 Tuberculous meningitis is a secondary inflammation of the spinal cord and brain membranes in people with tuberculosis of various organs.
Tuberculous meningitis is a secondary inflammation of the spinal cord and brain membranes in people with tuberculosis of various organs.
This disease, rare at the present time, affects mainly people from 40 to 65 years, as well as children under 5 years, although this happens rarely, since children are necessarily vaccinated against meningitis.
The causative agent of the disease is mycobacterium tuberculosis. This form is particularly difficult, because the body was previously stricken with tuberculosis - the immune system has weakened, there is no strength to fight the "scourge".
Contents
- How is the infection transmitted
- It should be distinguished - a variety of diseases
- Babies in the risk zone
- Features of the clinical picture
- Objectives and methods of diagnosis
- Medical care
- Conservative medicine
- Traditional medicine
- Is it dangerous?
- For the prevention of
How is the infection transmitted
? The cause of the disease is a tuberculous meningitis infection from patients with tuberculosis organs: lungs, bones, genitals, breast, kidneys, larynx and others. Contact with infection is rare.
In the presence of tuberculosis of the bones of the skull or spine, the infection can pass to the membranes of the brain. Approximately 17% of cases are infected through lymph.
The risk factors for the development of the disease include:
- age - in the elderly and children under 5 years of age, a weak immune system;
- seasonality - autumn and spring are a period of epidemics;
- other body infections, intoxication, head trauma .

There are different types of
disease. Tuberculosis meningitis has different forms, characterized by symptoms and appropriate treatment:
- Basal - has cerebral meningic symptoms in the form of impossibility to tighten the head to the breast due to hardening of the occipital muscles, violation of cranial innervation and reflexes of tendons.
- TB meningoencephalitis is the most severe form of the disease, there are brain and meningeal symptoms( vomiting, headache, limb paralysis, etc.), as well as hydrocephalus and abnormal cranial innervation.
- Tuberculous leptopachymeningitis - is extremely rare, at the beginning of the disease there are almost no symptoms or they are not noticeable.
If one or more symptoms are found, having a provoking factor( tuberculosis of one of the organs), you should immediately seek medical help from a doctor. Tuberculosis meningitis is dangerous due to its complications and adverse consequences.
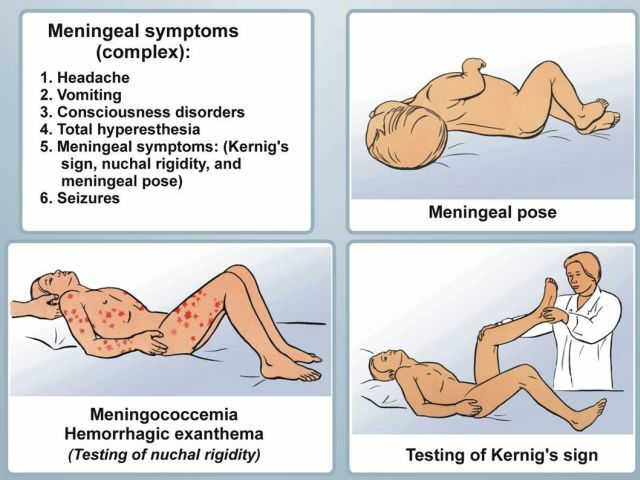
Meningitis symptoms
Babies at risk
More often tuberculous meningitis develops in young children due to lack of formed immunity or parents' refusal from 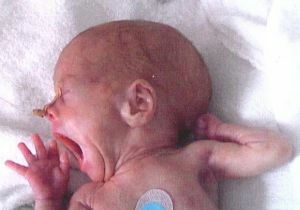 vaccination against tuberculosis.
vaccination against tuberculosis.
Mainly infants, weakened and premature infants, and children from 3 to 5 years old. Only in children until the year the disease begins in an acute form, the temperature rises sharply, vomiting, convulsions begins, hydrocephalic syndrome and bulging of the large fontanel are noted.
In children older than one year, it usually starts all with malaise, decreased appetite, drowsiness. Then the temperature rises, and vomiting begins - this happens within a week. Usually meningic symptoms appear after 1-3 weeks.
Features of clinical picture
Symptoms of tuberculous meningitis are divided into three stages:
- The prodromal period - lasts up to 6-8 weeks. Symptoms appear gradually: apathy, lethargy, drowsiness, weakness, dizziness and frequent headaches, which gradually become stronger, the temperature rises to 38 degrees, nausea and vomiting begin.
- Irritation period - signs of the disease intensify, the temperature grows, headaches in the nape, constipation, photophobia, intolerance of sounds, the appearance and disappearance of spots on the body. On the 6th-7th day of this period meningic symptoms occur: stiff neck muscles, Kernig and Brudzinsky's symptom, hearing impairment, vision problems, speech impairment, decreased limb sensitivity, hydrocephalus, increased sweating and salivation.
- The terminal period of is the last stage of the disease, paresis and paralysis begin, heart palpitations, loss of consciousness, difficulty breathing, temperature up to 40 degrees. The last stage of the disease ends with the death of a person.

In young children, the symptoms are similar to those in adults, only their development occurs in an acute form and the periods are shortened.
The main symptoms that are typical for tuberculous meningitis developing in children - on the 2nd day, convulsions, vomiting, fever, a baby crying, a fontanel swelling and pulsing may begin.
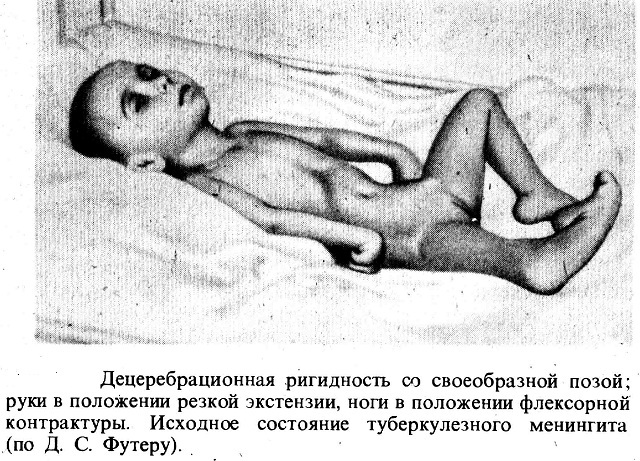
In older children, the disease occurs gradually, the manifestation of symptoms is blurred. Determine meningitis by the way the child lies, if he constantly lies on his side, tucked his legs to his stomach, and throwing his head back is a sure sign of the disease.
Objectives and methods of diagnosis
The diagnosis of this disease within 10 days is considered timely, after 15 days - late. The disease is determined on three grounds: the presence of symptoms, the definition of the source of infection and the study of cerebrospinal fluid.
Tuberculosis infection can be in any organ of the patient, therefore:
- on examination pay attention to the presence of tuberculosis of the lymph nodes;
- perform lung radiography, aimed at detecting tuberculosis;
- diagnose an increase in the liver and spleen;
- examination of the fundus is performed.
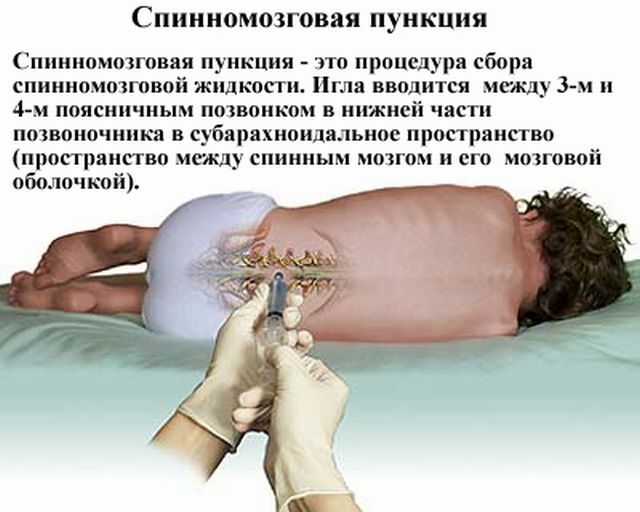
Selection of cerebrospinal fluid indicates tuberculous meningitis, if the liquor flows with a stream or rapid drops. A full study of the presence of changes in the fluid indicates an accurate diagnosis.
In addition, blood is taken for general and biochemical analysis, CT and MRI of the brain, lungs and other organs are performed.
Medical care
Therapy lasts a very long time and is conducted only in a hospital setting. After the treatment, which lasts up to a year, the patient is sent to a specialized sanatorium.
All treatment is aimed at destroying the tubercle bacillus and is carried out especially intensively against young children.
For example, if an adult patient is given the drug Streptomycin intramuscularly, the child needs to do this in the spinal canal, because in infants the disease proceeds in acute form, and the slightest delay can cost lives.
The aim of the treatment of tuberculous meningitis is to eliminate the focus of tuberculosis, therapy of inflammation of the brain envelopes and the exclusion of its edema, the prevention of complications, the relief of CNS lesions, and the removal of intoxication.
Conservative medicine
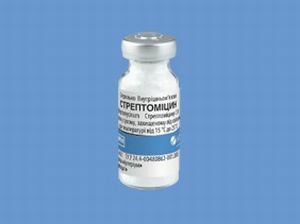 Treatment is carried out in a complex way with the use of preparations of specialized purpose: Streptomycin, PASK, Ftivazid and Salusid.
Treatment is carried out in a complex way with the use of preparations of specialized purpose: Streptomycin, PASK, Ftivazid and Salusid.
Complex treatment prevents the emergence of resistant makobaktery tuberculosis and has a beneficial effect on the removal of the inflammatory process, because all these drugs have anti-inflammatory effect. The combination and dosage is prescribed by the doctor depending on the severity of the disease, the tolerability of the drugs, the patient's condition.
Simultaneously, general restorative therapy is prescribed: glucose systems, vitamins C, B1, B6, aloe. When complications are prescribed drugs to eliminate them.
The patient is recommended a special diet and enhanced protein nutrition.
Dispensary follow-up is carried out for 2-3 years. Immediately after the sanatorium, the patient is enrolled in group 1 of the dispensary at the place of  residence and then is transferred to 2 and 3.
residence and then is transferred to 2 and 3.
Children are observed at the phthisiatrician during the year in group A, then 2 years in group B, and the last 7 years in group B. If notedcomplications, then the observation continues with a neurologist, an ophthalmologist, a psychiatrist. The first 2-3 years are preventive courses for 3 months with Isoniazid in conjunction with Etambutol.
Patients continue their working life if they do not have a disability. It requires light work, mental stress is unacceptable for a year after treatment.
Traditional medicine
Folk remedies in the treatment of tuberculous meningitis perform a supporting function and alleviate the suffering of the patient. But you can apply them by consulting with a doctor.
Recommended broths and tinctures of herbs: medinitsa, marshmallow, root elecampane. In the room where the patient is located, you can put a pot of glycinia - the phytoncides that it releases disinfect the air and kill the tubercle bacillus.
At home, to ease the patient's suffering, he should provide peace, both spiritual and physical, because he has a heightened sensitivity of hearing, sight and touch to the skin.
It is necessary to close the window with curtains, isolate the patient from sounds and touches to the body. On the head and limbs( hands and feet) put ice or rags, moistened with cold water, periodically changing them as they warm up. It is important to know that the patient should be hospitalized as soon as possible to immediately begin treatment.
Is it dangerous?
 The prognosis of treatment of tuberculous meningitis is favorable in 90% of cases, if the diagnosis is made on time. If the diagnosis is made after 15 days of illness, the consequences can be the saddest. If the patient was immediately taken to a hospital, a complete cure is possible even for young children.
The prognosis of treatment of tuberculous meningitis is favorable in 90% of cases, if the diagnosis is made on time. If the diagnosis is made after 15 days of illness, the consequences can be the saddest. If the patient was immediately taken to a hospital, a complete cure is possible even for young children.
A frequent complication is internal cerebral hydrocephalus, hemiparesis( paralysis of one side of the body), visual impairment, blindness. With the spinal form of meningitis, there may be paresis of the limbs and the development of pelvic pathologies.
In order to prevent
, the following preventive actions are recommended to prevent tuberculosis infection:
- vaccination before the 30th day of life;
- early diagnosis of patients who have entered into a relationship with the patient;
- isolating a patient with tuberculosis into a separate housing from an apartment building or hostel;
- observance of personal hygiene;
- regular examinations;
- passage of fluorography;
- moist cleaning of the room.
By observing the precautions, you can reduce the risk of infection. If all the same it happened, you should not self-medicate, but you should immediately call your doctor.