External form of otitis is a disease characterized primarily by inflammation in the external tissues of the outer ear and auditory canal. Otitis in the dynamics of development of the acute form, proceeds very painfully and in the absence of adequate treatment can go into a chronic stage. The risk group includes people of all ages, especially children due to the peculiarities of the structure of the ear canals.
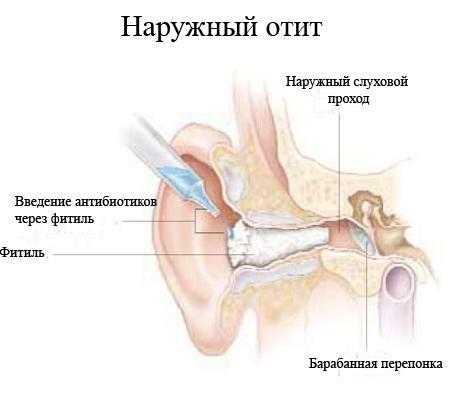
External otitis media: symptoms and treatment
Content of material
- 1 Types of external otitis and the causes of
- 2 Common causes of infectious and non-infectious types of external otitis
- 2.1 Causes of infectious otitis
- 2.2 Causes of non-infectious otitis
- 3 Symptoms of external otitis
- 3.1 Symptoms of limited otitis media
- 3.2 Symptoms of diffuse otitis media
- 3.3 Symptoms of hemorrhagic appearance
- 3.4 Symptoms of an erysipelatous disease
- 3.5 Symptoms of octomycosis
- 3.6 Symptoms of non-infectious otitis
- 4 Treatment of external otitis
- 4.1 Types of the disease and their treatment
- 4.2 Video - External otitis media: symptoms and treatment
External otitis media and causes of
External otitis media are divided into several types:
- limited form. The main reason is the formation of a furuncle filled with pus. It is localized in the region of one of the fat-removing skin glands or the hair follicle;
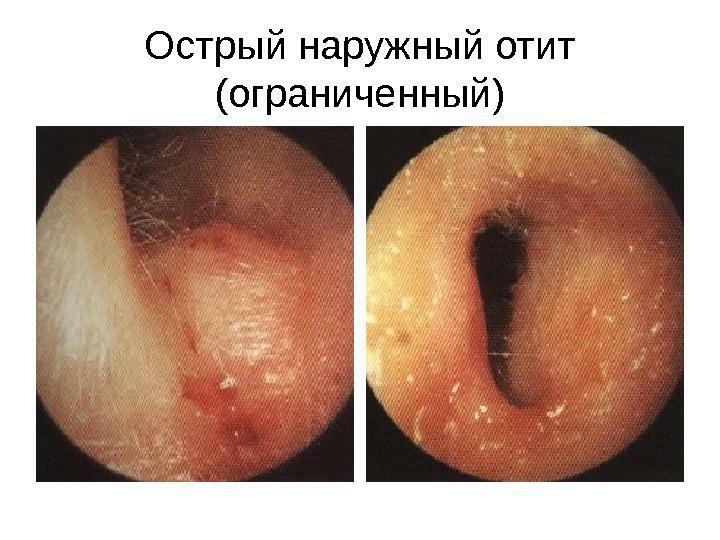
Limited form of otitis
- hemorrhagic appearance. It is formed as a concomitant disease;
- diffuse otitis media. Inflammation extends to the full length of the auditory canal;
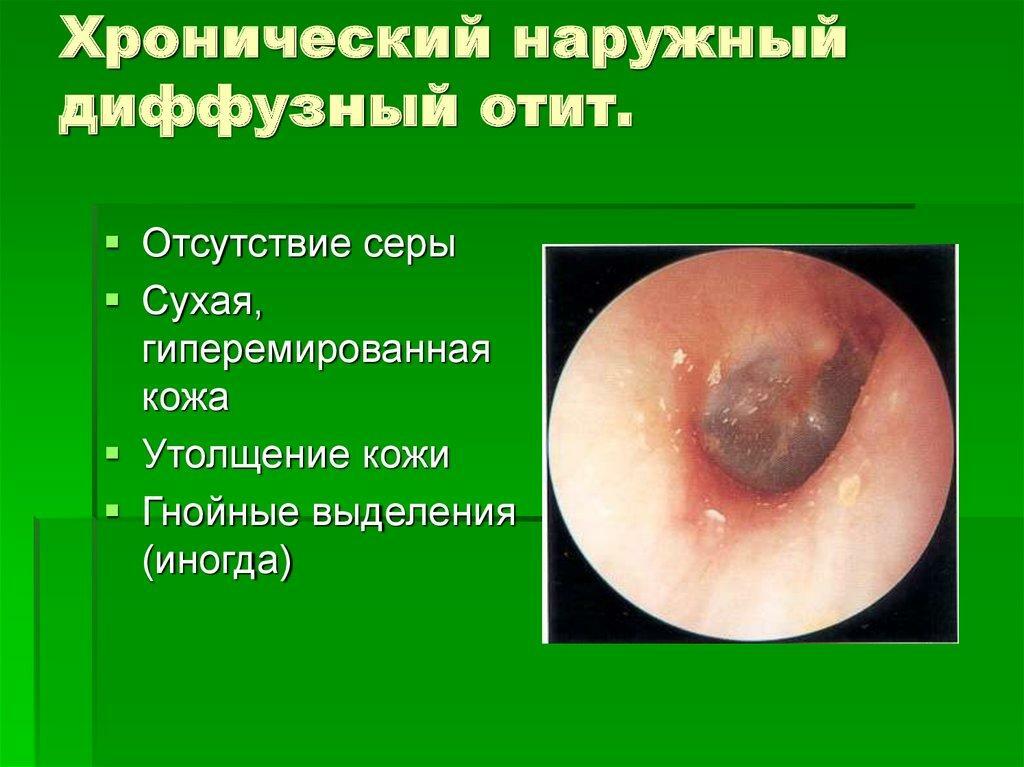
Diffuse otitis
- erysipelas is an erysipelas. Streptococcal infection;
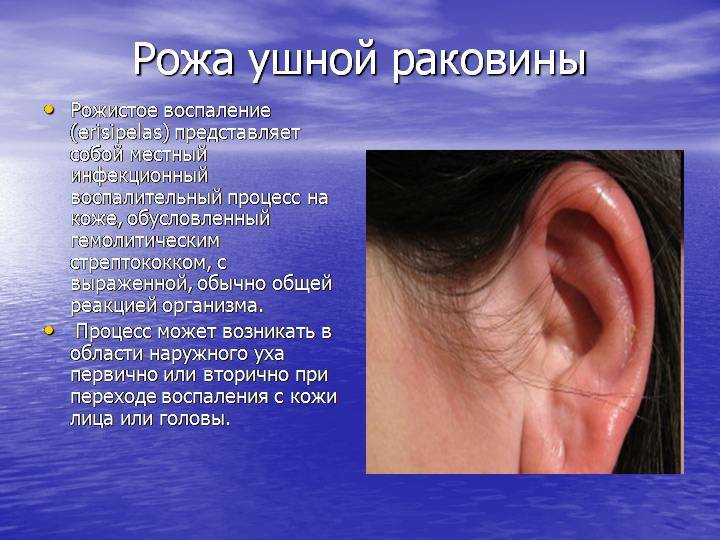
Erysipelas of the
- Otomycosis. Has a fungal etiology;
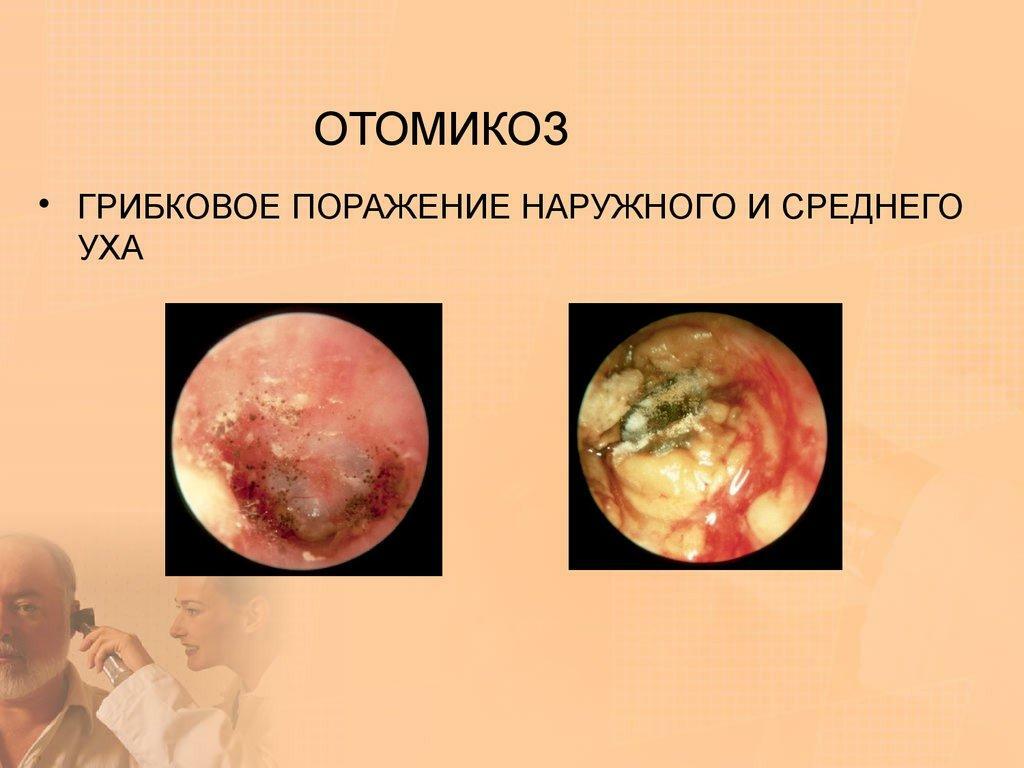
Otomycosis
- noninfectious external otitis media.
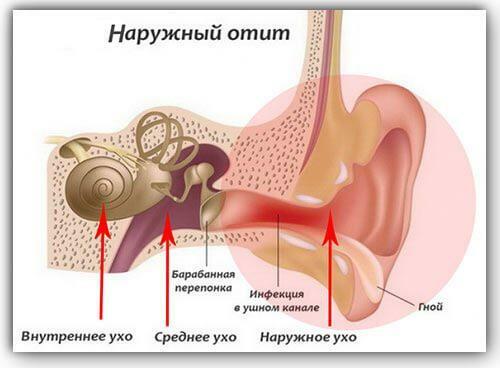
External Otitis
Common causes of infectious and non-infectious types of external otitis
The disease develops under the influence of pathogenic bacteria that enter the body in various ways. Microorganisms can be associated with a decrease in local immunity or due to infection of an external organ.
Causes of infectious otitis
Lack of adequate hygienic care for the ears, or improper cleaning of the surfaces of bone-cartilage canals. Outer shell parts need daily washing with soap and then wiping dry. This is one of the most important preventive measures to prevent ear inflammatory diseases. Daily cleaning with cotton buds, and even more with other sharp objects with attempts to penetrate as deeply as possible into the channels, injures the tissues and increases the risk of getting into them pathogenic bacteria. Ears can be cleaned no more than 2 times a week only by the devices designed for this purpose.
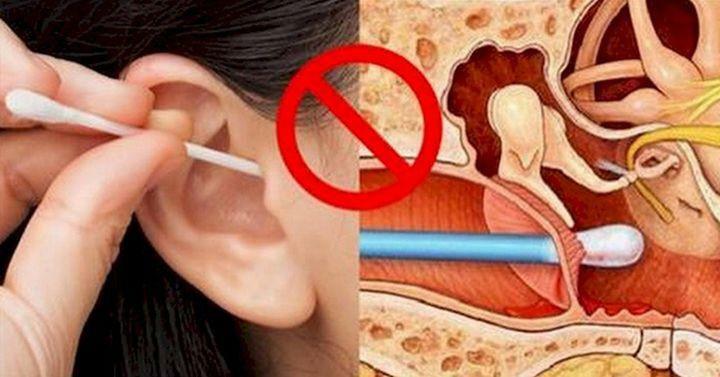
Wrong or too frequent cleaning of the ears can lead to otitis
Inside the ear of foreign objects and liquids. Wet environment is favorable for the development of infection. Items trapped in the auditory canal disrupt its normal functioning and cause trauma.

Water entering the ear can cause infection
Infections of the nearest organs. External otitis media, parotitis, purulent skin diseases, for example, furunculosis, can become the cause of the external form of ear canal inflammation.
Acupuncture of the ear
General decrease in the protective functions of immunity. Systemic and chronic damage to the body, viral diseases, excessive cooling - may be the cause of inflammation of the ear tissues. It also reduces the immune defense of long-term use of medications, such as antidepressants or antibiotics.

Otitis can be a consequence of other diseases
Violations of serous separation in the ear. With insufficient and excessive production of sulfur in the ear canal, an environment favorable for reproduction of pathogenic bacteria is formed.
Causes of non-infectious otitis
- Dermatological diseases such as eczema or psoriasis, allergies.
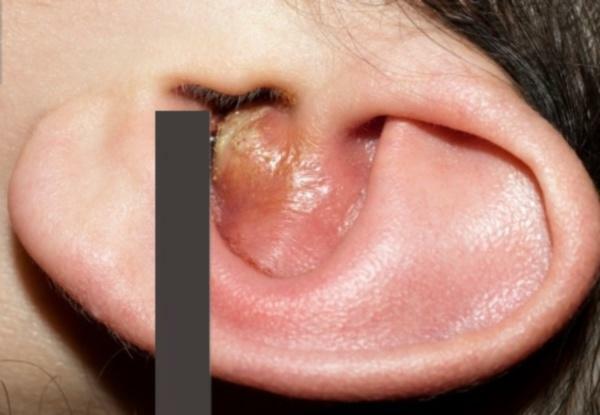
- Congenital pathology of the auricle - atresia. Characterized by proliferation of cartilaginous and bone tissue, narrowing of the aisles.
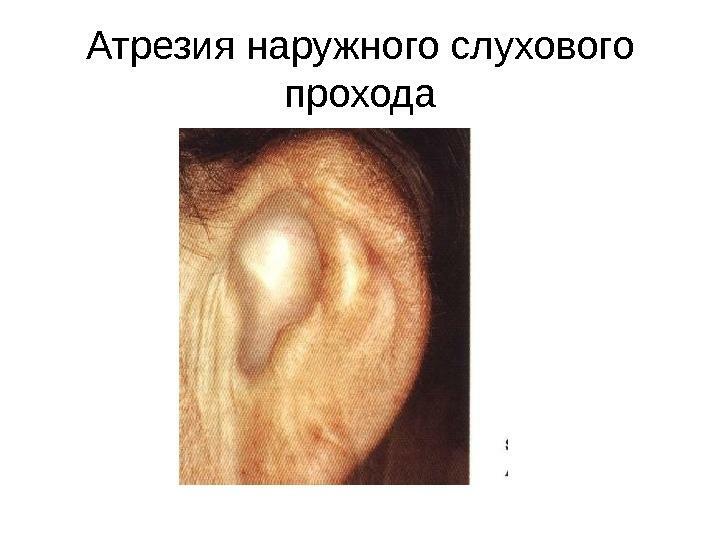
Atresia of the auricle
Symptoms of external otitis
Since external otitis has several types, its symptoms may vary depending on the form of the disease.
Symptoms of a limited form of otitis
- The ripening furuncle is often not visible to the naked eye and it is impossible to grope for it. The first warning sign is the itching inside the ear canal.
The first symptom of otitis is the itching inside the ear passage
- As the abscess develops, sharp and sharp pains radiate into the head and neck.

As the abscess grows, the pain begins to pour into the head and neck
- The intensity of pain increases with any jaw movement, head turns.

Pain is aggravated by movement of the head, jaw
- General feeling of malaise and fever. These two symptoms are individual and do not have strict indicators.

Possible temperature rise
- A few days after the onset of the disease, the boil may partially or completely open, causing pus to flow out of the ear canal outward. From this stage, all pain processes abate, and the patient feels better.
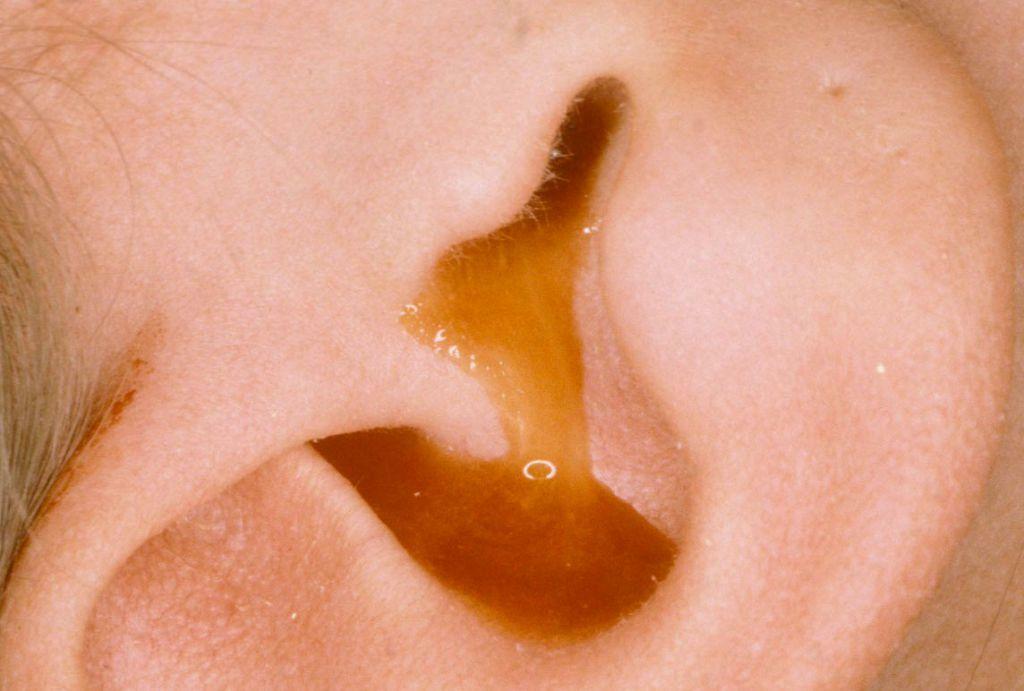
After opening the boil, the pus flows outwards
Important! The furuncle can be opened from the patient and without proper treatment, but the lack of adequate therapy can lead to the spread of infection to the middle ear.
Symptoms of diffuse otitis media
- As well as in limited form, the disease begins with an obsessive itchy sensation.
- The soreness is typical for palpation of the outer parts of the ear and the opening of the ear canal.
- Covers of tissues inside the auditory canal are swollen and acquire a reddish hue.
- Purulent discharge from the auricle.
- The patient feels uncomfortable, chills and weak.
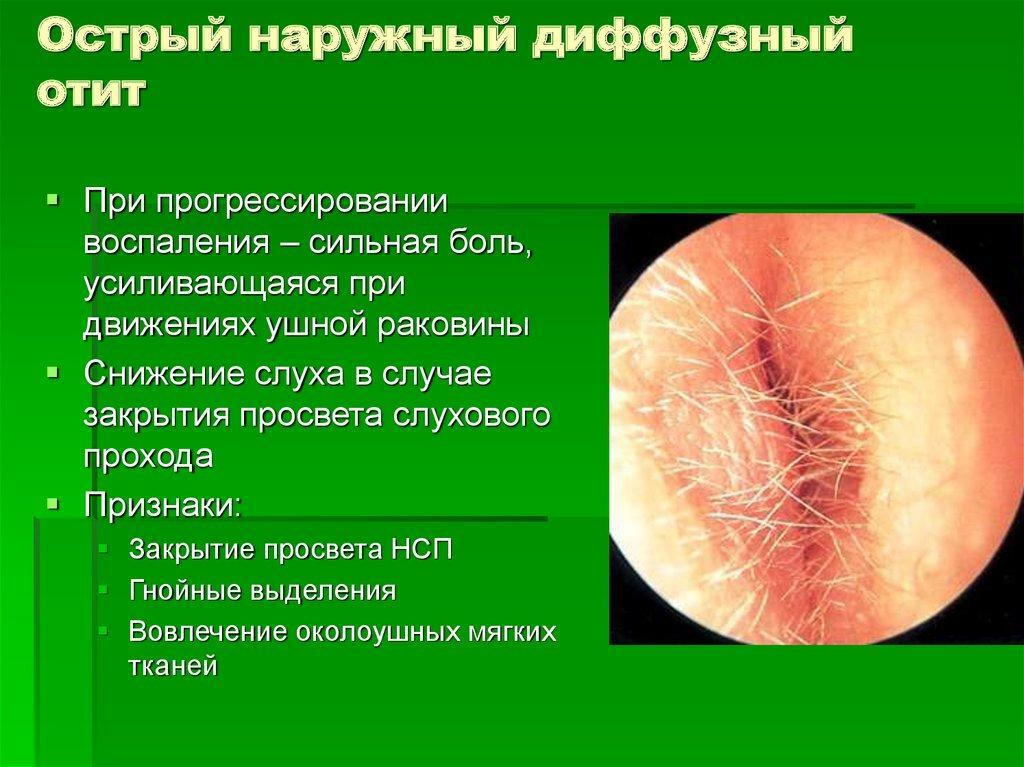
Symptoms of diffuse otitis
Symptoms of hemorrhagic appearance
- Deterioration in the quality of perception of the frequency of sound and stuffiness in the ear.
- Severe pain syndrome during palpation of the cartilage of the auricle and pressure on the tissues around it.
- Reddish hue of the inner walls of the channels. With the spread of edema, the outer layer of the epidermis of the eardrum acquires the bluish color of
- .
Help! The hemorrhagic form of otitis appears as a concomitant disease. He is preceded by such diseases as influenza, SARS.

Hemorrhagic form of otitis - a concomitant disease, the precursor may be the flu
Symptoms of the erysipelas of the disease
- Acute pain and severe itching.

The first symptom is acute pain and severe itching.
- Swelling and redness of ear tissue.
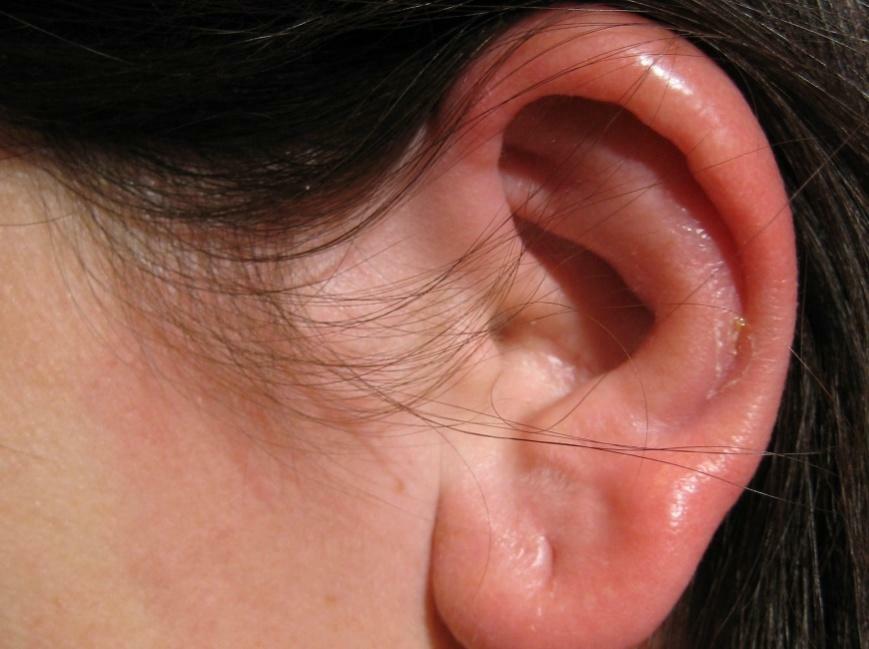
Swelling and redness of the ear
- Sensation of "hot skin" in the area of inflammation, local increase in temperature.
Local temperature increase, burning sensation
- Increased total body temperature. Can reach 40 degrees.
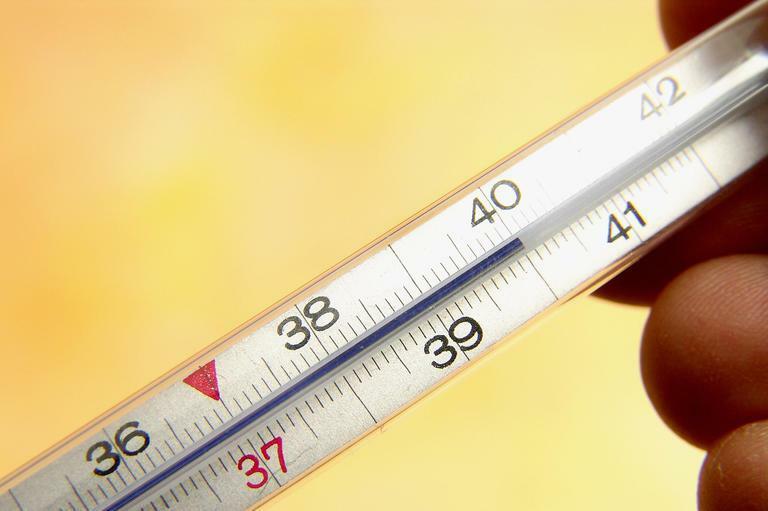

Body temperature can rise to 40 degrees
- Weakness and chills.

Appears weakness and chills
- In some cases, rashes in the form of watery blisters are formed on the auricle.
Help! This type of otitis often turns into a chronic stage with regular relapses.
Symptoms of octomycosis
- Pain in the ear canal and sensation of foreign matter.
- Noise in the ear and congestion.
- One-sided headache.
- Depending on the type of fungus that affects the tissues, the growths, characteristic for each case, are peels on the skin in the ear region.
- Allocations of their auditory meatus, corresponding to the type of fungus.
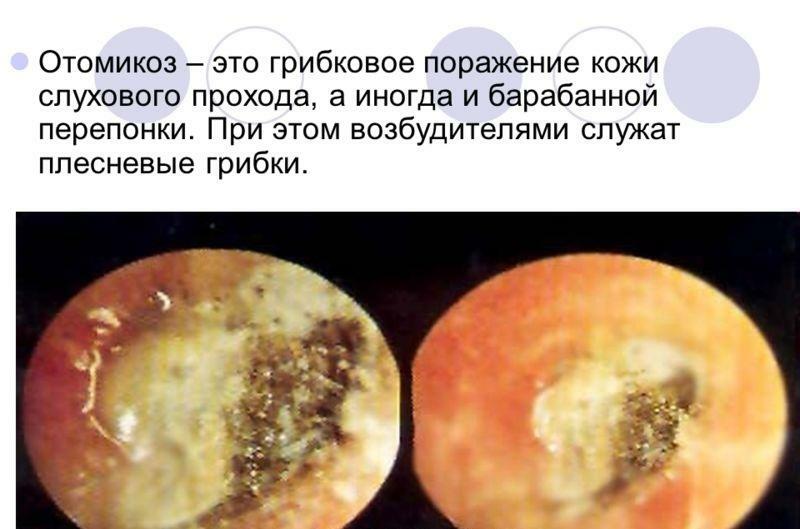
Octomycosis
Attention! Symptomatics has a dynamic growing character, in accordance with the depth and strength of tissue damage from the fungus. Without proper treatment, the disease will have a progressive nature.
Symptoms of non-infectious otitis
Symptoms such as pain, itching, and inflammation are similar to other types. In the case of atresia, connective cartilaginous tissues grow, thereby narrowing the auditory canals. Allergic reactions are characterized by rashes on the skin surface.
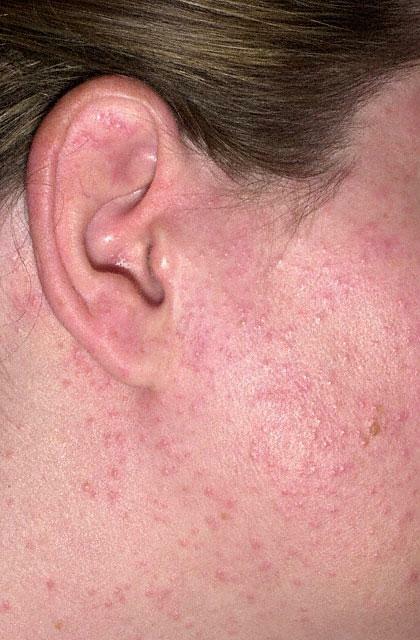
In case of an allergic reaction, rashes may appear
Treatment of external otitis
Otitis caused by pathogenic bacteria is treated with several medications and hygienic manipulations.
Attention! Do not engage in independent treatment. At the first symptoms of the disease, it is necessary to consult a doctor and use the prescribed means strictly according to the instructions. This will help to avoid relapses and complications.
To be treated by a special doctor, self-medication can aggravate the disease
Types of the disease and their treatment
Limited, diffuse and hemorrhagic otitis
- Antibiotics orally. Used to inhibit pathogenic bacteria causing inflammatory processes in the tissues of the ear canal and auricle. To identify the pathogen, tests are performed and an antibiotic is assigned to which the pathogenic microorganism is sensitive. Antibiotics of penicillin and cephalosporin series are often prescribed.

Amoxicillin
- Drops in the ear. These medications contain a local antibiotic and anesthetic. Also used are preparations in the composition that have an additional adrenal synthetic hormone, such as betamethasone. It has an anti-inflammatory and healing effect.
Drops in the ear
- At elevated temperature and pain, is prescribed antipyretic and analgesic. Usually it is paracetamol, ibuprofen or acetylsalicylic acid.
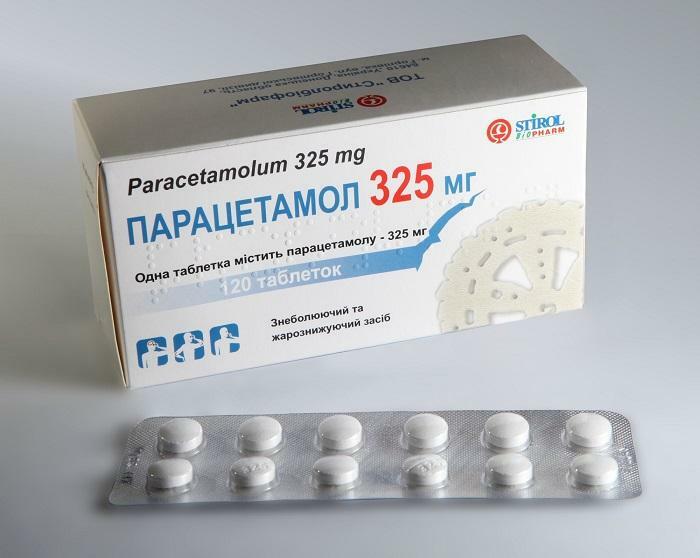
Paracetamol
- Therapy with ultraviolet radiation( UFO-therapy ).Has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect. The number of procedures from 10 to 15.

UFO-therapy
- Electromagnetic wave therapy( UHF therapy ).Improves the process of tissue regeneration and strengthens local immunity. Number of procedures from 5 to 15.
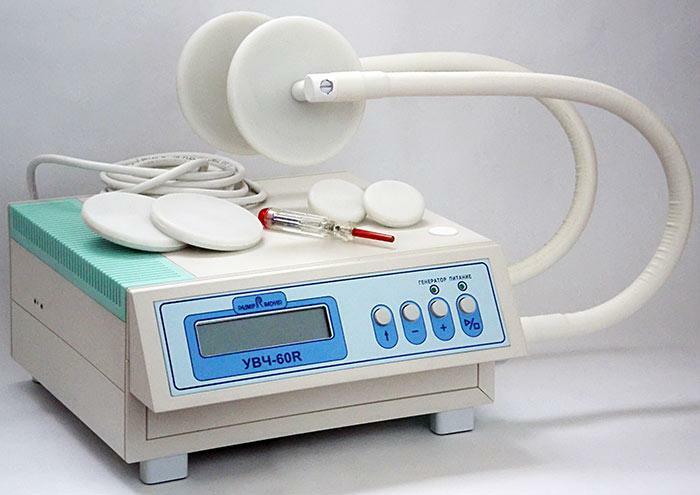
Apparatus for UHF therapy
- In the case of a purulent discharge, is prescribed to wash the ear canal with a furacilin solution .
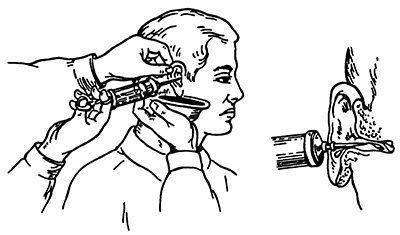
Flushing of the auditory meatus
- For rupture with a limited form of otitis, apply cotton swab dipped in a solution of boric acid and glycerin .
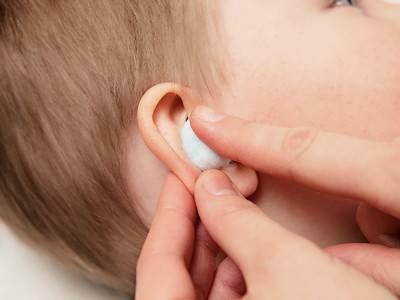
Cotton swab soaked in a solution of boric acid and glycerin
- For furunculosis, a self-blood transfusion - auto-therapy of can be prescribed.
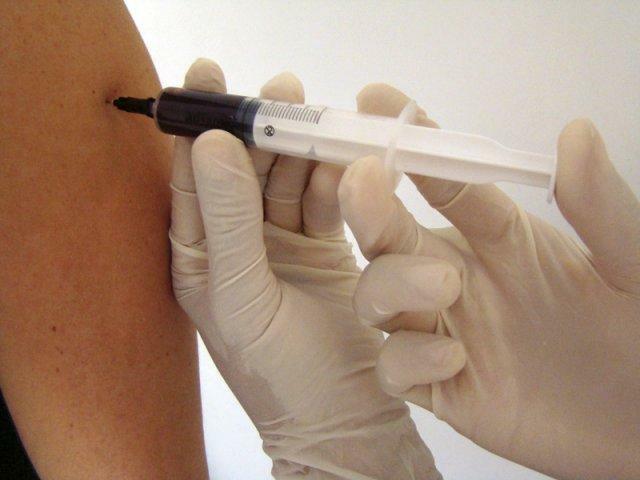
Autotherapy - introduction of the patient's blood into the muscle, under the skin
- If necessary, possible surgical opening of the boil.
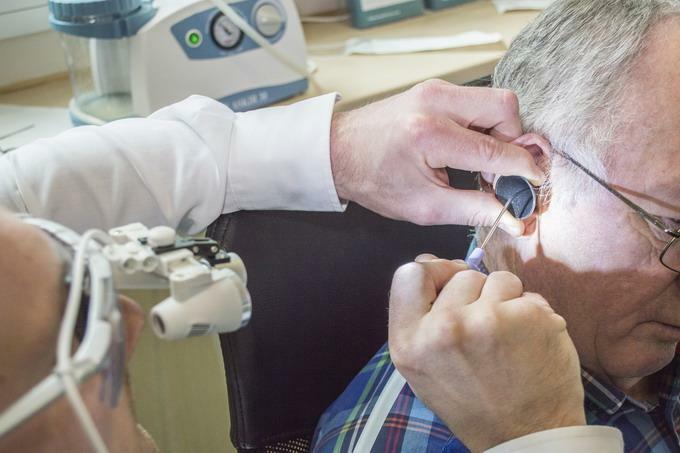
Surgical treatment of
Table 1. Fungal otitis
| Therapy | Description |
|---|---|
 Antifungal drugs | The basis of treatment for this otitis is antifungal drugs, or combined, which additionally includes adrenal hormones. Such preparations are used both in the form of creams, ointments, drops, and in the form of tablets. |
 Boric acid and silver nitrate | Additionally, in the treatment of this type of otitis boric acid and silver nitrate are used, as antiseptics and disinfectants. |
Table 2. Erysipelas
| Therapy | Description |
|---|---|
 Quarantine | This type of disease is contagious for healthy people, so the patient is recommended to be insulated for the duration of treatment. |
 Antibiotics | Treatment is performed with antibiotics and antibacterial agents. |
 Antihistamines | In addition, antihistamines are prescribed. |
 UFO-therapy | Physiotherapeutic treatment is prescribed in the form of UFO-therapy. |
Non-infectious otitis media
The basis for the treatment of dermatologically induced otitis media is the elimination of the underlying disease, which is the primary cause. Some chronic diseases that cause inflammation of the ear tissues are not treated completely, therefore, relapses of the ear canal inflammation are possible. One such disease - psoriasis, characterized by spontaneous flow, and having a complex and long-term treatment. In the case of allergies, antihistamines are prescribed.
Treatment of atresia is to restore the size of the hole and the cartilage of the ear canal. This is done surgically, a plastic channel is produced. It is also possible to establish devices for bone conduction, to restore the auditory function of the patient.
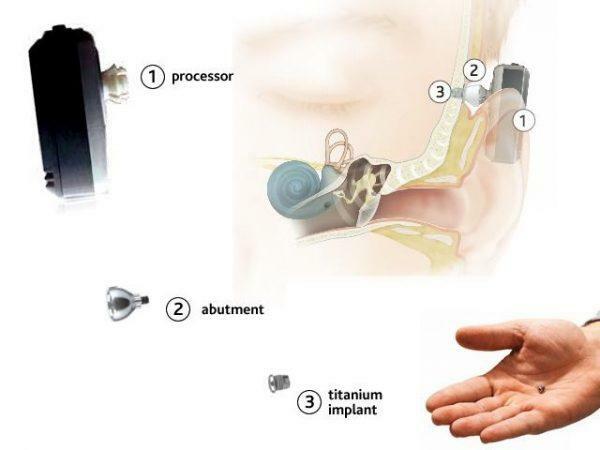
Headphones based on bone conduction sound
Help! When treating any form of otitis, vitamin products are additionally prescribed to improve overall immunity.