1 Causes of
pathology Hemorrhagic shock can occur even if 0.5-1 liter of blood is lost, if the amount of circulating blood volume( BCC) is sharply reduced in the body. A huge role in all this is played by the rate of blood loss. If the shock comes because of an injury, and blood loss is slow, then the body will have time to include compensation resources. The blood will receive lymph, and during this period the bone marrow will completely switch to the restoration of blood cells. With such hemorrhagic shock, the probability of a lethal outcome is rather low.
Do you have gastritis?
GALINA SAVINA: "How easy is it to cure gastritis at home for 1 month. A proven method - write down a recipe. ..!"Read more & gt; & gt;
However, if blood loss occurs very quickly due to damage to the artery or aorta, then it is almost impossible to do anything. Only fast stitching of blood vessels with the infusion of large amounts of donor blood will help. As a temporary measure, saline is used, with the help of which the weakening of the organism is not allowed due to a lack of micronutrients and oxygen.
Recommended to read
- Diarrhea in early pregnancy
- Treatment of diarrhea in early pregnancy
- Emergency care for gastrointestinal bleeding
- Effective remedy for gastritis and stomach ulcer
What kind of emergency care is acceptable with a significant loss of blood? First of all, you need to call an ambulance, then try to stop the bleeding, using all sorts of methods for this, from applying the tire and ending with the transmission of damaged arteries or veins.
It should be noted that the loss of 60% of BCC is fatal. At the same time, blood pressure drops to almost 60 mmHg, and the patient loses consciousness( sometimes recovering only spontaneously, literally for a few seconds).
Blood loss of up to 15% is considered an easy form of hemorrhagic shock. At the same time, blood pressure does not decrease, and the body completely compensates for the spent reserve( within 1-2 days).
2 Disease stages
Conditionally, doctors share hemorrhagic shock in 4 stages, which differ in the volume of lost blood, symptomatic manifestation:
- Blood loss from 5 to 15% BCC( ie, the entire volume).Has a compression character. The patient may experience temporary tachycardia, which passes itself within a few hours after the cessation of bleeding.
- Loss of 15 to 25% of BCC.At the same time, blood pressure drops slightly, the first signs of pallor appear. This is especially noticeable on the oral mucosa and lips. Occasionally, the limbs become cold, as blood is drained to feed the brain and other vital organs.
- Blood loss up to 35%.It is accompanied by a significant decrease in blood pressure and acute tachycardia. Already in this degree, the shock can cause signs of clinical death - depends on the physiology of a particular patient.
- Blood loss of up to about 50% or higher. High probability of death. Pale skin is observed throughout the body, sometimes accompanied by anuria, filiform, almost completely absent pulse.
-
 IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;

Conditionally also allocate a hemorrhagic shock of a lethal degree. The name is a conditional. This is a loss of over 60% of bcc. As a rule, even emergency care will not save the patient, as the body instantly begins to die from lack of oxygen and nutrient components. The brain is damaged after 2-3 minutes, the respiratory function is disrupted, neuronal collapse and paralysis occur. Together with this, the venous return of blood to the heart abruptly stops.
This is accompanied by a protective reaction of the body with the release of a huge number of catecholamines( including adrenaline).This is done to accelerate the contractions of the heart muscle, but because of this increases the vascular resistance, blood pressure drops.
-
 Gastroenterologist. IMPORTANT: "I beg you, if you began to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not in any way do gases. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
Gastroenterologist. IMPORTANT: "I beg you, if you began to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not in any way do gases. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
It should be noted that in women, hemorrhagic shock affects lower blood volume losses. For example, stage 4 of them is manifested with a loss of 30% of BCC( corresponding symptomatology).Men in their physiology can withstand bleeding, in which 40% of BCC is lost.

3 Syndrome of disseminated intravascular coagulation
The so-called DIC syndrome is the most dangerous consequence of hemorrhagic shock. In simple words, this is a situation in which the blood contacts with oxygen and starts actively coagulating, still in the vessels, in the heart. As is known, even a small blood clot leads to blockages of arteries that supply blood and micronutrients to the brain. In the same situation, a total thrombosis is formed, because of which the normal process of blood circulation is completely broken - it completely stops.
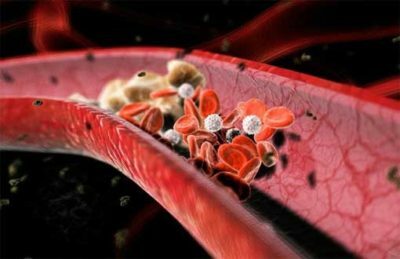
Hemorrhagic shock does not always cause air to enter the blood vessels. This happens only with a strong decrease in blood pressure, in which the heart simply can not resist the ingress of oxygen( previously this was due to the fact that the pressure in the vessels is slightly higher than the atmospheric pressure).
TIP FROM THE MAIN GASTROENTEROLOGIST
Korotov SV: "I can recommend only one remedy for the rapid treatment of Ulcer and Gastritis, which is now recommended by the Ministry of Health. .." Read the reviews & gt; & gt;
As a matter of fact, disseminated intravascular coagulation is a violation of macrocirculation, which entails a stop of microcirculation and a gradual withering away of vital organs. The first stroke is the brain, heart and lungs. This is followed by ischemia and atrophy of all soft tissues.
4
Disease Index In terms of compensation, hemorrhagic shock is divided into 3 stages:
- Compensated shock( ie when blood loss is slow or volume is low).
- Decompensated reversible shock( the body does not have time to restore normal blood volume and adjust blood pressure, but the amount of blood lost is such that it is not fatal).
- Decompensated irreversible shock( in such cases, doctors can not help in anything.) Whether the patient can survive depends on his individual physiological qualities.

For the separation on the stage by physicians, the so-called hemorrhagic shock index was introduced in due time. It is calculated by means of the ratio( proportion) of the heart rate( pulse) to systolic pressure. The higher the figure, the greater the risk to the patient. Not dangerous level - the index in the area of 1, dangerous - from 1.5 and above.
5 Medical actions
The only thing that can be done by a doctor with hemorrhagic shock is to stop bleeding in a patient. Naturally, first of all it is necessary to establish the cause of hemorrhage. If this is an open visible wound, then immediately use a tourniquet or at least a girdle and transfer the damaged vessel. This will reduce blood circulation and will give several additional minutes to eliminate hemorrhagic shock.

If it is impossible to establish the cause of blood loss, or if it is internal( for example, due to rupture of the artery), it is necessary to begin the introduction of blood substitutes as soon as possible.
Only a qualified surgeon can directly deal with the bleeding. Primary manipulation with the patient is performed by either a nurse or an obstetrician, if it is a question of significant blood loss during the birth of a child.
Hemorrhagic shock of an atypical nature is a rupture of feeding vessels. To establish the exact reason without medical examination will not work. Accordingly, emergency care is the prompt delivery of the patient to the hospital or at least to the ambulance station - there are drugs to sustain life with significant blood loss.

6 Possible consequences of
The body's response to significant blood loss can not be predicted in advance. Someone is disturbed by the work of the neural system, someone just feels weak, someone instantly loses consciousness. And the consequences, it should be noted, mostly depend on the amount of lost BCC, the massive bleeding, the physiology of the patient.
And not always timely delivery of infusion therapy completely eliminates the consequences of severe blood loss. Sometimes after this, there is a kidney failure or damage to the lung mucosa, partial atrophy of the brain( some of its departments).It is impossible to foresee all this.
After a severe hemorrhagic shock( 2-4 stages), a long-term rehabilitation is necessary. Especially important is the early restoration of normal working capacity of the kidneys, lungs, liver, brain. The development of new blood may take from 2 days to 4 weeks. To speed up this process, the donor's blood or saline is injected into the patient's body.
When it comes to childbirth, which caused hemorrhagic shock, it is possible that a woman will lose reproductive function due to surgical removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes. Therefore, doctors additionally prescribe enhanced psychological support in such situations. The obstetrician, in turn, monitors the strict implementation of the appointed rehabilitation program.
- 1 Causes of
- 2 pathology Stages of
- 3 Disease of disseminated intravascular coagulation
- 4 Disease index
- 5 Medical actions
- 6 Possible consequences
Hemorrhagic shock is the loss of a large amount of blood, which can lead to death. It is accompanied by tachycardia, arterial hypotension. With a large loss of blood, the patient develops pallor of the skin, clarification of the mucous membranes, and difficulty breathing. If urgent help is not provided in a timely manner, the probability of the patient's death will be too great.