Atherosclerosis is characterized by signs of systemic arterial lesions inner shell, manifested in the form of metal transfer and atherosclerotic plaques, which are partially or completely cover the lumen and reduce blood flow to the tissues that are in the pool the affected artery. Before the treatment of atherosclerosis, read their simptomamy.
Overview
The basis of vascular wall muscle fibers constitute the outside it covers the connective tunica adventitia, inside - endothelium, which together with the subject thin layer of connective tissue forms the inner shell of the vessel - intima.
The endothelium possesses barrier function and pushes away cellular elements therefore do not normally occur in intravascular thrombosis. If the intimal structure is broken, migrate to the site of injury leukocytes from the blood stream and precipitated lipoproteins - the formation of atherosclerotic plaques begins.
Causes and symptoms of atherosclerosis
Unified theory of the development of atherosclerotic lesions does not exist, however, most scientists and clinicians starting point for the formation of plaques consider damage vascular endothelium and reducing its barrier function. The damaged portion of the inner shell becomes a target artery to atherogenic factors.

Elevated blood levels of low density atherogenic lipoproteins as It contributes to the progression of atherosclerotic lesions. At the initial stage of the damaged intima impregnated lipoproteins - atheromatous spot formed - the initial stage of plaque formation.
Nonlinear blood flow normally occurs in places of branching arteries, and when they spasm and increase in blood pressure can occur in any place. In this case, favorable conditions for endothelial damage, and for the deposition of lipoproteins.
Risk factors for atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis - polietiologichesky process. This means that for the emergence of the defeat must be a combination of several unfavorable factors, rather than one launcher.
In this case, most do not speak about the reasons of the disease and risk factors. These include:
- Smoking - nicotine provokes a spasm of blood vessels and negatively affect the barrier properties of the endothelium. Furthermore, chronic toxicity of nicotine results in a change in the ratio of atherogenic and neaterogennyh lipoproteins in peripheral blood, which is an additional reason for the formation plaques.
- poor nutrition, Alcohol and a sedentary lifestyle can lead to the causes disorders of lipid metabolism and obesity, as well as trigger increased blood pressure. The combination of the increased content of low-density lipoproteins and high pressure gives rise to the top of atherogenesis.
- emotional overload combined with reduced physical activity: the stress response (preparation of the body for intense physical activity). If this mechanism is not implemented, the effect of stress hormones is too long and causes damage to the endothelium.
- Age and Gender: Female sex hormones prevent damage to the vessel wall, so atherosclerotic vascular lesions occur more frequently in women after menopause. In general, with age increases the likelihood of developing the disease.
- Heredity: Some structural features of the endothelium and fat metabolism, inherited, create favorable conditions for the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
Classification
Depending on which factor is primary, isolated hemodynamic and metabolic form of atherosclerosis. In the first case, the primary vascular abnormalities (structural abnormalities, defective endothelium, arterial hypertension), In the second - metabolic disorders (increased levels of low density lipoprotein, hyperglycemia).
Depending on the course of the period divided into three phases:

- The initial phase (preclinical) occurs without symptoms. Changes in the vascular sheath is already taking place, but they are not sufficient to break the organ or tissue function. At this stage of atherosclerosis can be detected by laboratory parameters, so the biochemical analysis of blood on lipoprotein content is included in the list of studies, compulsory when passing preventive health inspection.
- Deployed phase of clinical manifestations, which, in turn, subdivided into:
- ischemic -sformirovavshayasya plaque partially overlaps the vessel lumen, thus suffering blood supply to tissues; at high load ischemic lesion becomes manifest; in relation to the coronary vessels - is coronary heart disease;
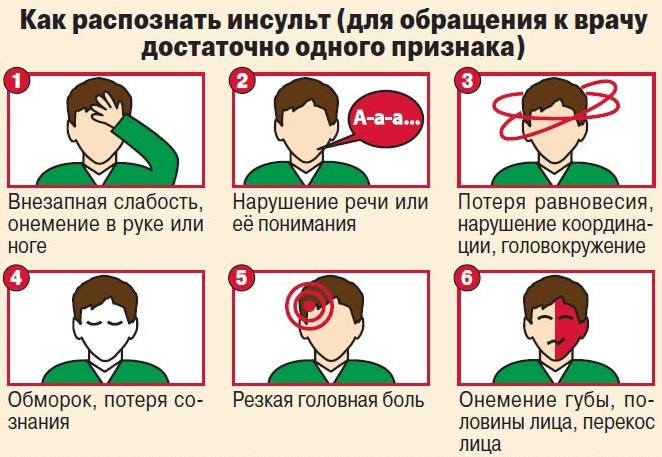
- trombonekroticheskuyu - overgrown atheromatous plaque easily injured, causing vessel thrombosis, wherein the tissue blood flow completely ceases, and it can necrotic; Example of clinical manifestations in this step is ischemic stroke or myocardial infarctionDry gangrene or mesenteric thrombosis.
- Sclerotic stage characterized by persistent vasoconstriction and progressive degeneration of the connective tissue, for example, cardio or cerebrovascular.
Depending on the activity flow atherosclerotic process is isolated:
- progressive atherosclerosis - the formation of new or continued growth of atheromatous plaques formed gradually compounded clinical manifestations, risk of complications - high;
- stable atherosclerosis - the development and formation of new plaque is suspended, clinical manifestations remain unchanged or regress, the risk of complications - low;
- retrogressive atherosclerosis - the clinical symptoms have subsided, the general condition improves and the laboratory blood values.
What are the main symptoms of atherosclerosis?
In the initial stages of the formation of atherosclerotic plaque is asymptomatic, violations of vascular permeability is not strong enough to cause clinical manifestations.
Circulatory disorders in the tissues start at the stage of fibrosis and calcification of the plaque and signs of atherosclerosis determined location of the lesion:
- atherosclerosis of arteries in the brain manifested chronic headache, memory impairment, decreased mental performance and concentration; progression of the process may lead to changes in personality and mental disorders; typical complication that occurs when a complete closure of the lumen of the vessel - ischemic stroke;
- atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries leads to the development of coronary heart disease; It is clinically manifested in the form of attacks of severe pain in the chest in the heart area after physical or emotional stress, as well as a decrease in physical performance; plaque can completely block the lumen of the coronary artery thrombosis or provoke it - in this case develops myocardial infarction;
- Atherosclerosis of the arteries of the abdominal cavity leads to a partial or total ischemia mesentery and intestine; in the first case concerned postprandial pain, bloating, and stool disorders, in the second - arises acute mesenteric vascular thrombosis - condition requiring emergency surgery;
- atherosclerosis of the aorta appears chronic hypertension; with prolonged duration of aortic aneurysms may occur.
Diagnostics
On the basis of the patient's complaints and changes identified during the clinical examination, a doctor may suspect the presence of atherosclerosis. To clarify and confirm the diagnosis appointed laboratory and instrumental studies:
- Blood chemistry on cholesterol. Using this method, defined as total cholesterol, and the ratio of the level of HDL and low density. The latter have a high atherogenic potential, therefore increasing their level, especially when combined with decrease in the level of high density lipoprotein, indicating active within atherosclerotic process.
- X-ray methods of investigation. Chest X-ray is performed in suspected aortic atherosclerosis, it can be used to judge the degree of deformation and the presence of calcification. To investigate the smaller vessels used angiography (coronary, cerebral angiography) - obtaining radiographs of the series after intravascular injection of radiopaque agents. With this research, you can see the location and size of plaques, as well as to evaluate the degree of narrowing of the vessel lumen.
- ultrasound often used to study the extremities, with its help you can also detect the presence of plaques and assess the degree of narrowing of the vessel.

treatment of atherosclerosis
Treatment of Atherosclerosis necessarily include lifestyle correction and flow control associated diseases (hypothyroidismDiabetes). If this is not enough, be appointed taking medication.
In lesions limbs, heart or vascular mesentery may restore their patency surgically.
Drug-free treatment of atherosclerosis
- A diet low in cholesterol. The best option is considered to be the Mediterranean diet. It is recommended to use olive oil, fish and seafood, vegetables, and fresh fruits and vegetables. Fatty meats excluded from meat dishes recommended chicken and lean beef.
- Rational physical activity contributes to the normalization of vascular tone, it is the best prevention of obesity and hypertension.
- Giving up smoking and drinking alcohol, to minimize the stress. It is very important to learn to deal with stress without the use of drugs and psychoactive substances.
- Correction of lifestyle - the basis of atherosclerosis therapy, without which no drugs and surgical methods will not be effective. For treatment using medicines that prevent the absorption of cholesterol in the digestive tract or accelerate its degradation. Selection of the drug and the dose should be carried out by the doctor.
Surgery
- Removal of the affected vesselIf the blood supply can be restored at the expense of the development of compensatory collateral. Most often it is the artery extremities of medium caliber. Remove vascular lesions at high risk of thrombosis, a blood clot separation and related complications.
- balloon angioplasty or coronary stenting is used in the defeat of the heart blood vessels to restore blood supply to the heart muscle during the critical supply artery lumen narrowing.
prevention
The only reliable method for preventing atherosclerotic vascular lesions - is healthy lifestyle. Studies have shown that the first cholesterol spots may appear on the walls of blood vessels in childhood, so prevention must begin in childhood.
Prevent complications have already developed atherosclerosis can be, if you take prescription drugs and follow the recommendations of the attending physician. If there are associated diseases, their treatment is also a mandatory measure in the prevention of complications.
The prognosis of atherosclerosis
Provided correct lifestyle, smoking cessation, and time begun treatment favorable prognosis: Stabilization and even regression of the atherosclerotic process are quite possible. Regression of atherosclerosis is possible only in the initial, pre-clinical stage. If any of the main symptoms of atherosclerosis has emerged, supportive treatment is lifelong.
Upon termination of the treatment and preservation of the risk factors the likelihood of complications becomes extremely high. In this case, the prognosis is for the health and life of the patient is unfavorable.
Found a bug? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter