Such a common pathology as perinatal encephalopathy, requires timely consultation with a neurologist and a comprehensive examination. The disease is characterized by disorders in the work of the brain. It is important to diagnose pathological changes at an early stage in order to start treatment and prevent possible complications.
Record content:
- 1 General information
- 2 Causal factors
- 3 Varieties
- 4 How is it developing?
- 5 Severity
- 6 Symptoms by species
- 7 Symptoms by age
- 8 Diagnostics
- 9 Treatment of the adult form
- 10 How is childhood encephalopathy treated?
- 11 Clinical guidelines
- 12 Predictions and consequences
- 13 Video about perinatal encephalopathy
General information
Perinatal encephalopathy is a pathological condition in which the functioning of the brain is impaired. The negative impact of the provoking factor on the child is carried out from the 22nd week of pregnancy to the first 7 days after birth.
In 60% of cases, it is perinatal encephalopathy that is diagnosed in children among all neurological diseases. The pathology is successfully treated, but there is a danger of its progression to other neurological disorders (cerebral palsy, epilepsy, hydrocephalus).
Causal factors
During the development of a small organism, it easily lends itself to negative influences from various negative factors.
There are certain reasons that provoke perinatal encephalopathy:
- acute infectious or purulent diseases;
- exacerbation of chronic pathologies in the body of the expectant mother;
- toxicosis, which can appear during any period of pregnancy;
- poor environmental situation;
- close location near the house of industrial enterprises where they work with radioactive or toxic substances;
- genetic changes that appeared as a result of impaired material metabolism or after a failure in the bloodstream;
- improper nutrition of a woman during the period of bearing a baby and during breastfeeding;
- congenital defects;
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol and drug abuse);
- hormonal disorders, endocrine disruptions, conflicts of Rh factors;
- emotional stress, frequent stress at work, at home;
- difficult labor (rapid or slow labor);
- premature birth of a child;
- the mistake of obstetricians during labor can negatively affect the development of the child in his first years of life.
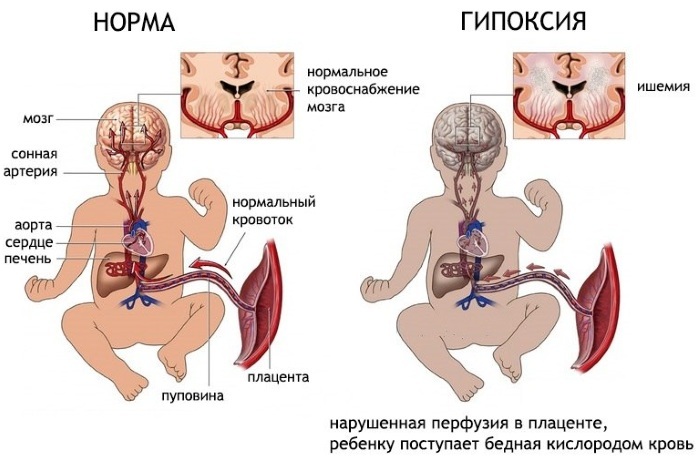
Perinatal encephalopathy can also be provoked by negative environmental factors that have a negative impact on a pregnant woman. This includes harmful gases, toxic substances.
The same goes for harmful work, taking certain medications and overdosing on them. Experts recommend that future parents carefully plan their pregnancy and monitor their health in order to prevent the occurrence of pathological changes.
Varieties
Perinatal encephalopathy is a pathology that develops against the background of numerous negative factors.
Given these reasons, the disease is classified as follows:
| Name | Description |
| Hypoxic encephalopathy | The pathological condition develops as a result of acute or chronic lack of oxygen. |
| Traumatic | The disease is a consequence of damage to the fetus during labor. This applies to injuries to the central and peripheral nervous system. |
| Toxic-metabolic | A pathological condition occurs against the background of the development of an inflammatory process in the mother's body or a defect in the internal organs of the fetus. |
| Infectious | The disease is provoked by intrauterine infectious processes. |

A comprehensive diagnosis prescribed by a doctor will help to establish an accurate diagnosis. The results will allow the specialist to select the most effective therapeutic methods.
How is it developing?
Perinatal encephalopathy is a set of clinical signs that indicate anatomical and physiological changes in the region of the brain.
The disease includes the following developmental phases:
- Antenatal. The period of perinatal encephalopathy, which lasts until the onset of labor.
- Intranatal. The phase of the disease that occurs directly during childbirth.
- Postnatal. The period of pathology, which falls on the first week of a baby's life (7 days).
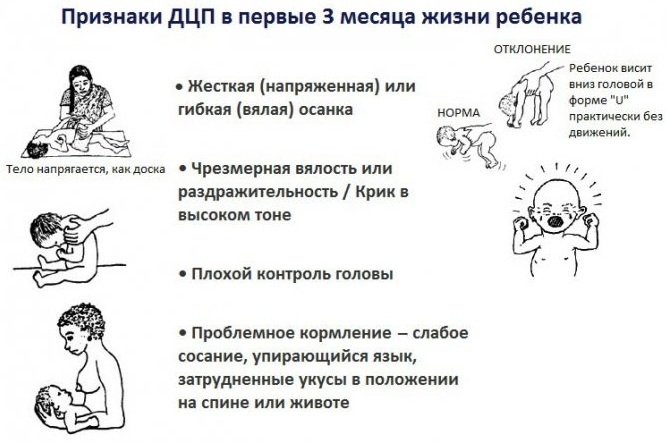
The first signs of perinatal encephalopathy can be detected by a neonatologist. A young mother should pay attention to the faint cry of the baby. At the same time, the skin remains cyanotic for a long time, the child's activity and reflexes decrease.
Severity
Perinatal encephalopathy is a disease that takes several stages and classified by severity:
| Name | Description |
| Acute period | The disease is diagnosed in the first month of a child's life. The functioning of the brain is impaired, convulsions appear. In some situations, the little patient falls into a coma. Nervous reflex excitability increases. Hydrocephalus leads to increased intracranial pressure. |
| Restorative | Pathology is diagnosed in children up to 2 years of age. The functioning of the brain is also impaired, convulsions, nervous irritability and high intracranial pressure are manifested. But with timely and adequate treatment, the patient's condition improves. |
| Residual changes | At this stage, there is a delay in speech and psychomotor development. The patient is also diagnosed with neurasthenia, hyperactivity. Severe disease is accompanied by convulsive syndrome and hydrocephalus. |
The Apgar scale will most likely help determine perinatal encephalopathy in a baby. Experts take into account the state of physiological reflexes, the activity of the child, the functioning of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, the color of the skin.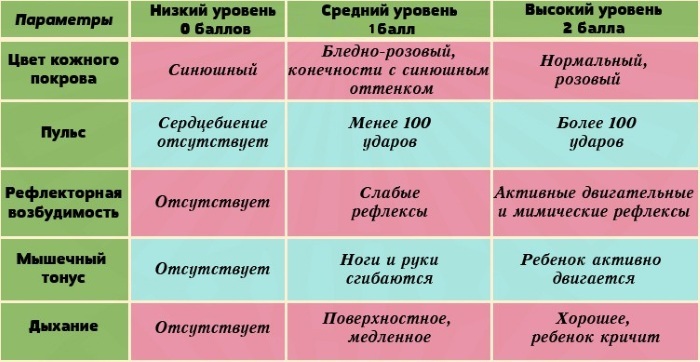

| Name | Indicators (points) |
| Satisfactory condition | 7-10 |
| Medium severity | 4-6 |
| Extremely serious condition | 1-3 |
Severe disease increases the risk of neurological disorders. The child needs urgent medical treatment in a hospital setting.
Symptoms by species
Perinatal encephalopathy is a disease, different types of which are accompanied by similar clinical signs.
They combine into certain syndromes:
| Name | Description |
| Nerve reflex | Sleep is disturbed, spontaneous movements appear. The child cannot fall asleep for a long time, often cries, he has a tremor of the limbs. The increased tone is replaced by a decreased one. In most cases, the child will have cleared up symptoms by the age of 12 months. Complex pathological processes lead to the development of epilepsy. |
| Convulsive | Clinical syndrome of perinatal encephalopathy, which occurs in a child in the first months of his life. It is characterized by twitching attacks, periodic flexion of the limbs, bending forward. The child shudders, imitates the sucking process, turns his head. |
| Hypertensive-hydrocephalic | The accumulation of large amounts of cerebrospinal fluid leads to an increase in intracranial pressure. The volume of cerebrospinal fluid also increases. The child's head is growing rapidly, a feature of the hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome is also an increased pulsation of the fontanelle. The baby's sleep becomes restless, he throws his head back and often spits up. |
| Vegeto-visceral | The clinical syndrome is diagnosed in a child in the second month of life. Excessive excitability appears, intracranial pressure increases. The functioning of the digestive system is also impaired. The same goes for the heart and breath. The baby often spits up, weakly gains weight. The skin becomes marbled. |
| Movement disorders | Muscle tone increases or decreases. In some situations, some muscles tense, while others weaken at this time. There is an involuntary activity in the child. There is a delay in speech, motor and psychological development. The same goes for visual and auditory reactions, emotions. With a delay, the baby begins to hold his head, crawl and sit. |
| Cerebral palsy | Complex syndrome of perinatal encephalopathy, which is represented by impaired speech, motor skills, intelligence and vision. The same goes for the emotional state. |
| Hyperactivity | A symptom of a disease that manifests itself at a later age. The child cannot sit in one place, attention is disturbed, it is difficult for him to concentrate. |
| Coma | Pathological processes affect numerous reflexes. The child is weak and motionless, in some situations there are convulsions, the functioning of the respiratory system is disrupted. |

The clinical signs that accompany perinatal encephalopathy in a child will allow a neurologist to establish an accurate diagnosis. Determine the stage and severity of the disease, prescribe the patient the most informative examination. Accurate results are essential for the correct treatment regimen.
Symptoms by age
Perinatal encephalopathy can be diagnosed as soon as the baby is born. As the pathological processes progress and the baby grows, the clinical signs of pathology intensify.
| Age | Symptoms |
| Newborn |
|
| 3 months |
|
| 6 months |
|
| 8-9 months |
|
| 12 months |
|
| 3 years |
|
Apathy for the surrounding world appears, there is no desire for new knowledge. The child does not learn simple social and household skills (dressing, going to the potty, using a spoon or fork). With any first violations, it is important to consult a specialist in a timely manner.
Diagnostics
Before carrying out a comprehensive diagnosis, the doctor examines and asks the young mother about how the baby is behaving.
Given the existing complaints, the following diagnostic measures are prescribed for suspected perinatal encephalopathy:
| Name | Description |
| Neurosonography | The specialist examines the internal structure of the brain, assesses the condition of the tissues, identifies possible pathological changes or neoplasms, the amount of cerebrospinal fluid. |
| Electroencephalogram | The doctor assesses the functioning of the brain, also identifies pathological disorders, neoplasms. |
| Electroneuromyography | A diagnostic method that allows you to identify neuromuscular diseases. |
| Doppler ultrasonography | An examination is done to assess the functioning of the blood vessels in the area of the brain. |
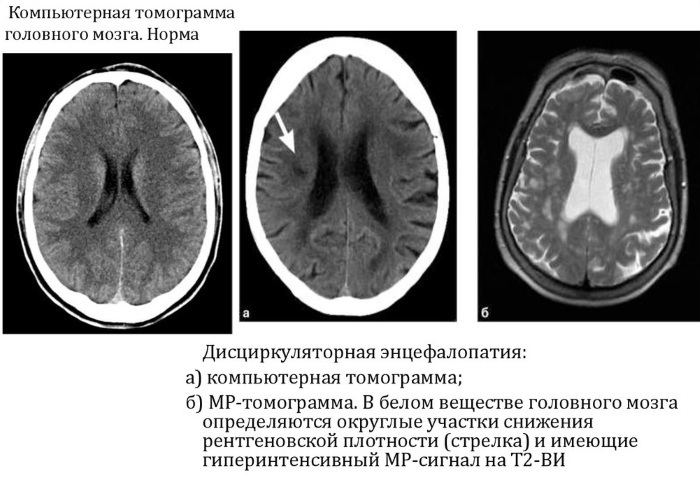
Additionally, a small patient may be prescribed computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging to confirm the preliminary diagnosis. In some situations, consultation of other specialized specialists (ophthalmologist) is required.
Treatment of the adult form
Therapy of any diseases and disorders of the functioning of the central nervous system is carried out immediately after an accurate diagnosis has been made, while the pathological processes are reversible.
Treatment of perinatal encephalopathy in children and adults will restore blood circulation and tone of blood vessels, eliminate edema and stop convulsive syndrome. The therapy also improves physical metabolism and stabilizes intracranial pressure.
How is childhood encephalopathy treated?
Perinatal encephalopathy is a medical condition that affects the functioning of the brain. Drug therapy in adults and children depends on provoking factors, against which pathological changes have appeared. A neurologist prescribes special drugs, taking into account the patient's condition.
It is important to adhere to the recommendations, since many drugs provoke side effects. This is especially true for young children, whose body is weaker compared to adults.
| Drug group | Name | Application |
| Diuretics | Diacarb, Acetazolamide | Medicines should be taken orally. Children's dosage depends on the condition of the child and body weight. The doctor prescribes 8-30 mg / kg. The indicated dosage is divided into 1-4 doses. |
| Anticonvulsants | Diphenin, Seduxen | The medicine should be given to the child by mouth during meals or after meals. Children's dosage depends on age and is 0.5-1 tablet 2 times a day (4-8 mg / kg per day). |
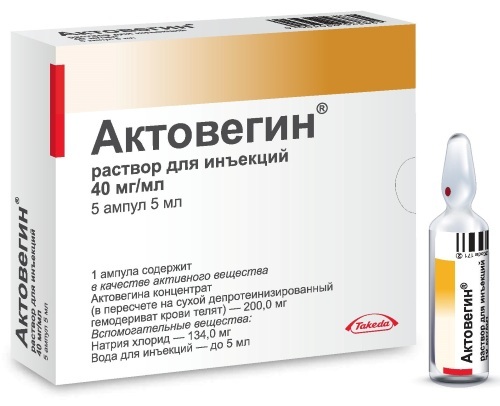
| Medicines to improve blood circulation | Actovegin, Pantogam | The drugs are administered intravenously or intramuscularly. The dosage depends on the severity of the disease. Patients are prescribed 5-20 ml every day for 2 weeks. |
| Hormonal agents | Prednisolone, Dexamethasone | The medicine is administered intramuscularly or through a dropper. The dosage is set taking into account the patient's condition, 4-20 mg 3-4 times a day. The first 3-4 days, the drug is injected in full, then they switch to a maintenance dosage. |
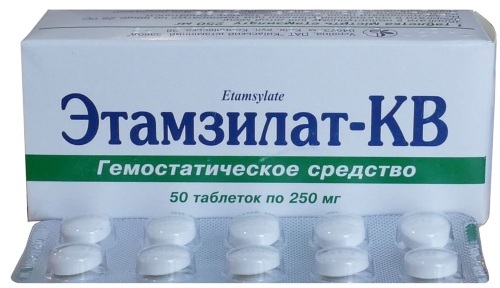
| Means for reducing the permeability of blood vessels | Kanavit, Etamsilat | For children, the medicine is administered intramuscularly. The recommended dosage depends on the patient's age and is 1-10 mg. |
| Sedatives | Novo-Passit, Glycine | Medicines have a sedative effect. For children, the remedy is given in the form of a solution, previously diluted with water. The recommended dosage is 5 ml 3 times a day before meals. The interval between doses should not be less than 4 hours. |
Infusion treatment is also carried out, taking into account the condition and body weight of the child. During drug therapy, patients are advised to perform special therapeutic exercises, massage and reflexology.
Clinical guidelines
Modern medicine can successfully combat perinatal encephalopathy if the disease is diagnosed in a timely manner.
It is important not only to adhere to the scheme of the developed therapy, but also to remember the recommendations of the neurologist:
- The child should be constantly monitored by specialists. You must visit your pediatrician regularly. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe an additional consultation with a cardiologist, orthopedist and neurologist.
- It is necessary to observe the mode of activity and rest.
- Give your baby a massage. It improves muscle tone, reduces neuropsychiatric disorders.
- Attend physiotherapeutic procedures as prescribed by a doctor (medicinal electrophoresis, therapeutic exercises, baths).
In the case of deep lesions of the brain structures, the child is shown a neurosurgical operation. During the recovery period, if the doctor permits, you can use the recipes of healers and healers, but only in combination with other rehabilitation means.
Predictions and consequences
In most cases, perinatal encephalopathy is successfully treated with prompt medical attention. But many consequences and complications can appear after a while:
| Name | Description |
| Epilepsy | Chronic brain disease of a neurological nature, which is accompanied by sudden seizures. The pathological condition proceeds with impaired sensory, autonomic, mental and mental functions. |
| Hydrocephalus | The disease in medicine is also called dropsy of the brain. The pathological condition is characterized by the accumulation of a large amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the cranial cavity. |
| Cerebral palsy (cerebral palsy) | A complex of violations of motor functions, which appears as a result of damage to certain brain structures during the perinatal period of fetal development. |
During school years, the child often complains of headaches, writing and reading, and concentration of attention are disturbed. Poor academic performance is the result of impaired memory and mental processing. The child quickly gets tired and restless.
Before conception, parents must carefully and thoroughly prepare, undergo a comprehensive examination. Perinatal encephalopathy is not a dangerous disease if you consult a neurologist in a timely manner and undergo treatment. It is necessary to strictly follow all the recommendations of a specialist in order to prevent possible consequences. Then the forecasts will be positive.
Video about perinatal encephalopathy
Neurologist's lecture on perinatal encephalopathy:



