In genetics and neonatology under stigmas dizembriogeneza understand minor deviations that do not break the bodies largely or disfigure a person's appearance. In another way, they are called small anomalies of development.
In newborns, they serve as markers of physiological disorders formation of the fruit (or embryogenesis). These symptoms may indicate the presence of severe genetic diseases.
The content of the article:
- 1 Causes of stigma dizembriogeneza in newborns
- 2 Risk factors
- 3 When it is possible to observe the development of abnormalities in the child?
-
4 symptoms
- 4.1 Skull
- 4.2 Face
- 4.3 Eyes
- 4.4 ears
- 4.5 Nose
- 4.6 Mouth
- 4.7 Neck
- 4.8 trunk
- 4.9 Hands
- 4.10 Feet
- 4.11 Leather
- 5 Evaluation of the newborn state
- 6 Procedures after birth
- 7 Advice for parents
- 8 How to cure the stigma dizembriogeneza
- 9 Prognosis and complications
- 10 Videos about diseases in newborns
Causes of stigma dizembriogeneza in newborns
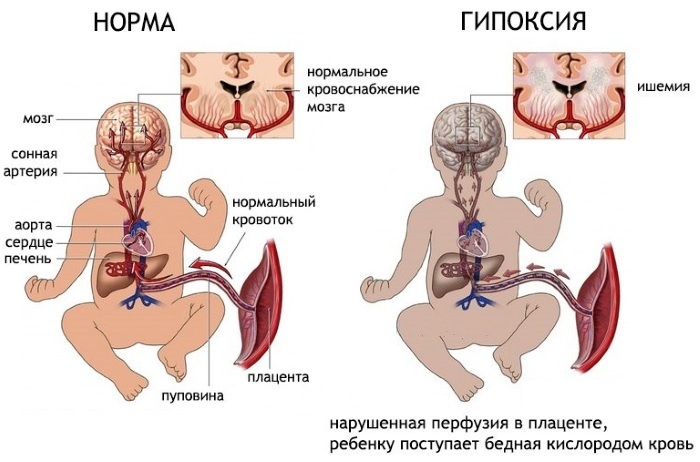
Stigmas dizembriogeneza neonatal occur under the influence of external (e.g., toxic substances, radiation) and internal adverse factors (maternal disease, fetal hypoxia, metabolic disorders substances). Such effects are called teratogenic, that is leading to the formation of anomalies and malformations.
The greatest sensitivity to negative factors observed in two stages of development of the human embryo - prior to its attachment to the uterine wall and during initial tab organs and tissues. In the later stages of pregnancy, the body of the child can already provide some compensatory reactions.

Also of great importance during fetal development during which the formation of of an organ, since the greatest susceptibility to the teratogenic effects coincides with this time. Thus, anomalies maxillodental system occur most often on week 5, and the nervous system - 7 months pregnant.
Most researchers attributed stigma dizembriogeneza with antenatal stage of development, from there, from the moment of fertilization until the birth of the child, thus, eliminating the genetic violations. However, in practice not always possible to determine the main reason that led to the development of the change, and the time period during which it occurred.
Risk factors
Risk factors for the occurrence of such abnormalities include the following:
- congenital abnormalities and genetic disorders in parents and relatives of 1-3 degree relatives (father, mother, grandparents, aunts and uncles);
- the birth of a previous child with developmental disabilities;
- the presence of abnormalities in pregnant women (diabetes, epilepsy, etc.);
- bad habits of the mother (alcoholism, drug addiction, smoking);
- infectious diseases, especially in the first 10 weeks of pregnancy (influenza, toxoplasmosis, rubella and others);
- intoxication during gestation;
- application of assisted reproductive technology;
- professional work in hazardous conditions;
- multiple pregnancy;
- late pregnancy in the mother;

Stigma dizembriogeneza in newborns can occur due to late pregnancy. - receiving medicines;
- obstetric diseases (uterine bleeding, abruptio placenta, narrowing pelvis, malposition).
When it is possible to observe the development of abnormalities in the child?
Stigma embryogenesis can be seen already in utero using ultrasonography. The standard external examination of the child after birth also includes the definition of such violations.
However, there are some signs in a delayed period. Thus, increased motor activity, unusual gait or posture inclination to skin diseases - six months after birth. Stigma is a symptom of genetic abnormalities may occur in later life.
symptoms
Stigmas dizembriogeneza conventionally divided into two groups:
- Signs of genetic abnormalities, which are symptoms of diseases of organs and systems. They have a pronounced character. These include chest deformity, total hirsutism, multiplicity skin folds, infantile hemangioma (benign tumor developing from cells that line the walls of blood vessels), lipomas ( "talc"), an abnormally low overhang century, strabismus, hernia formation violation genitals.

- Stigmas, are assessed to determine the overall level of stigma solutions and the need for more detailed diagnostics (set out below).
Skull
Stigmas dizembriogeneza in newborns can be expressed in the form of a skull changes described in the table below:
| sign | The main external characteristics | Features |
| Macrocephaly | The increased size of the skull, the shape of the head is normal, not bulging fontanelle. Mental retardation | May occur after birth. Hydrops is absent, the normal intracranial pressure. In many patients there comes a quick death on the background of an infectious disease |
| Microcephaly | The reduced size of the skull in normal proportions, the other parts of the body. Mental retardation | The most common causes are radioactive radiation, intrauterine infections, taking medicines, genetic disorders, alcohol abuse during pregnancy |
| Platitsefaliya | Flat head, poor development of the skull in the height of the brain. Mental retardation | Causes: hormonal disorders, mechanical compression of the cranial bones in the womb or during birth, genetic abnormalities |
| dolichocephaly | The long and narrow skull | It is the result of genetic and fetal abnormalities |
| plagiocephaly | The beveled shape of the skull (left, right or at the back) | It develops as a result of unilateral premature ossification of the skull, crushing the head in the womb, at birth or as a result of neuromuscular dysfunction |
| brachycephaly | Short and wide skull shape | Causes: Premature imperforate cross seam of the skull as a result of intrauterine infections or birth trauma |
| scaphocephaly | Long narrow head (when viewed from the side of the face), increased diameter of the head in front and behind (when viewed from the side) | It is the result of genetic and fetal abnormalities |
| Hydrocephalus | The increased size of the head, bulging fontanelle, throwing the head backward, downward displacement of the eyeballs, strabismus, involuntary oscillatory movements with his eyes fast rate, irritability, poor appetite, vomiting, lethargy, loss of vision and hearing. Convexity of the skull, the overhang of the frontal bones | Causes: intrauterine infections, meningitis in the newborn period, tumors, intoxication, traumatic brain injury |
| trigonocephaly | Triangular protrusion of the skull in the forehead | It is the result of genetic and fetal abnormalities |
Face
Changes in the area of the face of the child may be the following:
- asymmetry;
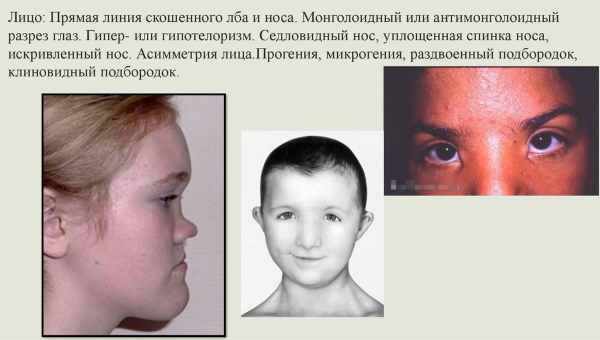
- lack of facial expression;
- unusual shape (too flat, long, narrow face);
- Increasing or decreasing the jawbone (upper or lower);
- protruding jaw forward;
- high or low line of hair growth on his forehead;
- fold on the forehead in the transverse direction;
- forked, oblique or wedge-shaped chin;
- low overhanging, sloping, too convex, narrow, wide and high forehead;
- pronounced brow ridges.
Eyes
Dizembriogeneza stigma against organs of the newborn are shown in the following:
- increased or decreased the distance between the eyes;
- abnormally low overhang of the century;
- double the growth of eyelashes;
- "Mongol" fold in the upper eyelid covering the lacrimal tubercle;
- long and narrow or asymmetric palpebral fissures;
- drooping outer corners of the eyes;
- protruding or sunken eyes;
- Different color of the iris of the left and right eyes;
- coloboma (no part of the iris);
- unibrow;
- blue sclera;
- abnormally reduced or increased sizes of one or both eyeballs;
- the absence or underdevelopment, ectropion;
- offset inner corners of the eyes in normal interpupillary distance;
- flattened or raised eyebrows;
- third eyelid;

- the irregular shape of the pupils.
ears
The structure of the ears are the following anomalies:
- asymmetry or abnormal arrangement auricles;
- different size of right and left ear;
- adnate lobes or their absence;
- too large or small ears (lobes);
- underdeveloped or calcified cartilage;
- protruding ears;
- Fold;
- excess skin appendages;
- fistulas or cysts in front of the ear.
Nose
Violation of the nose may be manifested as symptoms such as:
- turning in his nostrils;
- too big or small the length of the body;
- underdevelopment of the nose;
- irregular shape - saddle-shaped, curved, flattened, beak, flat, pear-shaped;
- bifurcated nose.
Mouth
The following abnormalities may occur in the mouth or on the lips:
- abnormally high, the arc-shaped sky;

- shortened frenulum lip or tongue;
- Insufficient or excessive number of teeth after their eruption;
- tongue splitting;
- short sky, cleft in it;
- folds in the language (lobulation);
- irregular shape of the teeth - or subulate pilkoobraznaya;
- abnormally large or small language;
- pendulous or twisted lips;
- is too small, large teeth or complete congenital absence;
- "Carp mouth";
- large interdental spaces;
- growth of teeth inside;
- abnormal development of dental enamel (its translucence, unusual color staining);
- underdevelopment and the tongue.
Neck
Developmental disorders of the neck and shoulder area is expressed in the following symptoms:
- abnormal length of the neck - is too big or small;
- presence of wing folds;
- extended base of the neck at the transition to the body;
- torticollis;
- narrow or too sloping shoulders;
- hypoplasia of the clavicles.
trunk
trunk anomalies have the following character:
- too narrow or broad chest;

- misshapen breasts - barrel, "chicken", concave, asymmetrical;
- extra nipples;
- breast enlargement;
- projecting or wing-shaped blade;
- too great a distance between the nipples;
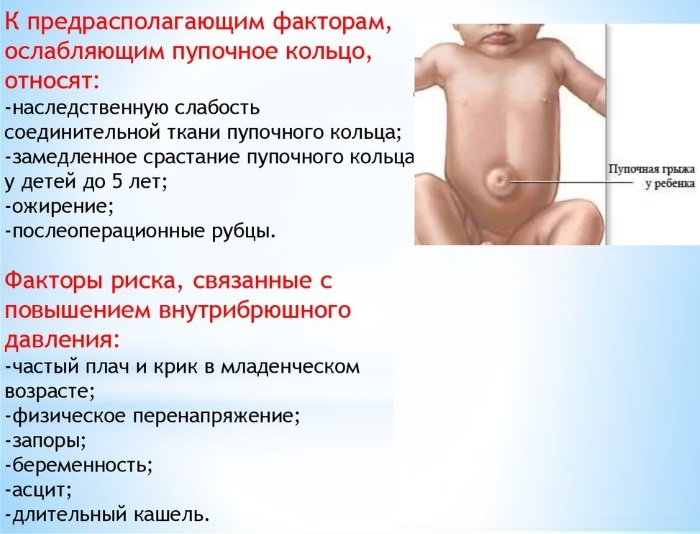
- hernia;
- misplacement navel;
- limited mobility of the spine or a curvature;
- additional edges.
Average total may differ low or high growth imbalances, obesity or muscle addition type, increasing the right or left side of the body, the body and narrow elongated limbs (or vice versa), a large weight (over 4 kg).
Hands
On the hands in newborns found these types of stigmas, such as:
- abnormally long fingers;
- a curved fifth or all fingers (phalanges);
- increase or decrease their numbers;
- fusion of the fingers;
- the absence or underdevelopment of the phalanges;
- the presence of transverse grooves on the palms;
- the same length of the second, third and fourth toes.
Feet
Relatively toes can be observed the same anomalies as for brushes fingers.
In addition, children are shown the following characteristics:
- wide gap between the first and second fingers;
- abnormal increase in the height of the curved arch of the foot;
- going down one finger to another;

- narrow shape of the foot.
Leather
Stigma dizembriogeneza in newborns and can affect the skin.
This is expressed as follows:
- light or dark spots, stand out;
- large mole with hair;
- excessive body hair all over the body or in certain areas;
- heavy or too thin skin;
- lack of subcutaneous fat layer;
- striae (stretch marks), scars, depressions;
- lack of pigment in the hair;
- eczema, excessive dryness, the formation of solid scales (ichthyosis);
- warts and other benign growths.
Evaluation of the newborn state
On examination, the child determine the total number of stigmas (regardless of location). The critical value is 5-6 abnormalities. Exceeding this level indicates a high risk of a constitutional violation in the development and availability of hereditary diseases.
Taken separately the signs listed above, by themselves do not have diagnostic significance. However, if a child has more than 5 such anomalies, it should undergo a thorough examination.
Assessment of the state of the newborn in the first days produce a neonatologist and pediatrician. Subsequently, they can be identified on the planned inspection surgery, neurology and ultrasound specialist. Typically, one or another hereditary syndrome is 1-5 corresponding features, but a wide variety of genetic diseases (the total number exceeds 3, 000), that considerably complicates the correct interpretation symptoms.
Procedures after birth
If after analyzing the stigmas dizembriogeneza doctor suspects the presence of hereditary diseases, the child designate careful clinical examination, which may be carried out using the following ways.
Scroll:
- Biochemical analysis of blood, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, sweat, hair, feces; punctates bone marrow and fetal fluid. Such assays can detect phenylketonuria, glycogen metabolism disorders, galactose, fructose and other substances; hypothyroidism, cystic fibrosis and other abnormalities.

- Cytogenetic study that helps to clarify the features of the structure and number of chromosomes. It is carried out both from the patient and for his family. Usually, it is administered in the presence of multiple malformations, with a combination of mental and physical gap, with low weight baby, despite the full-term pregnancy and birth in time.
- Molecular cytogenetic and molecular biological techniques (RFLP, PCR, ELISA). They allow you to diagnose disease at the molecular defect and the altered gene. These methods are the most accurate. However, for the majority of hereditary diseases diagnosis is hampered by the fact that the damage occurs in different genes.
conducted screening for some genetic abnormalities in the first days after birth, all newborns fail. For the analysis of a child's blood is taken from the heel, then the laboratory testing is carried out, allowing diagnose diseases such as congenital adrenal hyperplasia, galactosemia, hypothyroidism, cystic fibrosis, phenylketonuria.
Advice for parents
the following recommendations for parents developed in medicine:
- before planning pregnancy should undergo a full medical examination (and genetic desirable) to identify possible risk abnormalities in the unborn child;
- the presence of serious hereditary diseases genetics consultation is required;
- maintain a healthy lifestyle both during pregnancy and prior to it;
- time to pass routine inspections and inspections after the birth of the child;
- carefully observe the peculiarities of his behavior and the detection of any deviations consult a doctor;
- timely undergo ultrasound during pregnancy, as it allows you to identify the early stages of severe malformations;

- in the diagnosis of hereditary diseases - occur in relevant specialists (if indicated) and to comply with doctor's prescription in order to avoid possible complications.
How to cure the stigma dizembriogeneza
Stigmas dizembriogeneza not require treatment, unless they are symptoms of genetic diseases in which there is a disturbance of the organs or systems. The most common hereditary diseases and syndromes, stigma specific to them and methods of therapy described in the table below.
| Disease | Characteristic | stigma dizembriogeneza | therapies |
| mucopolysaccharidosis | Metabolic disorders, accompanied by defects in bone, cartilage and connective tissue. | Deformation of the skull, cloudy corneas, unibrow, large tongue, small stature, keeled or funnel shape of the breast, hernia, increased body hair. | enzyme preparations symptomatic therapy Bone marrow transplantation Gene therapy. |
| Down's syndrome | Chromosomal abnormalities, leading to mental retardation. | Flat face shape Mongoloid eye incision. | Therapy associated pathologies and malformations, drugs that improve blood circulation in the brain. |
| Microcephaly | Damage to the nervous system, leading to mental retardation. | described above | Symptomatic therapy (stimulating, sedative, anticonvulsant, dehydration), nootropic drugs. |
| Hydrocephalus | Violation of the ventricular system of the brain due to excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid. | Surgical treatment (grafting) Diuretics. |
|
| phenylketonuria | Violation of amino acid metabolism, leading to a decrease in intelligence. | Blond hair and skin; blue eyes and urging mating legs during walking and sitting posture due to an increased muscular tension, susceptibility to skin disorders (after 3-6 months. after birth). | A strict diet, enzyme replacement therapy. |

Most of genetically caused diseases amenable to symptomatic treatment only.
Prognosis and complications
Stigma dizembriogeneza in infants by themselves are not dangerous for the health of the child. They may have the character of only a cosmetic defect (e.g., excessive hairiness body portion, protruding ears). But if the stigma is a sign of a genetic disease, the prognosis is unfavorable.
The complications can be as follows depending on the pathology:
- many vices internal organs;
- violation of the disability;
- delay physical and mental development;
- disability and early death.
dizembriogeneza stigma allow you to set a preliminary diagnosis in newborns for a number of external signs. The incidence of these disorders is large enough - according to various estimates, it ranges from 15 to 42 cases per thousand children. When exceeding a critical level of such anomalies require a thorough diagnosis for the detection of hereditary pathologies.
Registration of the article: Lozinski Oleg
Videos about diseases in newborns
Diseases babies who do not need to be treated: