older. Typical forms of chickenpox are typical for toddlers and primary school age. As for the mild form, rudimentary, it is mostly found in infants.
symptoms
Doctors distinguish the following four periods during a typical varicella:
- incubatory period of chickenpox: from the moment when the virus enters the body. It takes an average of 14 days, During which the patient does not feel any changes in the body. Capable of catalyzing the incubation period attachment or other respiratory viral infections - in this case, it may shrink to 5-11 days.
- Prodormalny period of chickenpox: keeps for 1-2 days after the first symptoms. Expressed in a slight increase in temperature, aching joints, headaches. Sometimes the patient may suffer from eating disorders in different forms. At this stage misdiagnosed SARS chickenpox can be delivered to the patient. Prodormalny period appears not at all - quite often the disease immediately declares himself an acute onset.
- period rashes: normally occurs 2-3 days. By this time, the patient's condition can be normalized or worse depending on the form of chickenpox. The rash appears chaotic, affecting virtually the whole body: head, face, chest, arms, legs, stomach, back. There undulating rashes - hitting one area of the body of the patient, it may stop and the following papules begin to appear after 24-48 hours on another portion thereof.
- During the formation of crusts: papule form initially has a sufficiently large diameter (5-10 mm) spots, which is transformed quickly into a vial circular or oblong shape with a transparent liquid inside. In this form it It lasts about 2-3 daysAnd then it begins to dry out. It is the most difficult stage of the disease to the patient, who may torture him even more than other symptoms. Podsyhaya, pimple starts to itch and the natural desire of the patient to scratch her. To do this, you should not - if the tear dried up crust prematurely, in its place formed a noticeable scar. If the crust to fall itself (usually 6-8 days chickenpox disease), there are no traces in its place will be.
Diagnostics
To date, the differential diagnosis of typical chickenpox is not required, because the disease is easily distinguished from the similar diseases (herpes zoster, measles, rubella, scarlet fever, atopic dermatitis), appearance of rashes and location.
Positive role in the diagnosis of chickenpox plays that character rash appearing chickenpox, significantly differs from insect bites - lice, fleas, wasps.
With regard to laboratory diagnostic methods, then they may resort only under certain atypical forms of the disease - it is enough to do a blood test to detect gerpevirusa. There are also more sophisticated techniques such as light microscopy, as well as serological tests RSK and HI, but need use them appear very rarely, because most often the doctor for a correct diagnosis rather general clinical picture.
Treatment
Like all viruses that can penetrate into the body at the cellular level, Herpesviridae virtually unaffected by antiviral drugs. Therefore, the varicella-zoster therapy is aimed primarily at minimizing the risk of complications, and the second - to facilitate the patient's condition.
In the list of appointments are usually present:
- interferon - a drug capable of completely or partially prevent the occurrence of rashes strong accelerating their drying up and falling crusts;
- nucleosides;
- drinking plenty of fluids;
- humidification;
- antipyretic;
- bed rest for the entire period of poor health.
For surface treatment of the skin can be any available antiseptics: brilliant green, fukortsin, weak solution of potassium permanganate. This helps the bubbles as soon as possible to mature, dry and fall off, helps prevent scratching papules and recording their bacterial infection.
prevention

Despite the speed of its spread, gerpevirus - very weak organism. Outside the body, he is able to live only 10 minutes, and then dies. Good preventive measure is chickenpox and treatment of solid surfaces with solutions of soap, frequent washing of upholstered furniture, curtains, other interior textiles. All this must be done in the room where the sick as often as possible.
When a significant distribution of chicken pox in kindergartens and schools they can be quarantined for up to 21 days. The patient does not require special insulation.
Vaccine causes chickenpox virus vaccines can be carried out, but this is rarely done (for example, if Child found serious damage to the central nervous system or a history of autoimmune present disease).
complications
Moderate and severe forms of the typical chickenpox can be fraught with complications such as:
- cereals;
- meningoencephalitis;
- abscess;
- stomatitis.
Although chickenpox disease is usually characterized by mild, in adult patients, it is very rarely can give complications in the different organs, in rare cases may lead to death.
Forecast
Chickenpox It has positive forecasts - with timely treatment to the doctor, the correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment of the patient getting better at 3-7 day illness. However, during this period he was still infectious and should stay at home. the patient's skin is completely cleared of crusts after 15-20 days after the onset of rash.
Found a bug? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter