One of the main forms of proliferative diseases caused by abnormal growth of cells is endometrial hyperplasia( GE), the most common pathology of the inner shell of the uterus. In the International Classification of Diseases - ICD 10, endometrial hyperplasia has code 84.0, 85.0, 85.1, depending on the form of manifestation.
What is it? Hyperplasia of the endometrium of the uterus is a pathology characterized by excessive overgrowth and changes in the structure of the endometrioid tissue. The disease is based on hormonal disorders that stimulate the proliferative cellular activity of the endometrium, which increases its size and growth of the uterus.
The development of the disease is facilitated by changes in the structure of the endometrium during the menstrual cycle. In the middle of the cycle, under the influence of estrogen, its layer increases and is more supplied with blood, creating conditions for the adoption of a zygote( a fertilized cell).If this does not happen, part of the tissue cell elements is destroyed and leaves the body with menstrual excrement.
Disturbance of hormonal regulation, with a quantitative overbalance of estrogens over progestins, leads to an expansion of the endometrium, but its complete destruction does not occur. The internal master shell increases from 1 mm.up to 8 mm.and continues to grow, giving "food" for the development of hyperplastic processes.
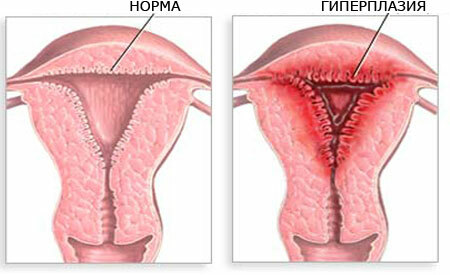 Changes in the internal mucous layer of the uterus can manifest themselves in various pathological forms.
Changes in the internal mucous layer of the uterus can manifest themselves in various pathological forms.
Contents of
- 1 Contents of
- 2 Disease of
- 2 Danger of endometrial hyperplasia
- 3 Symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia
- 4 Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia
- 5 Effect of endometrial hyperplasia on pregnancy
- 6 Prevention measures
Types of manifestation of
Depending on the developmental process and the clinical course of the hyperplastic process, the pathology manifests itself in various forms of endometrial hyperplasia,and varying degrees of severity of the course - mild, moderate and severe. It can not be said that endometrial hyperplasia is a cancer, but one can say with certainty that many of its forms are capable of malignancy.
1) Ferrous hyperplasia of the endometrium is a benign neoplasm, characterized by the ease of clinical course. Malignancy in malignant formation does not exceed 4% of cases.
Characterized by thickening of the internal uterine membrane with a tortuous and expanded structure of tubular glands, with a group or random arrangement. The exit of the mucus from the glands is free.
2) The development of the glandular-cystic form of is due to the strong growth of cells in the mouth of the glands, which block the mucous outflow, promote the formation of blister cystic benign lesions filled with mucus.
Sensitively respond to estrogens, as they develop during the period of hormonal changes - with puberty, the beginning of menstrual cycles and during menopause.
3) In the cystic form , the development process is similar to the previous type of pathology, with the only difference being that the cysts are filled not with mucus, but with healthy epithelial cells, which excludes the malignancy process.
4) Characteristics of focal pathology ( adenomatous polyp) indicates a focal cluster of rapidly proliferating cells, under the influence of hormonal disorders. On the mucosa, there are formations with altered cystic glands inside.
Possible development of malignant formation in the place of focal elevations.
5) Atopic GE ( adenomatosis) is the most dangerous pathology. Characterized by rapid cell division and the maximum growth of tissues with a constantly changing structure. High risk of cancer.
Almost a third of women undergo malignization of myoma, with endometrial hyperplasia of atypical form. The pathology is treated exclusively by the method of complete removal of the uterus.
6) Endometrial polyps containing rejectable functional or regenerating basal layer of endometrioid tissues
Danger of endometrial hyperplasia
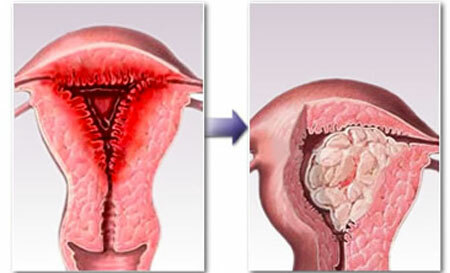
The greatest risk of hyperplastic changes in the inner layer of the uterus is a high risk of cancerous degeneration and deprivation of women of reproductive functions( infertility).In addition, against the background of GE, various gynecological diseases can develop:
- polyposis formation in the uterus and cervical canal;
- development of myomatous nodes;
- genital adenomyosis;
- cysts of the gonads;
- prolonged menstrual cycles.
The main cause of hyperplastic changes in the mucosal layer of the uterine membrane is due to many factors and special predisposing conditions contributing to the development of pathology. These include:
- Changes in the hormonal background, disrupting the imbalance of sex hormones. It is provoked - mastopathy and myomatous nodes, violations of the endocrine and reproductive function of the sexual glands, improper use of oral contraceptives.
- Failures in metabolic processes caused by a violation of carbohydrate and fat metabolism due to - obesity, chronic liver disease, diabetes mellitus or hypertension.
- Diseases of the adrenal, thyroid and pancreas, promoting enhanced cellular growth.
- Age factor that affects hormonal imbalance - the period of menopause and sexual maturity.
- Inflammatory and infectious gynecological diseases and intrauterine contraceptives.
- Diagnostic cleansing and abortions, which disrupt the receptor sensitivity of the mucous layer to progestins, promoting long-term cell division.
- Failure in the protective function of immunity caused by an erroneous attack of phagocytes on endometrial cells, taking them for foreign agents.
- Genetic factor.
Symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia

The main signs of endometrial hyperplasia are associated with changes in the nature and duration of menstrual flow. Symptoms that accompany hyperplasia are expressed:
- Disorders in the menstrual cycle, associated mainly with polyposic lesions on the normal mucous layer of the uterus. Against the background of a regular cycle, there may be a discharge in the form of a syphilis before the monthly cycle and after it, manifested with abundant menstrual secretions.
- Bloody "daub" between the cycles.
- Delayed discharge and sudden abundant and prolonged bleeding.
- The duration of menstrual flow( menorrhagia) in polyps of fibrous and glandular fibrous genesis.
- Dysfunctional uterine bleeding( metrorrhagia) in the intermenstrual period, manifested due to polyposis formation on the uterine mucosa. Such symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia are characteristic of women in the premenopausal phase.
- Endocrine factor of infertility due to impaired follicle formation or inability to implant a zygote.
Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia
The therapeutic process of hyperplastic changes in the intra-wall endometrioid tissue of the uterus is not an easy one and requires a complex approach consisting of four stages.
1. Bleeding stops with:
- Estogen-progestogen preparations( hormonal hemostasis);
- Scraping;
- Application of urethics( bleeding prophylaxis);
- Anti-anemia treatment - blood transfusion( transfusion of plasma, filtered or gamma-irradiated erythrocyte mass), intake of iron-containing agents;
- Applications of parenteral-fluid therapy;
- Vitaminotherapy and coagulant intake.
2. Suppressive hormone therapy( correction of hormone levels):
- Purpose of progestogen( from three months to six months in continuous mode);
- Normalization of the central nervous system and vegetative disorders - gestagens + GnRH agonists, in the same regime;
- Gestagenic monotherapy, if endometriosis atrophy is detected( after abortion, or age-related).
3. Restoration of hormonal status( recovery of the menstrual cycle):
- Women of reproductive age are prescribed drugs for hyperstimulation of ovulation processes and gonads, to elderly women, exclusively medicamental agents containing male hormones;
- The drug "djufaston" with endometrial hyperplasia is used as a substitute hormone therapy, which eliminates the deficiency of endogenous progesterone.
Clinical examination of
After effective treatment of endometrial hyperplasia with hormone therapy drugs, women should stand on dispensary records for five years, after surgery - up to six months.
In case of ineffectiveness of conservative methods of therapy, surgical techniques are used:
- freezing of lesions by cryodestruction;
- laser moxibustion( ablation);
- uterine resection( hysterectomy) - complete removal of the organ with a high risk of malignancy.
Influence of endometrial hyperplasia on pregnancy
With pathological processes of endometrioid tissues, pregnancy is impossible, ovulation does not occur. But, if this fact has happened, the egg can not develop on the damaged sections of the mucosa.
The only form of hyperplasia at which pregnancy may occur is focal. Such cases are very rare and require careful and sparing treatment, with special control of the doctor.
Usually, pregnancy is recommended to be interrupted and complex treatment should be carried out - this disease has a great risk of developing various pathologies in the fetus, spontaneous abortion or development of oncology is not ruled out.
Timely diagnosis and treatment completely restore reproductive function.
Prevention measures
It should be realized that endometrial hyperplasia is a background pathology for development of oncological processes. And the main measure of prevention - compliance with the rules of routine surveys, which will help to identify the disease in time and begin treatment.
It is possible to prevent the development of the disease independently by observing completely uncomplicated rules:
- use contraceptive methods to exclude medical abortions;
- give preference to hormonal contraception and abandon intrauterine device;
- normalize body weight.