Encephalopathy - a slowly progressive disease of the brain associated with abnormalities of the brain vessels that cause disorders in the central nervous system.
Vascular insufficiency results in uneven feeding of various areas of the brain. Deprived of oxygen and nutrients, they cease to perform their functions and are gradually destroyed.
When vascular encephalopathy observed in mental disorders and psycho-emotional sphere, it is also possible the development of movement disorders.
In practice neurologists disease is considered one of the most common. According to statistics, cerebrovascular disease detected in 5-6% of the population. Severe complications described syndrome is the development of senile dementia and ischemic stroke.
CAUSES
Encephalopathy develops against the background of diseases, contributing to a gradual decrease in the lumen of the arteries that provide blood to the brain. The syndrome progresses over the years and causes irreversible changes in the brain structures. The most vulnerable are the white matter and subcortical structures.
Provoking pathology:

- arterial hypertension;
- diabetes;
- atherosclerotic defeat of vessels of the brain;
- hypercholesterolemia;
- low back pain, spinal cord injuries;
- venous stasis of blood;
- vascular dystonia;
- arrhythmia;
- blood diseases;
- vasculitis.
Precipitating factors:
- genetic predisposition;
- body weight, exceeding normal levels;
- low physical load;
- brainwork;
- stress;
- smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages.
All these factors cause a violation of the blood supply to the brain, hypoxia and atrophy of its tissue. Discirculatory vascular encephalopathy is diagnosed in 2 times more common among hypertensive patients.
CLASSIFICATION
Cerebral circulatory encephalopathy classified on several grounds.
Form of the disease, depending on the etiology:
- atherosclerotic encephalopathy;
- hypertension;
- venous;
- mixed.
Forms in nature of the disease:
- slowly progressive or classic;
- rapidly progressive;
- remitting.
Isolated circulatory encephalopathy in which brain tissue progressive changes occur, accompanied by neurotic syndrome.
SYMPTOMS

Many middle-aged and elderly celebrate at fatigue and fatigue. In 65% of patients have a disorder of the emotional sphere in the form of depression. These symptoms are non-specific and changeable, so often are not the reason for seeking medical care. It is possible that these are signs of vascular encephalopathy, which should be identified and treated in the early stages of development.
The clinical picture of the disease depends on the affected area of the brain, and is described by the characteristic syndromes.
Symptoms of vascular encephalopathy:
- Pathological changes in the capillaries of the brain enveloping shell, chronic vascular encephalopathy appear as headache.
- With the destruction of subcortical areas shown fatigue, mild pain, drowsiness, ringing in the ears and mood swings.
- When changes in the gray matter of the notes aphronia, A person is difficult to focus, plan of action and to remember new information.
- The defeat of the pyramidal structures causes violation of traffic functions. This manifests itself in the human gait and facial expressions.
- With the destruction of neurons in the cerebral cortex the patient becomes overly impulsive.
- Necrotic changes in the subcortical layer frontal lobe provoke depression, apathy and inability to self-service.
- Abnormalities in the cortico-nuclear pathways outwardly appear involuntary movements of the lips of skin irritation.
- When the death of neurons in the occipital subcortical parts deteriorating eyesight.
Severity of illness
Depending on the severity of symptoms of encephalopathy is divided into a number of degrees.
The severity of vascular encephalopathy:

- first degree. At the first sign of vascular encephalopathy in a patient manifested emotional disorders such as tearfulness, depression and irritability. Sometimes it may appear headaches. Fatigue increases rapidly even after minor physical activity, mental abilities decrease.
- II degree characterized by the active progression of the symptoms described. There are signs of organic brain damage. The patient is disturbed coordination, developing pathological reflex, paralysis and paresis.
- III degree. Sick apathetic, his work is unproductive or non-existent. Probable epileptic seizures. Man can not serve themselves, needs the help of others.
DIAGNOSTICS
With the purpose of early diagnosis of vascular encephalopathy all persons at risk, regular check-ups are recommended by a neurologist. If the diagnosis of atrophy grade 2 enables to suspend the pathological process, then in the third stage marked changes in the nerve cells do not respond to treatment.
To identify structural and functional changes in a number of surveys carried out in the brain.
Methods of diagnosing vascular encephalopathy:
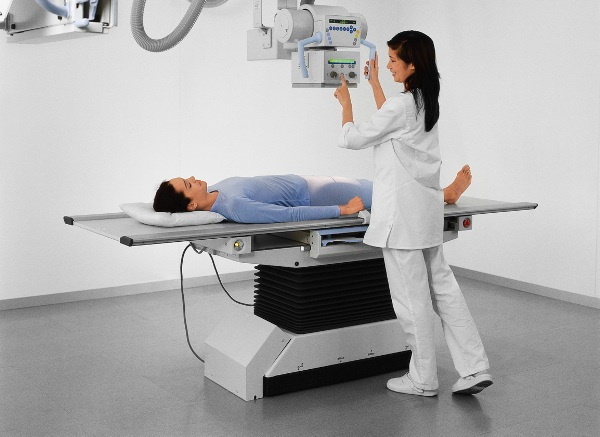
- computed tomography (CT, MRI);
- neurosonography;
- galvanotherapy;
- electroencephalography;
- rheoencephalography.
Tomography provides a clear picture of pathological changes at 2 and 3 stages of the disease. At diagnosis, doctors rely on MRI signs.
MR signs of vascular encephalopathy:
- the presence of atherosclerotic plaques (calcification);
- signs of hydrocephalus;
- vascular hypotensive inclusion.
Narrowing, occlusion, atherosclerotic changes in vessels may show nonspecific symptoms. Signs that it's encephalopathy, can be detected using Doppler ultrasound.
TREATMENT
Therapy should begin at the earliest stages of the disease, the first signs of vascular encephalopathy. Such measures are taken to prevent stroke and are in the nature of complex treatment.
At 1 and 2 step vascular encephalopathy treatment is aimed at restoring nerve cells and improving the cerebral circulation. The key to successful treatment is also the stabilization of blood pressure and normalization of lipid metabolism. To do this, assign a number of drugs and physiotherapy.
Drug treatment of vascular encephalopathy:

- Antihypertensive drugs, lowering blood pressure.
- Venotonics - to increase the tonus of vascular walls.
- Nicotinic acid preparations to stimulate blood circulation.
- Statin drugs are recommended to lower cholesterol in the blood.
- Nootropic drugs increase the activity and conductivity neurons.
- B vitamins have a positive effect on metabolic processes in the nerve cells.
- Antigipoksanty reduce the severity of hypoxia.
Physiotherapy vascular encephalopathy:
- UHF vessels in the neck;
- Galvanic currents on the collar zone;
- therapeutic radon, carbon dioxide and oxygen baths;
- electrosleep;
- acupuncture;
- using a laser.
Also pay attention to the observance of a low-calorie diet with the rejection of fatty animal products.
Medication and physical therapy may be effective until such time as symptoms of vascular encephalopathy not acquired features of the third stage of the disease.
Significant vasoconstriction caused by atherosclerotic or changes arising due to cervical osteoarthritis, is treated promptly to restore their patency.
Found a bug? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter