Mortality from cardiovascular disease confidently holds the first place. Such ailments are usually exposed to older people, but often pathological processes are identified at an early age.
A particular difficulty in diagnosis is pulmonary embolism due to lack of specific signs.
Contents of
- 1 Thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery( PE), what is it?
- 2 Causes of pulmonary embolism
- 3 Symptoms of pulmonary embolism of the pulmonary artery
- 4 Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism of the pulmonary artery
- 5 Treatment of pulmonary embolism( pulmonary embolism)
Pulmonary arterial thromboembolism( PE), what is it?
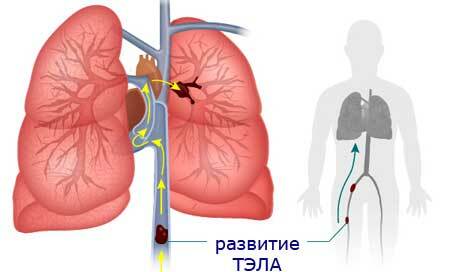
Pulmonary artery thromboembolism( PE) is a blockage of the pulmonary artery or its branches by blood clots formed( most often) in large veins of the lower limbs.
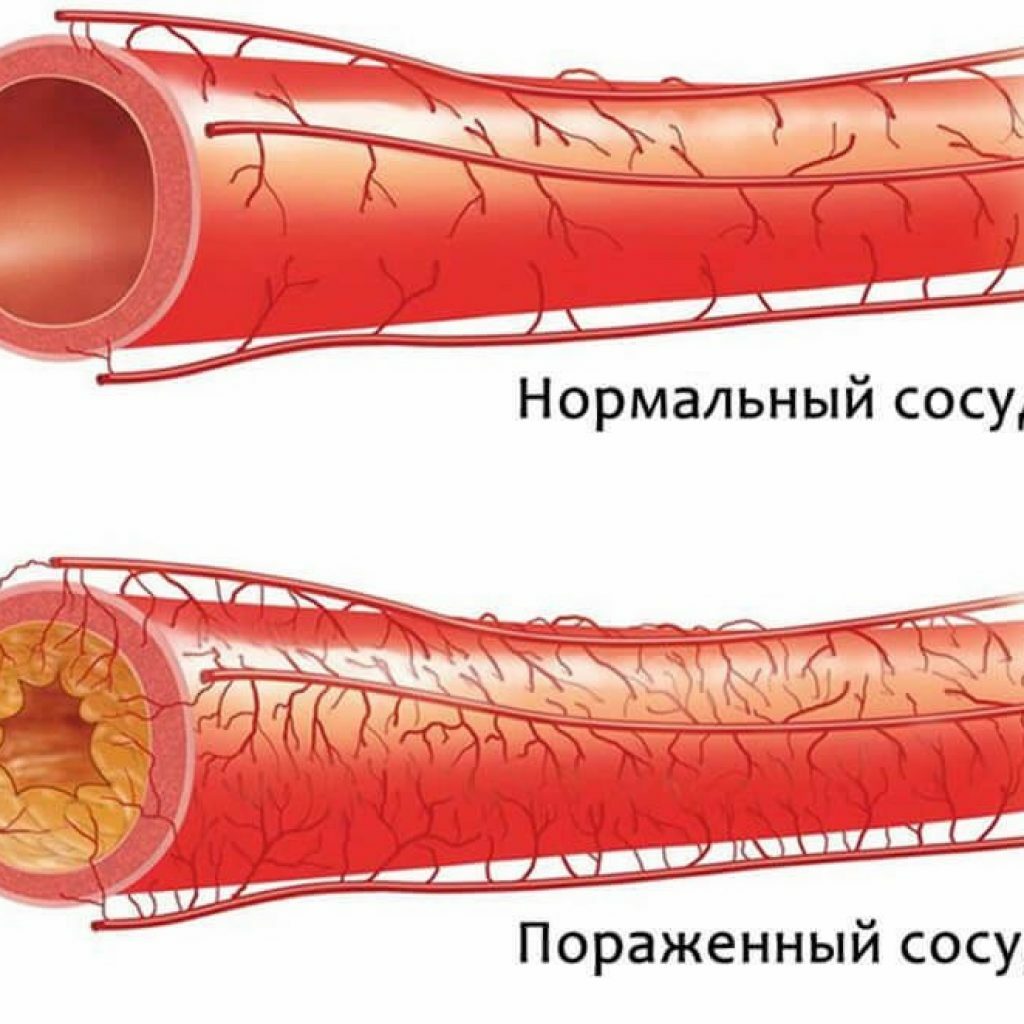
Embolism refers to a disorder accompanied by circulation in the vessels of elements unusual for the normal state. A thrombus is a blood clot that occurs as a result of clotting. The process of coagulation is vital, because it damages the damaged vessels. But it is possible and pathological coagulation, due to a number of reasons.
If a flotating thrombus forms in the veins of the lower limbs or pelvis( weakly attached to the vessel wall) - the probability of its detachment and movement to the heart and into the mainstream of the pulmonary artery is great.
At large sizes, the lump is capable of clogging large vessels, and at small ones it reaches small capillaries, where it gets stuck. Thus, the essence of thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery( PE) is the clogging of pulmonary vessels with thrombi.
Causes of pulmonary disease
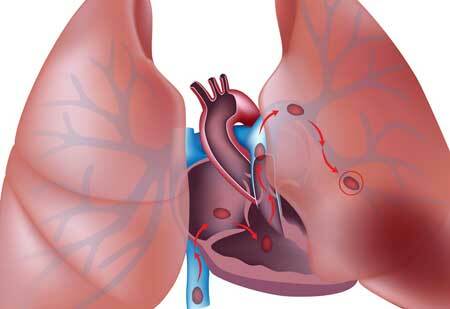
The cause of the disease is one - a blood clot interferes with normal blood flow and gas exchange in the lungs. This provokes a reflex narrowing of the vessels and, as a consequence, an increase in pressure in the pulmonary artery and an increase in the load on the right ventricle. Physicians call 3 factors that contribute to the development of this pathology:
- Too low blood flow velocity in the area of the lower limbs and pelvis.
- Damage to the endothelium of the vascular wall.
- Increased blood clotting.
Each of these factors( together or separately) provokes thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery. The causes of the decrease in the rate of blood flow are seen in primary diseases, which include varicose veins and the destruction of veins. In addition, there is a possibility of pressure on the vessels from the outside - for example, in the case of the appearance of a tumor. This neoplasm is quite capable of squeezing the vein and causing stagnation of blood.
You can not discount the sedentary lifestyle - perhaps the only factor in the history, which is the result of a careless attitude of a person to health.
Endothelial integrity disorder itself triggers coagulation. The damage can occur both in surgical intervention and in case of physical trauma. Possible variant of the action of leukocytes, which are especially activated in the inflammatory process in the body. In addition, toxins and viruses can also damage the endothelium.
Increased blood clotting usually provokes a high level of fibrinogen - a special protein responsible for the formation of blood clots.
If the blood plasma contains little water and many uniform elements, the probability of coagulation increases significantly. In turn, the number of erythrocytes, platelets and other cells increases with polycythemia, so PE can be considered a secondary disease.
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism of the pulmonary artery

Acute thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery develops when the blood vessels clogged with a large thrombus, while the risk of death is 15%.But small blood clots are not so dangerous, although you can not ignore them, of course. In general, physicians divide the pathology into 3 species that are characterized by the degree of vascular lesion and the corresponding symptoms of PE:
1. Non-massive ( occluded <30% of the vessels):
- cough;
- slight increase in temperature;
- pain in the sternum;
- hemoptysis
- lung infarction.
2. Submassive ( occluded 30-50% of the vessels):
- increased pulmonary artery pressure;
- right ventricular failure.
3. Massive ( clogged & gt; 50% of the pulmonary arteries, including the largest ones):
- hypotension( pressure less than 90/50);
- shortness of breath;
- tachycardia( heart rate more than 100 beats / min);
- fainting.
In the non-mild form of thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery, symptoms are often absent, so the patient may not even know about his disease. More pronounced signs make you go to the hospital, but doctors do not immediately understand the cause of the disorder.
Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism of the pulmonary artery
A quick examination and conversation with the patient will not give any worthwhile information. The fact is that this pathology has no specific signs, so it is often confused with myocardial infarction, pulmonary heart, pneumothorax and other diseases. With such symptoms, physicians prescribe electrocardiography in the first place, but this method does not always give an unambiguous answer. ECG signs of PE( although indirect) are as follows:
- Sinus tachycardia.
- Overload of the right atrium and ventricle.
More informative is the X-ray study. In the picture, usually a dome of the diaphragm, elevated from that side of the lung, in which there was a blockage of blood vessels, is allocated. In addition, there is a noticeable increase in the right parts of the heart, and in the largest pulmonary arteries. If the picture shows a cone-shaped seal( Hampton's triangle), then there is every reason to suspect a lung infarction.
ECG and radiography are usually used to exclude other pathologies, but modern medicine has in its arsenal and special methods:
1. Determination of the amount of d-dimer( fibrin degradation product):
- if the substance concentration is less than 500 μg / l, it is unlikelydisease - PE;The
- method does not give an exact answer.
2. Echocardiography:
- reveals a malfunction of the right ventricle;
- is likely to find thrombi right in the heart;
- the detected oval window explains the violation of hemodynamics.
3. Computed tomography:
- uses contrasting;
- create a three-dimensional image of the lungs;
- effectively detect thrombi.
4. Ultrasonography:
- studies the velocity of blood flow in the veins of the lower limbs;
- examines the cross section of the veins.
5. Scintigraphy:
- reveals areas of the lungs in which blood does not flow;
- is used for the prohibition of computed tomography;
- excludes PE in 90% of cases.
6. Angiography of the lung vessels:
- is the most accurate method;
- reveals thrombi and narrowed vessels;
- requires an invasion, so there are certain risks.
Symptoms of thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery do not always indicate this pathology - doctors need time to conduct a complete examination of the patient. And only after confirmation of the diagnosis proceed to treatment.
Treatment of PE( pulmonary embolism)
If a person enters the hospital in an unconscious state, with low blood pressure, rapid pulse and severe shortness of breath, he is immediately placed in the intensive care unit.
If there is a suspicion of pulmonary embolism, emergency assistance consists in normalizing the gas exchange within the respiratory system. This requires artificial ventilation of the lungs with oxygen, and as an additional measure intravenously injected vasopressors( for example, adrenaline), to somehow increase the pressure.
After primary care the patient is thoroughly examined. If PE is confirmed, the treatment is prescribed as follows:
1. Decrease blood clotting:
- nonfractional heparin( intravenously);
- fondaparinux and low molecular weight heparin( administered subcutaneously, contraindicated in renal failure);
- direct anticoagulants are treated for at least 5 days;
- dosages are individual and depend on the weight of the patient;
- indirect anticoagulant warfarin is used 3 months after the end of the intensive course.
2. Reperfusion therapy ( removal of thrombi by a medicamentous method):
- preparations - Streptokinase, Alteplase and others;
- danger is a high risk of bleeding, incl.and intracerebral.
3. Surgical intervention :
- in the field of renal veins install special cava filters to catch clots;
- filters are injected into the femoral or jugular vein through the skin.
First of all, the patient is trying to help with medicines, however, medicines have a number of contraindications that must be observed without fail. There may be a situation where drugs simply do not lead to the desired result. In such cases, only surgical intervention remains.
Conclusion
Although thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery is difficult to diagnose, nevertheless there are effective methods for treating PE.But, in some cases, the patient's condition is so neglected that it can not be saved. Therefore, with pain in the chest, frequent palpitations and shortness of breath, you should immediately go to the hospital.